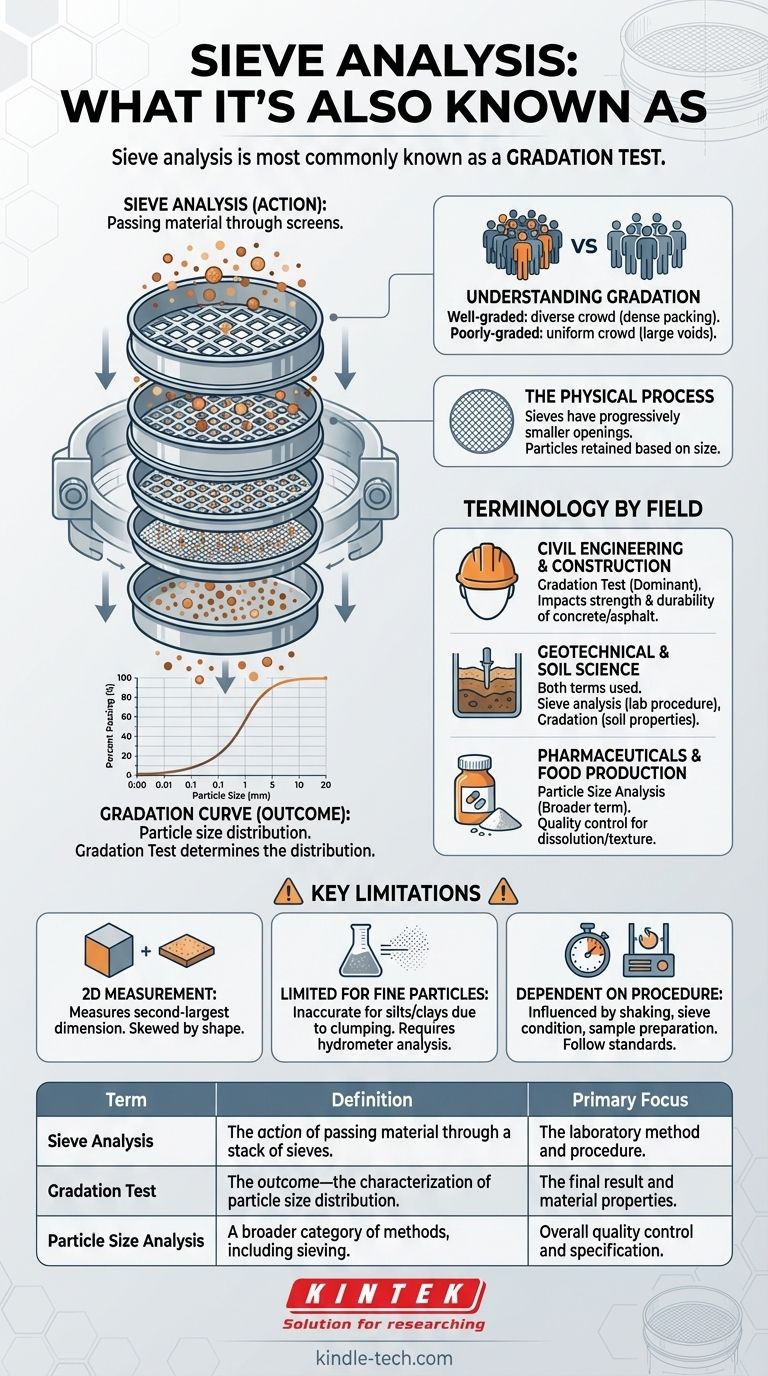
Sieve analysis is most commonly known as a gradation test. This is a fundamental laboratory procedure used across many industries to determine the particle size distribution—or gradation—of a granular material like sand, gravel, soil, or powders. While "sieve analysis" describes the method, "gradation test" describes the purpose and the result.
The core distinction is simple: "sieve analysis" refers to the action of passing material through a series of screens, while "gradation test" refers to the outcome—the characterization of the material's particle size distribution.

What Does a Gradation Test Actually Measure?
Understanding what this test reveals is key to understanding why the different names exist. The goal is to separate a material into a series of size ranges to predict its physical properties and performance.
The Concept of Gradation
Gradation is the distribution of different particle sizes within a sample of granular material.
Think of a mix of aggregates as a crowd of people. A "well-graded" mix is like a diverse crowd with people of all heights, which allows for very dense packing. A "poorly-graded" or "uniformly-graded" mix is like a crowd where everyone is the same height, leaving large, inefficient voids between them.
The Physical Process
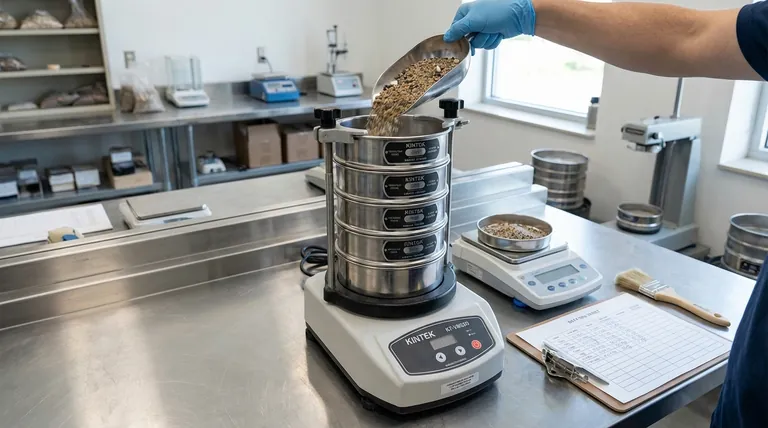
The analysis uses a stack of sieves, which are pans with wire mesh screens of specific, progressively smaller square openings.
The material sample is placed in the top sieve, and the entire stack is agitated by a mechanical shaker. Particles fall through the openings until they are retained on a sieve with a mesh too small for them to pass.
The End Result: A Gradation Curve
After shaking, the material retained on each sieve is weighed. These weights are calculated as a percentage of the total sample weight.
This data is then plotted on a graph to create a particle size distribution curve, also called a gradation curve. This curve is the primary output and provides a clear visual summary of the material's characteristics.
Why Terminology Matters in Different Fields
The preferred term often depends on the industry context and what aspect of the process is being emphasized—the method or the result.
In Civil Engineering and Construction
The term gradation test is dominant here. The gradation of aggregates (sand and gravel) directly impacts the strength, workability, and durability of concrete and asphalt. The final result is what engineers care about most.
In Geotechnical and Soil Science
Both terms are used frequently. Sieve analysis is often used when referring to the specific lab procedure for classifying soil. The resulting gradation is then used to determine soil properties like permeability and shear strength.
In Pharmaceuticals and Food Production
Here, the test is often one of several methods under the broader umbrella of particle size analysis. While sieving is used for coarser powders, other methods like laser diffraction are required for finer particles. The focus is on quality control and ensuring the product meets precise size specifications for things like dissolution rates or texture.
Understanding the Limitations
As a technical advisor, I must emphasize that while this test is invaluable, it has inherent limitations you must understand to interpret the results correctly.
It's a 2D Measurement
Sieves measure particles based on their ability to pass through a square opening. This means the test effectively measures the second-largest dimension of a particle.
It does not fully capture the three-dimensional shape. Elongated or flat particles can pass through openings that a more spherical particle of the same mass could not, which can skew the results.
Limited Effectiveness for Fine Particles
Sieving becomes impractical and inaccurate for very fine-grained soils like silts and clays. These tiny particles are subject to electrostatic forces that cause them to clump together, preventing them from passing through the fine mesh.
For these materials, other methods like hydrometer analysis are required to measure the distribution of fine particles.
Dependent on Procedure and Equipment
Results can be influenced by the duration and intensity of shaking, the condition of the sieves (e.g., worn or clogged openings), and how the initial sample was prepared. Strict adherence to standardized procedures (like those from ASTM) is critical for producing repeatable and reliable data.
How to Interpret the Terminology
Your understanding of the terms should be guided by your specific field and objective.
- If your primary focus is construction or materials specification: Think of it as a gradation test, as the aggregate's size distribution is a critical performance metric for concrete or asphalt.
- If your primary focus is soil classification: Be fluent with both sieve analysis (the lab procedure) and gradation (the resulting soil property used for classification).
- If your primary focus is quality control for powders: View sieve analysis as one specific tool within the broader category of particle size analysis, and be aware of its limitations for very fine materials.
Ultimately, understanding these terms empowers you to focus on the essential goal: characterizing a material's particle distribution to predict its real-world performance.
Summary Table:
| Term | Definition | Primary Focus |
|---|---|---|
| Sieve Analysis | The action of passing material through a stack of sieves. | The laboratory method and procedure. |
| Gradation Test | The outcome—the characterization of particle size distribution. | The final result and material properties. |
| Particle Size Analysis | A broader category of methods, including sieving. | Overall quality control and specification. |
Need precise and reliable particle size data for your materials?
Accurate sieve analysis is critical for predicting material performance in construction, soil science, and manufacturing. KINTEK specializes in high-quality lab equipment, including durable test sieves and mechanical shakers, to ensure your gradation tests are consistent and compliant with industry standards.
Let our expertise enhance your lab's capabilities. Contact our team today to discuss your specific application and find the perfect sieving solution for your needs.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Test Sieves and Vibratory Sieve Shaker Machine
- Three-dimensional electromagnetic sieving instrument
- Laboratory Multifunctional Small Speed-Adjustable Horizontal Mechanical Shaker for Lab
- Laboratory Vibratory Sieve Shaker Machine Slap Vibrating Sieve
- Vibratory Sieve Shaker Machine Dry Three-Dimensional Vibrating Sieve
People Also Ask
- Which Cannot be separated by sieving? Understanding the Limits of Particle Size Separation
- Why is sieve test important? Ensure Product Quality and Performance with Precise Particle Analysis
- What is the primary function of fine-mesh test sieves? Master Natural Mordenite Purification
- Why is a 325-mesh standard sieve used for gold recovery? Enhance Adsorption Precision with 0.044mm Particle Control
- What are the limitations of sieve analysis experiment? Key Constraints for Accurate Particle Sizing
- What is the preferred size in sieving method? Optimize Your Particle Analysis Accuracy
- What is the wet method of sieve analysis? A Guide to Accurate Particle Sizing for Clumpy Materials
- What is the size range for sieving? From 125mm Gravel to 20µm Powders



















