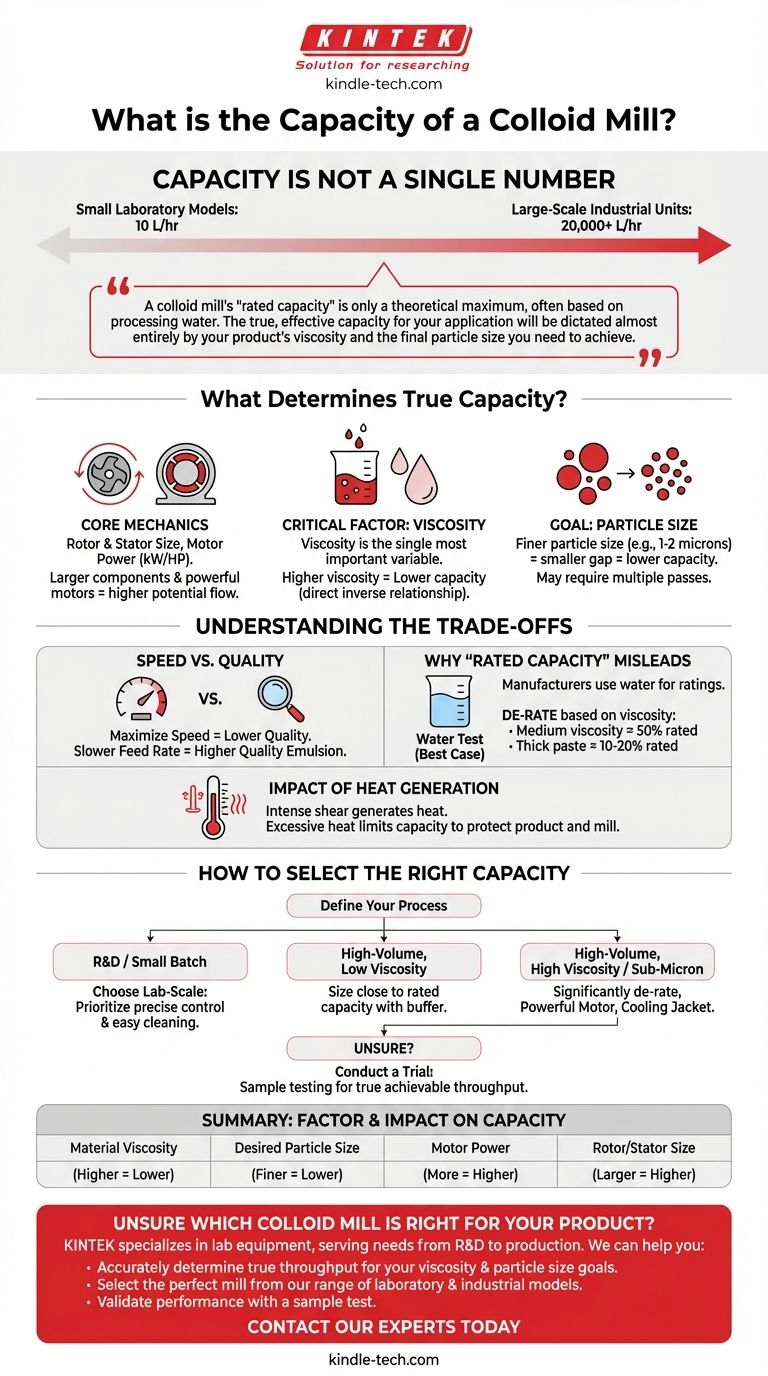
The capacity of a colloid mill is not a single number but a wide spectrum, ranging from small laboratory models that process as little as 10 liters per hour to large-scale industrial units capable of handling over 20,000 liters per hour. The specific model's design, motor power, and the nature of the material being processed are the true determinants of its actual throughput.
A colloid mill's "rated capacity" is only a theoretical maximum, often based on processing water. The true, effective capacity for your application will be dictated almost entirely by your product's viscosity and the final particle size you need to achieve.

What Determines a Colloid Mill's True Capacity?
Selecting a mill based solely on its catalog capacity rating is a common mistake. To properly size a machine, you must understand the interplay between its mechanical design and the properties of your product.
The Core Mechanics: Rotor, Stator, and Motor Power
A colloid mill works by subjecting a fluid to intense hydraulic shear between a high-speed rotating cone (rotor) and a stationary cone (stator). The machine's potential capacity is directly linked to the size of these components and the power of the motor driving them.
A larger rotor diameter provides a greater surface area for processing, allowing for higher flow rates. Likewise, a more powerful motor (measured in kW or HP) can maintain the necessary rotational speed when processing thick, viscous materials that would otherwise slow it down.
The Critical Factor: Material Viscosity
Viscosity is the single most important variable affecting throughput. There is a direct inverse relationship: as the viscosity of your product increases, the effective capacity of the mill decreases, often dramatically.
Processing a low-viscosity liquid like a beverage is fast and requires less energy. Processing a high-viscosity product like peanut butter or a thick cosmetic cream creates immense resistance, drastically reducing the rate at which it can flow through the mill.
The Goal: Desired Particle Size
The purpose of a colloid mill is to reduce particle size to create a stable emulsion or dispersion. The fineness of the final product is controlled by the gap between the rotor and stator, which is often adjustable.
Achieving a very fine particle size (e.g., 1-2 microns) requires setting a very small gap. This restricts the flow path, thereby lowering the overall capacity. If an extremely fine result is needed, you may even need to pass the product through the mill a second time, halving the effective hourly output.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Capacity is not an independent variable. It exists in a constant balance with processing quality and operational limits. Understanding these trade-offs is crucial for realistic expectations and process design.
Speed vs. Quality
This is the fundamental trade-off. Running a product through the mill at its maximum possible flow rate (speed) reduces the time it spends in the high-shear zone. This results in less particle size reduction and a lower quality emulsion or dispersion.
To achieve a finer, more uniform product, you must slow the feed rate. This increases the "residence time" in the shear gap, imparting more energy into the product and producing a higher-quality result, but at the cost of lower throughput.
Why "Rated Capacity" Can Be Misleading
Manufacturers typically test and rate their equipment using water or a similar low-viscosity fluid. This establishes a "best-case scenario" flow rate that is rarely achievable with real-world products.
When evaluating a mill, you must de-rate the manufacturer's stated capacity based on your product's viscosity. For a medium-viscosity product, the actual throughput might be 50% of the rated capacity; for a very thick paste, it could be as low as 10-20%.
The Impact of Heat Generation
The intense shear action inside a colloid mill generates significant heat. This heat is transferred directly into your product. Pushing a viscous material through the mill too quickly can cause a rapid temperature rise.
This can be a limiting factor on capacity, as excessive heat may damage heat-sensitive products, degrade the final quality, or even harm the mill's mechanical seals. In many applications, the process must be slowed down simply to manage heat generation.
How to Select the Right Capacity for Your Process
Choosing the right mill involves matching the machine's capabilities to your specific product and production goals.
- If your primary focus is R&D or small-batch production: Choose a lab-scale model where precise control, easy cleaning, and adjustability are more critical than high throughput.
- If your primary focus is high-volume production of a low-viscosity product: You can size the mill closer to the manufacturer's rated capacity, but always factor in a reasonable buffer.
- If your primary focus is processing a high-viscosity paste or achieving a sub-micron emulsion: You must significantly de-rate the nominal capacity and prioritize a model with a powerful motor and potentially a jacketed housing for cooling.
- If you are unsure: The most reliable method is to conduct a trial. Provide a sample of your product to the equipment manufacturer for testing to determine the true, achievable throughput for your specific application.
Ultimately, understanding these core principles allows you to move beyond simple ratings and select a machine truly engineered to meet your production needs.
Summary Table:
| Factor | Impact on Capacity |
|---|---|
| Material Viscosity | Higher viscosity = Lower capacity |
| Desired Particle Size | Finer particles = Lower capacity |
| Motor Power (kW/HP) | More power = Higher capacity for viscous products |
| Rotor/Stator Size | Larger components = Higher potential capacity |
Unsure which colloid mill capacity is right for your product?
Don't risk under-sizing or over-spending on your equipment. KINTEK specializes in lab equipment and consumables, serving laboratory needs from R&D to production scaling.
We can help you:
- Accurately determine the true throughput for your specific material viscosity and particle size goals.
- Select the perfect colloid mill from our range of laboratory and industrial models.
- Validate performance with a sample test to ensure the machine meets your production targets.
Contact our experts today for a personalized consultation and let us engineer a solution for your mixing, grinding, and dispersing challenges.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Ball Mill Jar Mill with Metal Alloy Grinding Jar and Balls
- Laboratory Grinding Mill Mortar Grinder for Sample Preparation
- Laboratory Micro Tissue Grinding Mill Grinder
- Laboratory Single Horizontal Jar Mill
- Laboratory Four-Body Horizontal Jar Mill
People Also Ask
- What is the average speed of a ball mill? Optimize Grinding with Critical Speed Calculations
- What is the difference between a ball mill and a sag mill? A Guide to Primary vs. Secondary Grinding
- Why are excellent sealing and corrosion resistance required for WC-10Co ball milling? Ensure High-Purity Mixing Results
- What is the preventive maintenance of ball mill? Ensure Maximum Uptime and Reliability
- What is the primary function of the grinding process in LiCoO2/LSPS mixtures? Optimize Solid-State Battery Conductivity



















