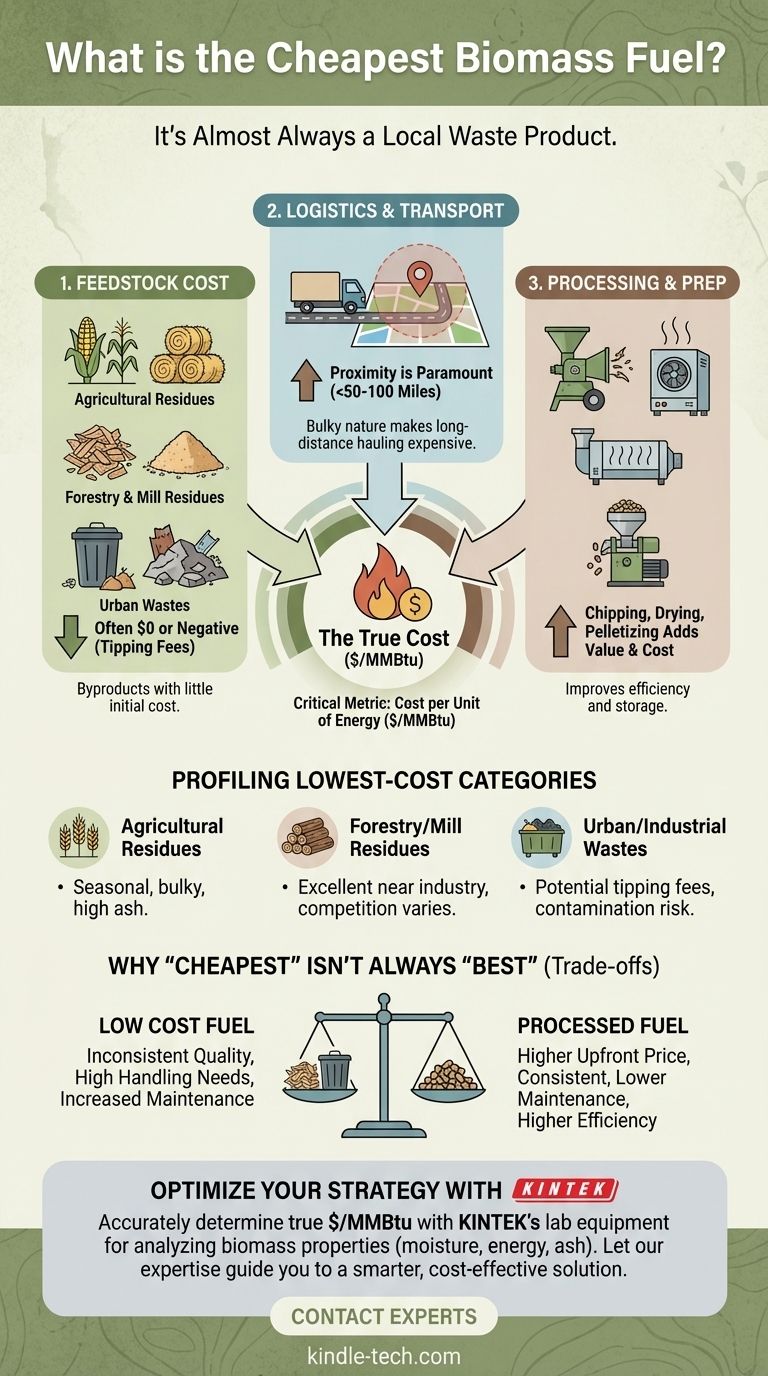
The cheapest biomass fuel is almost always a local waste product. Specifically, materials like agricultural residues (corn stover, straw), forestry residues (sawdust, wood chips), or sorted municipal solid waste (MSW) are typically the lowest-cost options. Their low price is a direct result of being byproducts of other industries, often having little to no initial feedstock cost.
The concept of a single "cheapest" biomass fuel is a misconception. The true cost is not the price of the raw material, but the delivered and processed cost per unit of energy ($/MMBtu), a figure heavily dictated by local availability, transportation distance, and processing requirements.

Deconstructing the True Cost of Biomass
To identify the most economical option for your specific application, you must look beyond the purchase price of the raw material and analyze the entire supply chain. The total cost is a sum of three distinct components.
The Starting Point: Feedstock Cost
This is the price of the biomass at its source. For waste-stream fuels, this cost is often zero or even negative.
A facility might be paid a "tipping fee" to accept waste materials like untreated construction wood or sawdust, turning a fuel cost into a revenue stream. In contrast, purpose-grown energy crops like switchgrass or poplar have a significant initial cost tied to land use and farming.
The Dominant Factor: Logistics and Transportation
Transportation is frequently the single largest driver of the final fuel cost. Biomass is bulky and has a relatively low energy density, making long-distance hauling economically unviable.
A "free" source of agricultural residue 200 miles away will almost certainly be more expensive than a source of wood chips you pay for 20 miles away. Proximity is paramount. The economical radius for sourcing biomass is typically under 50-100 miles.
The Value-Add: Processing and Preparation
Raw biomass is rarely ready for combustion. It must be processed, and each step adds cost.
- Chipping/Grinding: Reduces raw logs or scrap wood to a manageable size.
- Drying: Lowers moisture content, which increases energy value per ton and improves combustion efficiency. Wet fuel is cheap per ton but poor value per unit of energy.
- Pelletizing: Dries and compresses biomass into dense, uniform pellets. This significantly increases cost but creates a commodity fuel that is easy to transport, store, and automate.
The Critical Metric: Cost per Unit of Energy
Comparing fuels on a price-per-ton basis is misleading due to vast differences in moisture and energy content. The only accurate way to compare costs is dollars per million British thermal units ($/MMBtu).
A ton of green wood chips (50% moisture) may be cheap, but it contains half the energy of a ton of dry wood pellets (8% moisture). The dry pellets will almost always be cheaper on a $/MMBtu basis when factoring in combustion efficiency.
Profiling the Lowest-Cost Biomass Categories
While local factors are key, certain categories of biomass consistently represent the lowest-cost opportunities.
Agricultural Residues
These are the materials left in a field after a harvest, such as corn stover, wheat straw, and rice husks. Their primary cost is collection and transportation. However, they are often seasonal, bulky, and can have high ash content, which can affect boiler operation.
Forestry and Mill Residues
This category includes sawdust, bark, shavings, and wood chips from sawmills, furniture factories, and land clearing operations. These are excellent, low-cost sources if your facility is located near the forest products industry. Competition from industries like particleboard or paper pulp can sometimes drive up prices.
Urban and Industrial Wastes
Sorted municipal solid waste (MSW), untreated construction and demolition wood, and food processing waste are high-potential sources, especially in urban areas. These can carry tipping fees, making them exceptionally cheap. However, they may suffer from contamination (plastics, metals, chemicals) and require more robust and technologically advanced energy conversion systems.
Understanding the Trade-offs: Why "Cheapest" Isn't Always "Best"
Opting for the absolute lowest-cost fuel source introduces significant operational and financial trade-offs that must be carefully considered.
Fuel Quality and Consistency
Waste-derived fuels are inherently inconsistent. Moisture content, particle size, and energy value can vary from truckload to truckload. This variability can wreak havoc on an automated combustion system, leading to inefficiency and flameouts.
Handling and Storage Requirements
Wet, bulky, and non-uniform fuels like raw chips or straw require more sophisticated (and expensive) handling equipment—larger receiving bays, "walking floor" bunkers, and more robust conveyors—than uniform pellets.
Equipment Compatibility and Maintenance
Burning low-quality, high-ash, or potentially contaminated fuel can increase slagging (ash buildup) inside a boiler. This leads to more frequent shutdowns, increased cleaning labor, and higher long-term maintenance costs that can negate the initial fuel savings.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Your optimal biomass fuel choice depends entirely on your operational capabilities, location, and tolerance for complexity.
- If your primary focus is rock-bottom fuel cost and you have robust handling systems: Investigate local agricultural residues or byproducts from nearby forestry operations, and be prepared for fuel variability.
- If your primary focus is operational reliability and automation: A processed fuel like pellets or uniform dry chips may have a higher purchase price but will likely result in a lower total cost of ownership through higher efficiency and reduced maintenance.
- If you are located in a dense urban or industrial area: The most economical path may be to invest in a system capable of handling sorted municipal or industrial waste to take advantage of tipping fees.
Ultimately, the most cost-effective biomass fuel is the one you can source reliably and affordably from your immediate geographic area.
Summary Table:
| Factor | Impact on Cost | Key Considerations |
|---|---|---|
| Feedstock Cost | Low to Negative | Waste products may have zero cost or tipping fees. |
| Transportation | High | Proximity (<50-100 miles) is critical due to bulkiness. |
| Processing | Variable | Drying, chipping, or pelletizing adds cost but improves efficiency. |
| Energy Content ($/MMBtu) | Critical Metric | Compare fuels based on energy value, not just price per ton. |
Optimize your biomass fuel strategy with KINTEK!
Choosing the right biomass fuel is a complex balance of upfront cost, logistics, and long-term operational efficiency. KINTEK specializes in lab equipment and consumables for analyzing biomass properties, helping you accurately determine the true cost per unit of energy ($/MMBtu) for your specific location and needs.
We provide reliable tools to test moisture content, energy value, and ash composition, ensuring you select the most economical and sustainable fuel for your laboratory or facility. Let our expertise guide you to a smarter, more cost-effective energy solution.
Contact our experts today to discuss your biomass analysis requirements!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Teflon Parts Manufacturer for Culture Dish and Evaporation Dish
- Custom PTFE Teflon Parts Manufacturer for PTFE Mesh F4 Sieve
- Proton Exchange Membrane for Batteries Lab Applications
People Also Ask
- What are the specific applications of PTFE in micro-batch slug flow systems? Enhance Your Microfluidic Reaction Purity
- Why must a Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) reactor be used for Ti3C2TX MXene etching? Ensure Safety and Purity
- Are there any chemical substances that an all-PTFE electrolytic cell should not be exposed to? Know the Critical Limits
- How does PTFE aqueous dispersion contribute to the performance of modified MFC anodes? Boost Stability and Durability
- Is PTFE corrosion resistant? Discover the Ultimate Chemical Resistance for Your Lab


