At a fundamental level, the difference between a 1-stage and a 2-stage vacuum pump lies in how they compress and exhaust air. A single-stage pump uses one mechanism to compress captured gas from the system's vacuum level directly to atmospheric pressure. A two-stage pump uses two pumping mechanisms in series, allowing it to work more efficiently and achieve a significantly deeper (lower pressure) ultimate vacuum.
The decision is not about which pump is "better," but which is appropriate for your task. A 2-stage pump is essential for applications requiring a deep, pure vacuum to remove contaminants like moisture, while a 1-stage pump is a cost-effective workhorse for jobs where a moderate vacuum is sufficient.
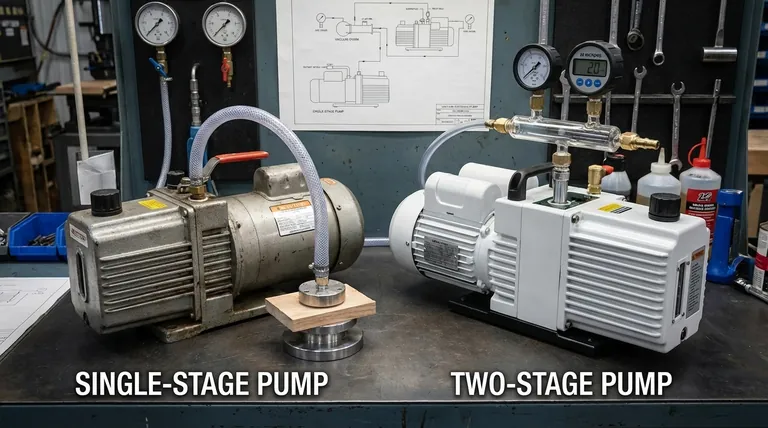
How Vacuum Pumps Create a Void
The Goal: Removing Molecules
A vacuum pump doesn't "suck" air out; it removes gas molecules from a sealed system. Its effectiveness is measured by how many molecules it can remove, resulting in a lower internal pressure. This pressure is often measured in Microns, where one micron is 1/1000th of a Torr (760,000 Microns is roughly atmospheric pressure).
The Basic Rotary Vane Mechanism
Most common pumps use a rotary vane mechanism. An off-center rotor spins inside a cylindrical chamber. Spring-loaded vanes slide in and out of the rotor, sealing against the chamber wall. This action traps a volume of gas at the inlet, compresses it by reducing the volume, and finally expels it through an exhaust valve.
The Critical Difference: One Stage vs. Two
The Single-Stage Pump: A Direct Approach
A 1-stage pump performs this entire compression cycle in a single motion. It draws gas from the vacuum system and must compress it all the way to atmospheric pressure to push it out the exhaust.
This large pressure difference between the inlet and the exhaust limits the pump's efficiency. As the system vacuum gets deeper, it becomes increasingly difficult for the single stage to effectively capture and compress the few remaining gas molecules against the full force of the outside atmosphere.
The Two-Stage Pump: A Series Approach
A 2-stage pump is essentially two single-stage pumps connected in series inside one housing.
The first stage (the low-vacuum stage) draws gas from the system. However, instead of exhausting to the atmosphere, it exhausts to the inlet of the second stage.
The second stage (the high-vacuum stage) then takes this partially compressed gas and exhausts it to the atmosphere. This teamwork means the first stage works against a much lower pressure, allowing it to operate far more efficiently at deeper vacuum levels.
The Result: Deeper Ultimate Vacuum
This efficiency gain is the core benefit of a 2-stage pump. While a 1-stage pump may only reach an ultimate vacuum of 75-150 microns, a 2-stage pump can routinely achieve 15-25 microns.
This deeper vacuum is critical for processes that depend on reaching the boiling point of water at room temperature (which occurs around 20,000 microns but requires a much deeper vacuum to happen quickly).
Understanding the Trade-offs
Performance and Purity
For achieving the lowest possible pressure and removing the maximum amount of air, moisture, and other non-condensable gases, a 2-stage pump is unequivocally superior. The deeper vacuum ensures a purer, drier system.
Cost and Complexity
A 1-stage pump has fewer internal components. This makes it simpler to manufacture, less expensive to purchase, and potentially more robust for rough, general-purpose use. A 2-stage pump is inherently more complex and therefore costs more.
Application Suitability
This is the most important consideration. Using a 2-stage pump for a simple task like vacuum chucking is overkill and a waste of money. Conversely, using a 1-stage pump for HVAC dehydration is a critical error that will leave damaging moisture in the system, leading to poor performance and future failure.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Choosing between these pumps requires a clear understanding of your goal. The required depth of vacuum is the deciding factor.
- If your primary focus is HVAC/refrigeration service: A 2-stage pump is mandatory. It's the only way to achieve the deep vacuum required to boil off and remove moisture from refrigerant lines.
- If your primary focus is scientific lab work or freeze-drying: You need a 2-stage pump. These applications demand the purity and deep vacuum that only a series-compression design can provide.
- If your primary focus is general degassing of silicones or simple resins: A 1-stage pump is often sufficient and provides excellent value for the cost.
- If your primary focus is mechanical work like woodworking or vacuum clamping: A 1-stage pump is the clear choice. It provides more than enough force at a fraction of the cost.
Ultimately, choosing the right pump is about precisely aligning the tool's capability with your project's technical requirements.
Summary Table:
| Feature | 1-Stage Vacuum Pump | 2-Stage Vacuum Pump |
|---|---|---|
| Mechanism | Single compression cycle | Two compression stages in series |
| Ultimate Vacuum | 75-150 microns | 15-25 microns |
| Best For | General degassing, vacuum clamping, mechanical work | HVAC/refrigeration, scientific labs, freeze-drying |
| Cost | Lower cost, simpler design | Higher cost, more complex |
| Purity Level | Moderate vacuum, sufficient for many tasks | Deep vacuum, essential for moisture removal and purity |
Unsure which vacuum pump is right for your laboratory's specific needs? KINTEK specializes in lab equipment and consumables, offering expert guidance and high-performance vacuum solutions tailored for applications like freeze-drying, degassing, and HVAC service. Our team can help you select the ideal pump to ensure efficiency, purity, and cost-effectiveness. Contact us today to discuss your requirements and enhance your lab's capabilities!
Visual Guide

Related Products
- Laboratory Rotary Vane Vacuum Pump for Lab Use
- Circulating Water Vacuum Pump for Laboratory and Industrial Use
- Laboratory Benchtop Water Circulating Vacuum Pump for Lab Use
- Laboratory Vertical Water Circulating Vacuum Pump for Lab Use
- Oil Free Diaphragm Vacuum Pump for Laboratory and Industrial Use
People Also Ask
- What are the advantages of rotary vane pumps? Unlock Cost-Effective, High-Performance Vacuum
- How do you inspect a vacuum pump? A Step-by-Step Guide to Ensure Peak Performance
- Why is a rotary vane mechanical vacuum pump necessary for sub-surface etching? Ensure Precision in ALD/ALE Experiments
- What are the fundamental differences between low-cost and high-end industrial rotary vane vacuum pumps? | KINTEK
- What are the common configurations and typical performance specifications of Rotary Vane Vacuum Pumps? Expert Guide



















