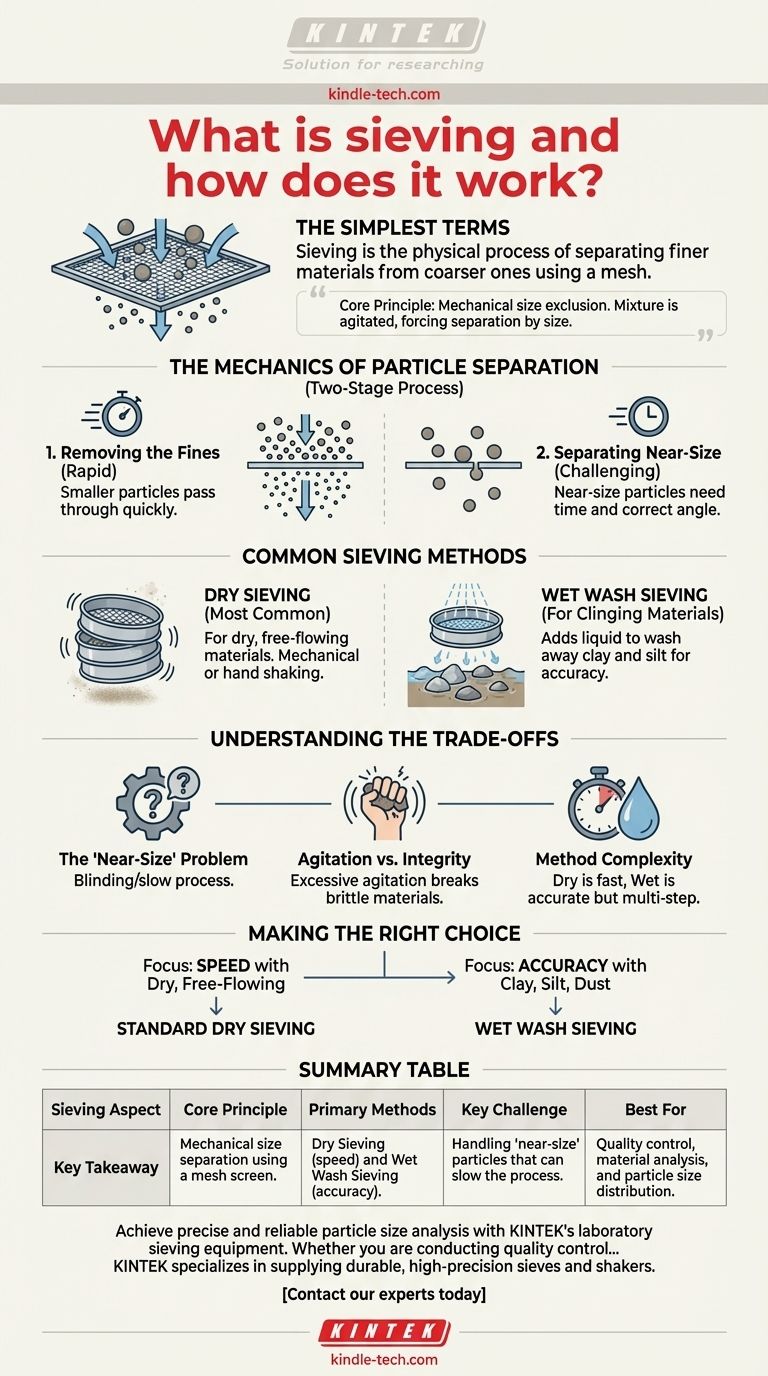
In the simplest terms, sieving is the physical process of separating finer materials from coarser ones. This is accomplished by using a meshed or perforated surface, like a screen, which allows smaller particles to pass through while retaining the larger ones.
The core principle of sieving is mechanical size exclusion. A mixture is agitated on a surface with uniform openings, forcing a separation where particles smaller than the openings fall through, and larger particles are left behind.

The Mechanics of Particle Separation
Sieving is a fundamental technique used across countless industries for quality control and material analysis. Understanding its two-stage process reveals how it achieves a reliable separation based on particle size.
The Fundamental Principle
The entire process relies on a sieve mesh or screen with precisely sized apertures. When a sample of material is placed on this surface, a combination of gravity and agitation is used to encourage separation.
Stage One: Removing the Fines
The initial phase of sieving is rapid. Particles that are significantly smaller than the sieve's openings quickly pass through the mesh with minimal effort. This first step efficiently clears out the bulk of the fine material.
Stage Two: Separating Near-Size Particles
The second stage is more challenging and time-consuming. This phase focuses on particles that are very close to the size of the mesh openings. These "near-size" particles must be presented to an opening at the correct angle to pass, which requires sustained agitation of the sieve.
Common Sieving Methods
While the principle remains the same, the method can be adapted based on the characteristics of the material being tested. The primary distinction is whether or not a liquid is used.
Dry Sieving
This is the most common method, used for materials that are dry and free-flowing. The sample is simply placed in the sieve (or a stack of sieves) and shaken mechanically or by hand until a sufficient separation is achieved.
Wet Wash Sieving
For some materials, simply shaking is not enough. Wet wash sieving involves adding water or another liquid to the sample. This is critical in industries like aggregate production, where it helps wash away clay and silt that may be clinging to larger rocks, ensuring an accurate measurement.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While sieving is a straightforward concept, achieving accurate and repeatable results requires acknowledging its inherent limitations and making conscious choices.
The "Near-Size" Particle Problem
The most significant challenge is dealing with particles that are only slightly smaller or larger than the mesh openings. These particles can become lodged in the openings (blinding) or take a very long time to pass through, affecting the efficiency and accuracy of the separation.
Agitation vs. Particle Integrity
Effective sieving requires agitation (shaking or vibrating) to ensure all particles are tested against the mesh. However, excessive or improper agitation can cause brittle materials to break down, creating more fines and skewing the final results.
Method Complexity
Dry sieving is fast and requires minimal setup. Wet sieving provides a more accurate result for sticky or agglomerated materials but introduces more steps, including the need to dry the material afterward before weighing it.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting the correct sieving method is crucial for obtaining meaningful data about your material's particle size distribution.
- If your primary focus is speed with a dry, free-flowing material: Standard dry sieving is the most efficient and practical approach.
- If your primary focus is accuracy with materials containing clay, silt, or fine dust: Wet wash sieving is essential to clean the particles and prevent clumping for a true size analysis.
Ultimately, mastering sieving is about understanding how to apply this foundational technique to reveal the true character of your material.
Summary Table:
| Sieving Aspect | Key Takeaway |
|---|---|
| Core Principle | Mechanical size separation using a mesh screen. |
| Primary Methods | Dry Sieving (speed) and Wet Wash Sieving (accuracy). |
| Key Challenge | Handling "near-size" particles that can slow the process. |
| Best For | Quality control, material analysis, and particle size distribution. |
Achieve precise and reliable particle size analysis with KINTEK's laboratory sieving equipment.
Whether you are conducting quality control for construction aggregates, analyzing powders for pharmaceuticals, or characterizing soil samples, the right sieving tools are critical for accurate results. KINTEK specializes in supplying durable, high-precision sieves and shakers that deliver the consistent performance your laboratory demands.
Contact our experts today to find the perfect sieving solution for your specific materials and application requirements.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Test Sieves and Vibratory Sieve Shaker Machine
- Three-dimensional electromagnetic sieving instrument
- Laboratory Vibratory Sieve Shaker Machine for Dry and Wet Three-Dimensional Sieving
- Laboratory Vibratory Sieve Shaker Machine Slap Vibrating Sieve
- Laboratory Wet Three-Dimensional Vibratory Sieve Shaker Machine
People Also Ask
- How do you measure particle size distribution? Match the Right Technique to Your Material
- What are the disadvantages of sieving? Key Limitations for Accurate Particle Analysis
- What is the primary purpose of using a standard sieve in rice straw processing? Achieve Perfect Uniformity
- How do I choose a sieve size? A Step-by-Step Guide to Building the Perfect Sieve Stack
- What is sieve screening? A Guide to Particle Size Distribution Analysis
- What is using a sieve to separate a solid from a liquid? A Simple Guide to Mechanical Separation
- How do you calculate sieve mesh size? Use Official Standards for Accurate Particle Analysis
- What is the maximum sieving deviation permitted? A Guide to ASTM & ISO Precision Limits



















