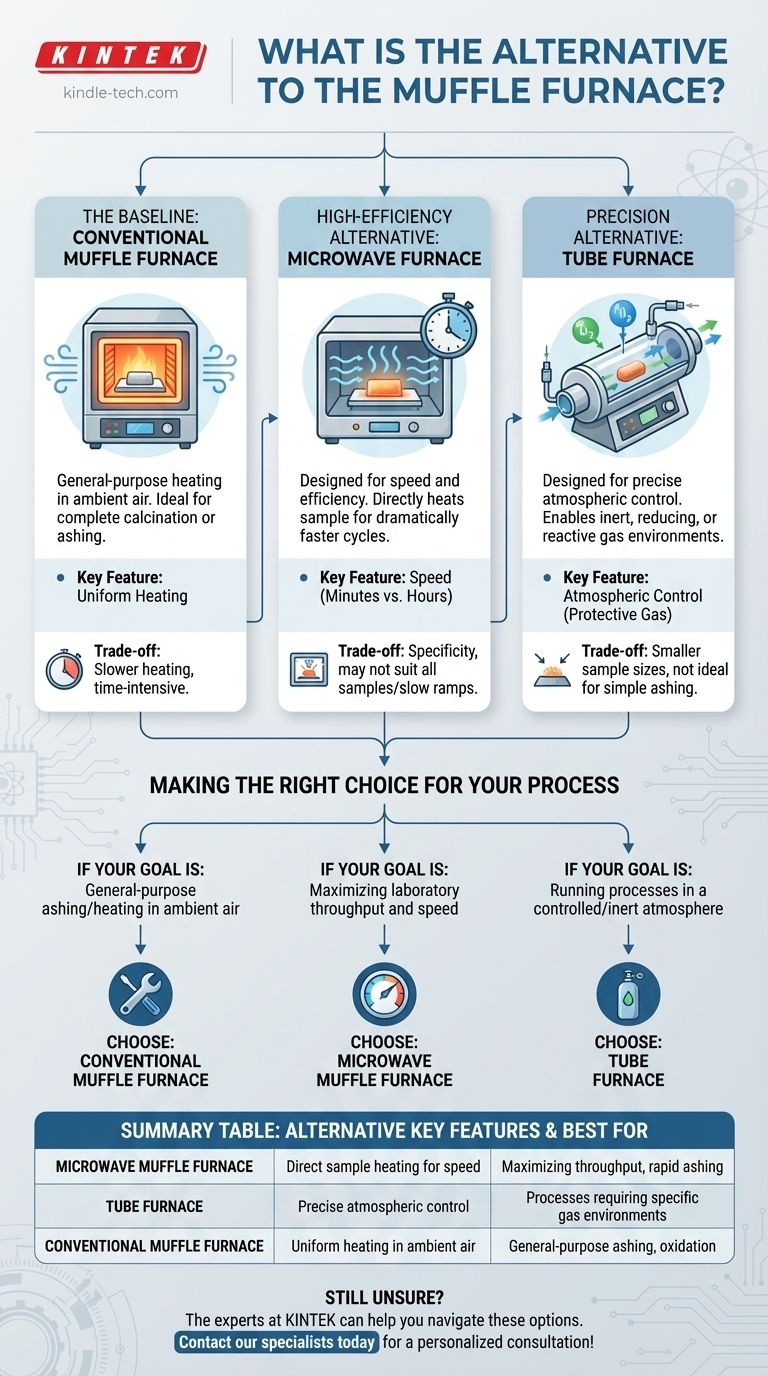
The primary alternatives to a conventional muffle furnace are the microwave muffle furnace and the tube furnace. Each serves a distinct purpose: the microwave furnace is designed for speed and efficiency, while the tube furnace is built for processes requiring precise atmospheric control. The choice between them depends entirely on the specific requirements of your application.
Your goal is not to find a one-to-one replacement for a muffle furnace, but to match the right heating technology to your specific process. The decision hinges on whether your priority is speed, atmospheric control, or general-purpose heating in ambient air.

The Baseline: The Conventional Muffle Furnace
A clear understanding of the standard muffle furnace is necessary to evaluate its alternatives. It is the workhorse for many high-temperature applications.
How It Works
A conventional muffle furnace, also known as a resistance furnace, uses heating elements that heat a high-temperature chamber made of refractory material. This design isolates the sample from direct contact with the heating elements, ensuring uniform heat distribution.
Core Application
Its primary strength is heating samples in the presence of ambient air. The chamber design allows for full air contact, making it the preferred tool for complete calcination or ashing processes that require oxidation.
The High-Efficiency Alternative: Microwave Furnace
For laboratories where speed and throughput are critical, the microwave muffle furnace presents a significant technological advantage.
A Fundamentally Different Approach
Instead of heating the chamber to indirectly heat the sample, a microwave furnace uses microwave energy to heat the sample material directly. This results in dramatically faster heating cycles.
Key Advantage: Speed
The direct heating mechanism is exceptionally efficient. This technology can reduce process times from hours to minutes, significantly improving laboratory productivity for applications like ashing.
The Precision Alternative: Tube Furnace
When the atmosphere surrounding the sample must be controlled, the tube furnace is the necessary tool. It is designed for precision, not just heat.
Designed for Atmospheric Control
A tube furnace uses a cylindrical chamber through which specific gases can be passed. This allows for processes to be carried out in inert, reducing, or other controlled atmospheres.
When to Use It
This furnace is essential when you must prevent oxidation or introduce a reactive gas during calcination. You would select a tube furnace when a process requires a protective gas to achieve the desired chemical reaction.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Each furnace type is optimized for a different task, and choosing one involves inherent compromises.
Muffle Furnace Limitations
The primary trade-off for a conventional muffle furnace is time. Heating the entire refractory chamber is an energy- and time-intensive process, making it slower than microwave alternatives.
Tube Furnace Constraints
While a tube furnace offers unparalleled atmospheric control, it typically accommodates smaller sample sizes. It is also not ideal for simple ashing in air, as the muffle furnace provides better air circulation for complete combustion.
Microwave Furnace Considerations
The main consideration for a microwave furnace is its specificity. It excels at rapid ashing and heating, but it may not be suitable for all sample types or for processes where a slow, gradual temperature ramp is critical.
Making the Right Choice for Your Process
Your specific goal is the only factor that should guide your decision.
- If your primary focus is general-purpose ashing or heating in ambient air: The conventional muffle furnace remains the reliable, industry-standard tool.
- If your primary focus is maximizing laboratory throughput and speed: The microwave muffle furnace is the definitive choice to reduce process times.
- If your primary focus is running processes in a controlled or inert atmosphere: The tube furnace is the only option that provides the necessary gas-handling capabilities.
By correctly identifying your core process requirement, you can select the furnace that will deliver the most accurate and efficient results.
Summary Table:
| Alternative | Key Feature | Best For |
|---|---|---|
| Microwave Muffle Furnace | Direct sample heating for speed | Maximizing throughput, rapid ashing |
| Tube Furnace | Precise atmospheric control (inert/reactive gases) | Processes requiring specific gas environments |
| Conventional Muffle Furnace | Uniform heating in ambient air | General-purpose ashing, oxidation processes |
Still Unsure Which Furnace is Right for Your Lab?
Choosing the right heating equipment is critical for your process efficiency and accuracy. The experts at KINTEK can help you navigate these options. We specialize in providing the perfect lab equipment solutions for your specific needs, whether you require the speed of a microwave furnace, the precision of a tube furnace, or the reliability of a conventional muffle furnace.
Let us help you optimize your laboratory workflow. Contact our specialists today for a personalized consultation!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1700℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- Laboratory High Pressure Vacuum Tube Furnace
- 1200℃ Split Tube Furnace with Quartz Tube Laboratory Tubular Furnace
- Laboratory Rapid Thermal Processing (RTP) Quartz Tube Furnace
People Also Ask
- What is the physical description of a tube furnace? A Detailed Breakdown of its High-Temperature Design
- How do you clean a tube furnace tube? A Step-by-Step Guide to Safe and Effective Cleaning
- What are the advantages of using an alumina liner in a tube furnace for biomass combustion corrosion simulations?
- What is the ceramic tube high temperature? From 1100°C to 1800°C, Choose the Right Material
- What happens when quartz is heated? A Guide to Its Critical Phase Transitions and Uses



















