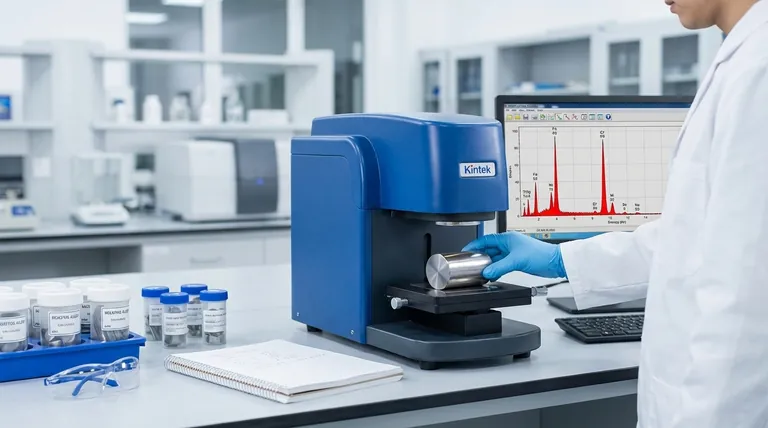
In essence, X-ray Fluorescence (XRF) is a powerful and non-destructive analytical technique used to determine the elemental composition of a material. It works by bombarding a sample with high-energy X-rays, which causes the atoms within the sample to emit their own characteristic "secondary" X-rays. By measuring the energy and intensity of these emitted X-rays, a spectrometer can rapidly identify which elements are present and in what quantities.
XRF provides a fast, non-damaging way to discover "what something is made of." Its primary value lies in its ability to perform rapid elemental screening and quantification, especially for heavier elements, directly on a solid or liquid sample with minimal preparation.

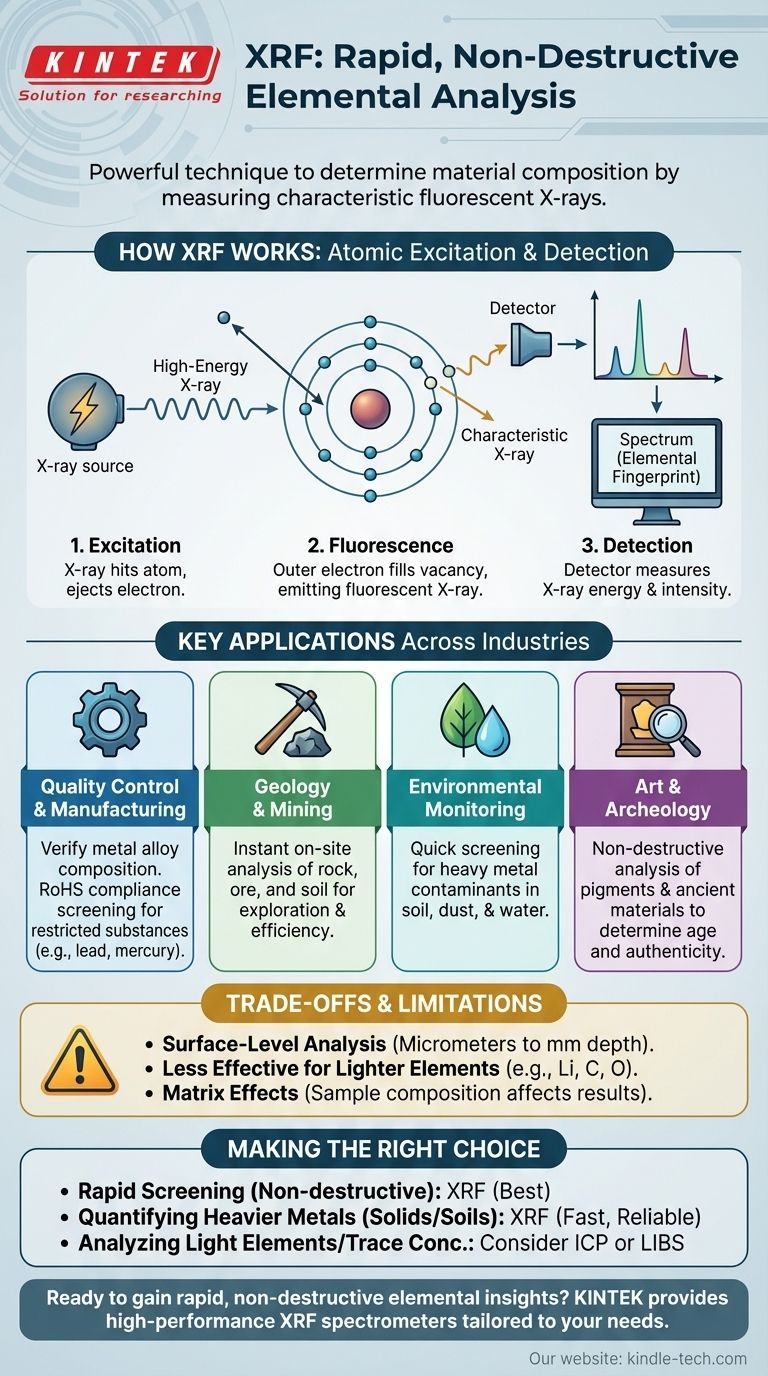
How XRF Identifies Elements
The Fundamental Principle: Atomic Excitation
At the atomic level, every element has electrons arranged in specific energy shells. When a high-energy X-ray from the spectrometer strikes an atom in the sample, it can knock an electron out of an inner shell.
This creates an unstable vacancy. To return to a stable state, an electron from a higher-energy outer shell immediately drops down to fill the empty spot.
The excess energy from this drop is released as a fluorescent X-ray. The energy of this emitted X-ray is unique and characteristic of the specific element it came from, acting like an atomic fingerprint.
From Signal to Spectrum
An XRF instrument coordinates this process. An X-ray source generates the initial beam that is directed at the sample.
As the atoms in the sample fluoresce, a detector captures the secondary X-rays they emit. The detector measures both the energy and the number of X-rays at each energy level.
Reading the Results
This data is processed into a spectrum, which is a graph that plots X-ray intensity versus energy. Each peak on the graph corresponds to a specific element.
The position of the peak on the energy axis identifies the element, while the height or intensity of the peak is proportional to its concentration in the sample.
Key Applications Across Industries
Quality Control and Manufacturing
XRF is a cornerstone of quality assurance for verifying the composition of metal alloys, ensuring they meet precise specifications. It is also widely used in electronics to screen for restricted hazardous substances (RoHS), such as lead, mercury, and cadmium.
Geology and Mining
Portable XRF analyzers allow geologists to get instant elemental data on rock, ore, and soil samples directly in the field. This rapid feedback is crucial for guiding exploration, mapping deposits, and making mining operations more efficient.
Environmental Monitoring
Regulators and consultants use XRF to quickly screen for heavy metal contaminants in soil, dust, and water. This is vital for assessing polluted sites, monitoring industrial waste, and ensuring public safety.
Art and Archeology
Because it is non-destructive, XRF is invaluable for analyzing priceless artifacts. It can identify the pigments used in a painting to determine its age and authenticity or reveal the composition of ancient coins and tools without causing any damage.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Limitations
Surface-Level Analysis
A critical point to understand is that XRF is primarily a surface technique. The initial X-rays only penetrate a shallow depth into the material, from a few micrometers to several millimeters depending on the sample.
Therefore, the results represent the composition of the surface, which may not be the same as the bulk material if the sample is coated, corroded, or inhomogeneous.
Detection Limits for Lighter Elements
XRF is less effective for very light elements (e.g., lithium, carbon, oxygen). The characteristic X-rays these elements emit have very low energy and are often absorbed by the air or the detector window before they can be measured.
Matrix Effects
The overall composition of the sample (the "matrix") can affect the accuracy of the results. The X-rays emitted by the element of interest can be absorbed or enhanced by other elements present, which can skew quantitative results if not properly corrected with calibration standards.
Making the Right Choice for Your Analysis
- If your primary focus is rapid, non-destructive screening: XRF is an exceptional choice for quickly identifying alloys, sorting scrap metal, or checking for restricted substances without damaging the item.
- If your primary focus is quantifying heavier metals in solids or soils: XRF provides fast and reliable results for environmental screening, mining exploration, and quality control of most metals.
- If your primary focus is analyzing light elements or trace concentrations: You may need to consider alternative techniques like Inductively Coupled Plasma (ICP) or Laser-Induced Breakdown Spectroscopy (LIBS), which have better sensitivity for these applications.
By understanding its core principles and practical limitations, you can effectively leverage XRF for immediate and reliable elemental insights.
Summary Table:
| Application Area | Primary Use of XRF | Key Advantage |
|---|---|---|
| Quality Control | Verifying metal alloy composition; RoHS compliance screening | Fast, non-destructive on-site analysis |
| Geology & Mining | Instant elemental analysis of rocks, ores, and soil in the field | Guides exploration and improves operational efficiency |
| Environmental Monitoring | Screening for heavy metal contaminants in soil, dust, and water | Rapid assessment for public safety and site remediation |
| Art & Archaeology | Identifying pigments and material composition of artifacts | Completely non-destructive analysis of priceless objects |
Ready to gain rapid, non-destructive elemental insights for your laboratory?
KINTEK specializes in providing high-performance XRF spectrometers and lab equipment tailored to your specific analytical needs. Whether you're in quality control, research, or environmental monitoring, our solutions deliver the accuracy and reliability you require.
Contact our experts today to discuss how XRF technology can enhance your capabilities and streamline your workflow.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Automatic Lab Cold Isostatic Press CIP Machine Cold Isostatic Pressing
- KF Ultra-High Vacuum Observation Window 304 Stainless Steel Flange High Borosilicate Glass Sight Glass
- Optical Window Glass Substrate Wafer Barium Fluoride BaF2 Substrate Window
- Custom PTFE Teflon Parts Manufacturer for PTFE Stirring Bar Recovery Rod
- Warm Isostatic Press for Solid State Battery Research
People Also Ask
- What is cold isostatic pressing of metal powder? Achieve Uniform Density in Complex Metal Parts
- What are the advantages of using a Cold Isostatic Press for perovskite solar cells? Unlock High-Pressure Performance
- What temperature is cold isostatic pressing? A Guide to Room-Temperature Powder Compaction
- What are the disadvantages of cold isostatic pressing? Key Limitations in Dimensional Accuracy & Speed
- What advantages does CIP equipment offer for W-TiC composites? Achieve High-Density, Defect-Free Materials
















