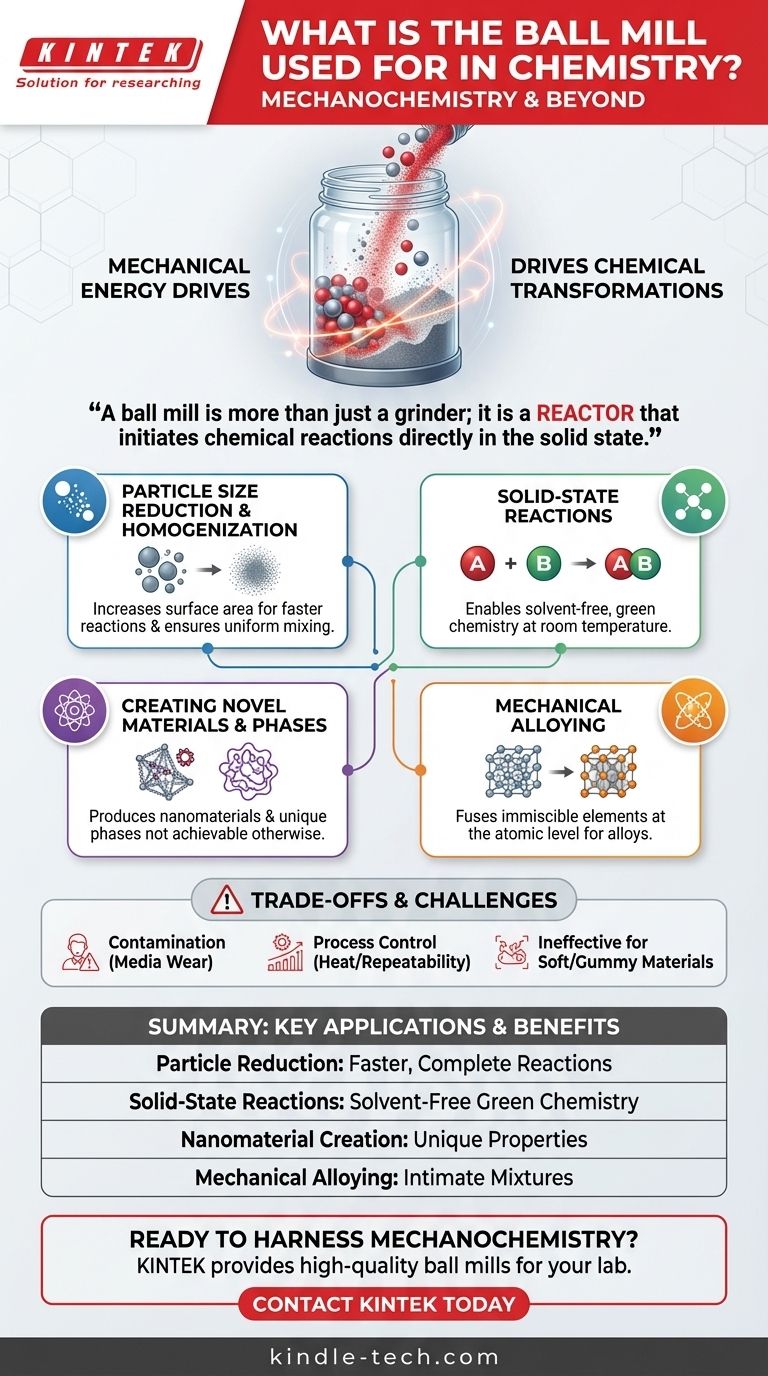
In a chemistry context, a ball mill is a powerful tool for mechanochemistry. While its most basic function is to grind solids into fine powders or mix them intimately, its true value lies in using mechanical energy to drive physical changes and chemical reactions, often without the need for solvents.
A ball mill is more than just a grinder; it is a reactor that uses intense physical forces to reduce particle size, create novel material phases like nanomaterials, and initiate chemical reactions directly in the solid state.

Beyond Grinding: The Role of Mechanochemistry
A ball mill is a rotating cylinder filled with grinding media (balls) and the material to be processed. As the cylinder tumbles, the balls cascade and collide, imparting high-impact energy to the material trapped between them. This energy does far more than just break particles apart.
Particle Size Reduction and Homogenization
The most fundamental application is reducing the particle size of solid reagents. This dramatically increases the surface area available for a reaction, leading to faster and more complete conversions.
It also ensures materials are mixed on a microscopic level, creating a homogenous blend that is critical for uniform reactions and consistent final products.
Enabling Solid-State Reactions
Ball milling is a cornerstone of mechanochemistry, a field that uses mechanical force to induce chemical transformations.
The high-energy impacts can break chemical bonds and create highly reactive surfaces, allowing reactions between solids to occur at room temperature without any solvents. This makes it a key technique in green chemistry.
Creating Novel Materials and Phases
The intense energy and pressure inside a ball mill can force atoms into arrangements they would not normally adopt.
This is used to produce nanomaterials, where the grain size is reduced to the nanometer scale, unlocking unique properties. It is also a classic method for creating amorphous materials (solids lacking a crystalline structure) from crystalline starting materials.
Mechanical Alloying
Ball milling can be used to alloy metals or compounds that are normally immiscible. The repeated fracturing and cold-welding of particles forces the different elements to mix at an atomic level, creating true solid solutions or finely dispersed composites.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While powerful, the ball milling process is not without its challenges and limitations. Understanding these is key to its effective use.
Contamination from Grinding Media
The grinding balls and the jar itself are subject to wear. Over time, trace amounts of material from the media (e.g., steel, zirconia, agate) can be introduced into your sample, which can be a critical issue for high-purity applications.
Process Control and Repeatability
Controlling the exact temperature inside the mill is difficult, as the process generates significant heat. The energy input is also complex, depending on mill speed, ball size, and fill ratio, which can sometimes make results difficult to perfectly replicate.
Ineffectiveness with Certain Materials
Very soft, ductile, or "gummy" materials can be difficult to process. Instead of fracturing, they may simply deform or coat the inside of the jar and the grinding media, preventing effective size reduction.
How to Apply This to Your Project
Choosing to use a ball mill depends entirely on your end goal.
- If your primary focus is simple sample preparation: Use it for grinding solid reagents to increase reaction rates or for creating highly homogeneous powder mixtures.
- If your primary focus is green or solvent-free synthesis: Use it to drive solid-state reactions, avoiding the cost, hazard, and waste associated with solvents.
- If your primary focus is advanced materials development: Use it as your primary tool for synthesizing nanomaterials, amorphous phases, or unique alloys that are inaccessible through traditional methods.
Ultimately, the ball mill transforms materials through force, making it a versatile and indispensable instrument in the modern chemistry lab.
Summary Table:
| Key Application | Primary Benefit in Chemistry |
|---|---|
| Particle Size Reduction | Increases surface area for faster, more complete reactions. |
| Solid-State (Mechanochemical) Reactions | Enables solvent-free synthesis, a core principle of green chemistry. |
| Nanomaterial & Amorphous Phase Creation | Produces materials with unique properties not achievable by other methods. |
| Mechanical Alloying & Homogenization | Creates intimate mixtures and alloys of normally immiscible elements. |
Ready to harness the power of mechanochemistry in your lab?
Whether your project requires solvent-free synthesis, precise particle size reduction, or the development of novel nanomaterials, having the right equipment is crucial. KINTEK specializes in providing high-quality lab equipment, including ball mills, to meet the rigorous demands of chemistry research and development.
Contact us today to discuss your specific application. Our experts will help you select the ideal solution to enhance your lab's efficiency and unlock new possibilities in materials science.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Single Horizontal Jar Mill
- High-Energy Omnidirectional Planetary Ball Mill Milling Machine for Laboratory
- High-Energy Omnidirectional Planetary Ball Mill Machine for Laboratory
- High Energy Planetary Ball Mill Milling Machine for Laboratory
- High Energy Planetary Ball Mill Milling Machine for Laboratory
People Also Ask
- Why are tungsten carbide grinding jars and balls preferred for high-purity lithium ceramic powders? Ensure Peak Purity.
- Why use zirconia ball milling jars for SiC/ZTA composite powders? Ensure High Purity & Efficient Particle Refinement
- Why are zirconia (ZrO2) milling jars recommended for sulfide electrolytes? Ensure Purity in Li6PS5Cl Synthesis
- Why are silicon nitride or zirconia preferred for milling iodo-vanadate-lead precursors? Ensure High Purity Results
- How do stainless steel grinding jars and balls contribute to mechanical alloying? Optimize HEA Powder Synthesis



















