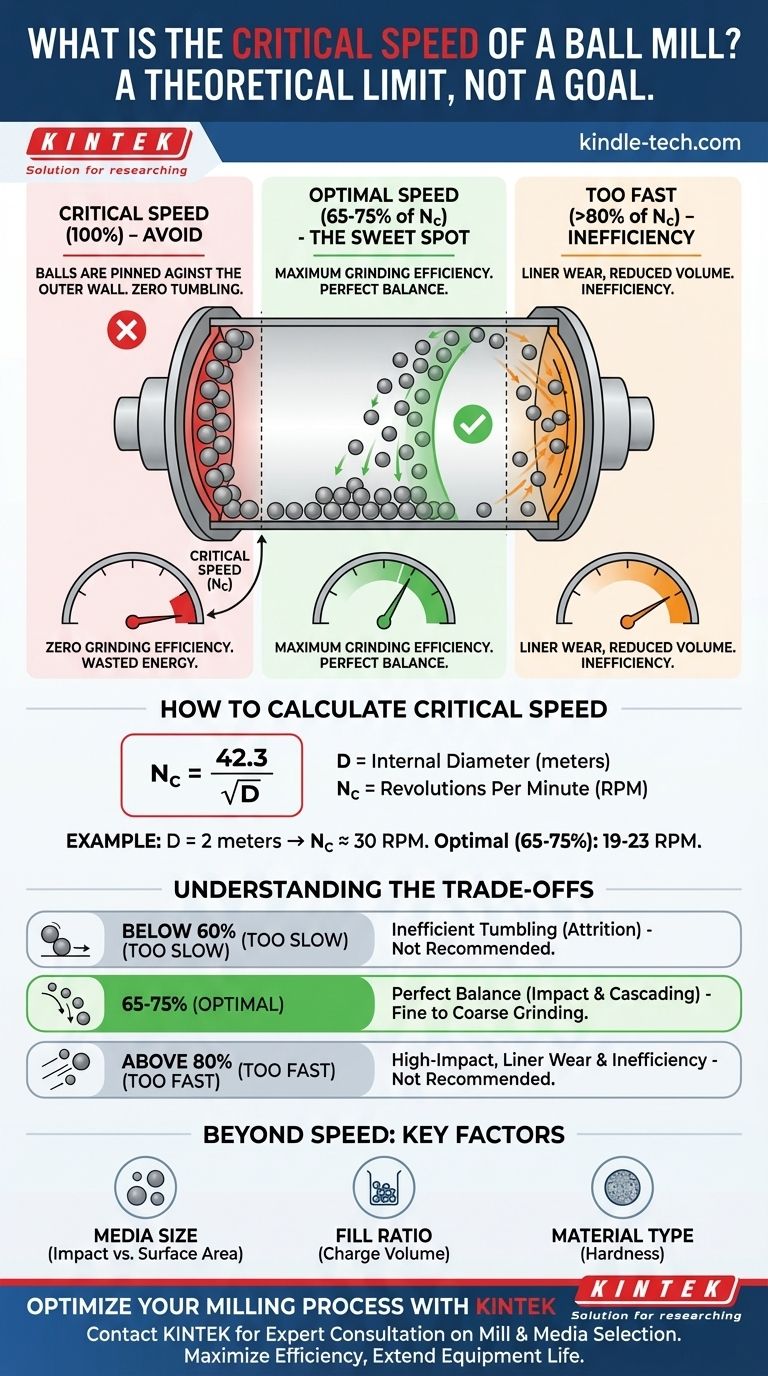
The critical speed of a ball mill is not an operational target, but a theoretical limit you must avoid. It is the rotational speed at which centrifugal force causes the grinding media (the balls) to cling to the inner wall of the mill, ceasing all grinding action. Therefore, there is no useful "average" critical speed; instead, the optimal operating speed is calculated as a percentage of this critical limit.
Your goal is not to reach the critical speed, but to operate within a specific range below it. Effective grinding occurs when the mill runs between 65% and 75% of its calculated critical speed, balancing the lifting of the media for impact and the tumbling action required for pulverization.
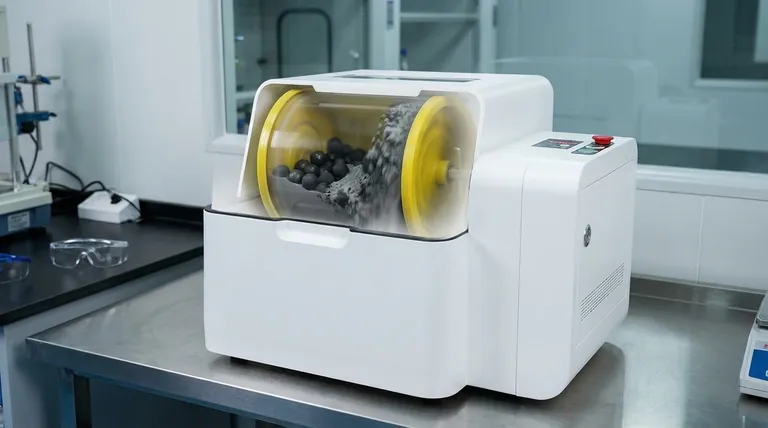

What is Critical Speed, Exactly?
The concept of critical speed is fundamental to understanding how a ball mill functions. It is purely a function of physics, specifically the balance between gravity and centrifugal force.
The Point of No Grinding
At critical speed, the centrifugal force perfectly overcomes gravity. The grinding balls are pinned against the mill's interior shell and rotate with it in a fixed position.
In this state, there is no tumbling, no cascading, and no impact between the balls and the material. Grinding efficiency drops to zero. Operating at or above the critical speed is a waste of energy and serves no purpose.
The Role of Centrifugal Force
Think of swinging a bucket of water over your head. If you swing it fast enough (reaching a "critical speed"), the water stays in the bucket.
The same principle applies inside a ball mill. As the mill spins faster, the balls are pushed outwards. Critical speed is the exact point where that outward force is strong enough to hold them against the wall for the entire rotation.
Finding the Optimal Speed (Not the Critical Speed)
The real objective is to find the optimal operating speed. This is the "sweet spot" that maximizes grinding efficiency for your specific material and desired particle size.
The "Sweet Spot": The Operating Speed Range
The universally accepted range for effective grinding is 65% to 75% of the mill's critical speed.
Within this range, the balls are carried high enough up the side of the mill to create significant impact energy when they fall, but not so high that they begin to centrifuge. This continuous tumbling and cascading motion is what grinds the material.
How to Calculate Critical Speed
While you never operate at critical speed, you must calculate it to determine your optimal operating speed. The formula is based on the mill's internal diameter.
The critical speed (Nc) in revolutions per minute (RPM) is calculated as: Nc = 42.3 / √D
Where D is the internal diameter of the mill in meters. For example, a mill with a 2-meter internal diameter has a calculated critical speed of approximately 30 RPM. Its optimal operating speed would therefore be between 19 and 23 RPM.
Understanding the Trade-offs
The speed you choose within the optimal range has a direct effect on the grinding action.
Operating Too Slow (Below 60%)
If the mill speed is too low, the balls will not be lifted high enough. They will simply tumble over each other at the bottom of the mill.
This results in a gentle, abrasive action (attrition) rather than high-energy impacts. This is inefficient for most grinding tasks and significantly increases processing time.
Operating Too Fast (Above 80%)
As you approach critical speed, the balls are thrown further and begin to "cateract." They fly across the diameter of the mill and strike the liner on the opposite side.
While this creates high impact, it concentrates wear on a small area of the mill liner and reduces the overall volume of material being actively ground, lowering efficiency. Go any faster, and they begin to centrifuge, stopping the grinding action entirely.
Beyond Speed: Other Key Factors
Optimal grinding isn't just about speed. It's an ecosystem of variables, including:
- Media Size: Larger balls provide higher impact for coarse material; smaller balls provide more surface area for finer grinding.
- Fill Ratio: The volume of the mill filled with media (typically 30-45%) affects how the charge moves and the efficiency of the grind.
- Material Type: Harder materials may require speeds on the higher end of the optimal range to ensure sufficient impact energy.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Use the critical speed calculation as a baseline, then adjust your operating speed to match your specific grinding objective.
- If your primary focus is coarse grinding and maximum impact: Operate closer to the upper end of the optimal range, around 75% of critical speed.
- If your primary focus is fine grinding and attrition: Operate closer to the lower end of the optimal range, around 65% of critical speed.
- If you are processing a new or unknown material: Start at 70% of critical speed and adjust based on the resulting particle size and efficiency.
Ultimately, treat critical speed as a crucial boundary for your calculations, not as an operational goal for your machine.
Summary Table:
| Speed (% of Critical) | Grinding Action | Best For |
|---|---|---|
| Below 60% | Inefficient tumbling (attrition) | Not Recommended |
| 65% - 75% (Optimal) | Perfect balance of impact & cascading | Fine to Coarse Grinding |
| Above 80% | High-impact, but causes liner wear & inefficiency | Not Recommended |
| 100% (Critical Speed) | No grinding; balls centrifuge to the wall | Avoid at All Costs |
Optimize Your Milling Process with KINTEK
Achieving the perfect balance of impact and efficiency in your ball mill is critical to your lab's productivity and cost-effectiveness. The theoretical critical speed is just the starting point; the real challenge is fine-tuning your entire grinding ecosystem—from media size to fill ratio—for your specific materials.
KINTEK specializes in lab equipment and consumables, serving all your laboratory needs. Our experts can help you select the right mill and media to ensure you operate within the optimal 65-75% range for superior results.
Let us help you maximize your grinding efficiency and extend the life of your equipment.
Contact KINTEK today for a expert consultation and let's refine your process together.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Single Horizontal Jar Mill
- High-Energy Omnidirectional Planetary Ball Mill Milling Machine for Laboratory
- High Energy Planetary Ball Mill Milling Machine for Laboratory
- Laboratory Horizontal Planetary Ball Mill Milling Machine
- High-Energy Omnidirectional Planetary Ball Mill Machine for Laboratory
People Also Ask
- How does a planetary vacuum ball mill ensure the uniform dispersion of SiC? Master Advanced Nano-Composite Milling
- How does a planetary ball mill contribute to Inconel 625/TiB2 mixing? Achieve Perfect Homogenization for SHS
- What is the function of high-energy ball milling for Ti-3Al-2.5V master alloys? Optimize Particle Size and Diffusion
- What is the role of planetary ball mills in preparing self-passivating tungsten alloy? Master Atomic-Level Mixing
- What is the principle of planetary ball mill? Achieve Rapid, High-Energy Grinding for Your Materials
- What is the primary function of high-energy ball milling in Ti–6Al–7Nb alloy preparation? Expert Insights
- What are the steps in ball milling? A Guide to Effective Particle Size Reduction
- What is the capacity of a ball mill? Optimize Your Grinding Process for Maximum Efficiency



















