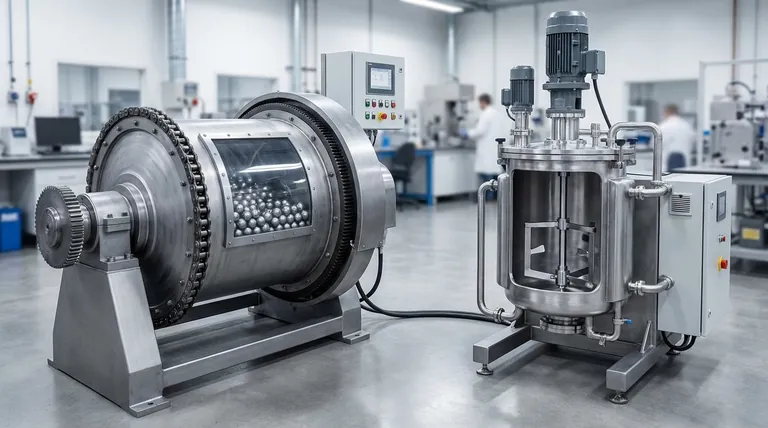
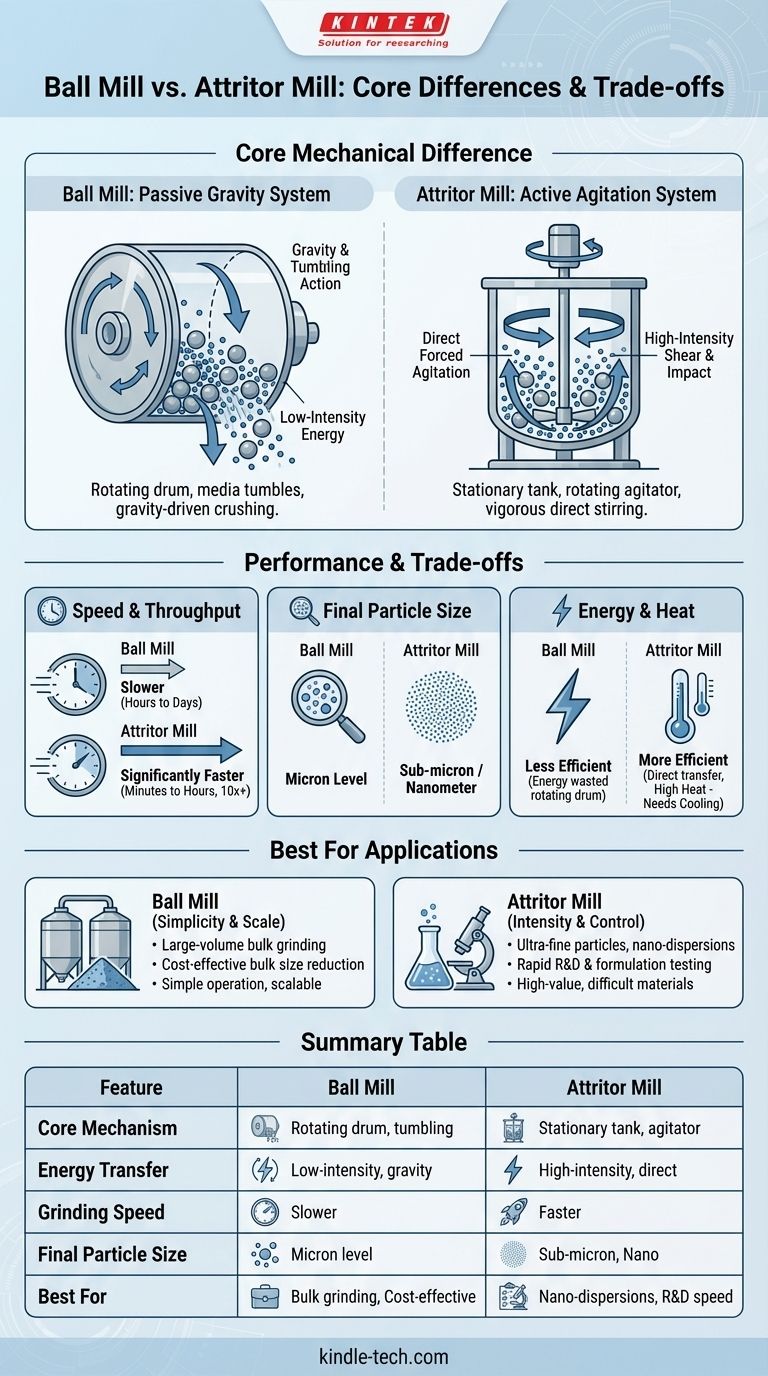
At its core, the difference between a ball mill and an attritor mill lies in how they transfer energy to the grinding media. A ball mill is a passive system that uses gravity by rotating a large drum, causing the media inside to tumble and crush the material. In contrast, an attritor mill is an active system that uses a central, rotating shaft with arms to vigorously agitate the media, resulting in a much more energetic and efficient grinding process.
The choice between these two mills is a fundamental trade-off between process intensity and scale. Attritor mills offer speed and the ability to produce extremely fine particles, while ball mills provide a simpler, more scalable solution for larger volume, less intensive grinding applications.

The Core Mechanical Difference
To understand which mill is right for you, you must first grasp how each one works. The distinction is not just a detail; it dictates the entire performance profile of the milling process.
How a Ball Mill Works: Gravity and Cascading
A ball mill is essentially a hollow, rotating cylinder partially filled with grinding media (like steel or ceramic balls) and the material to be ground.
As the cylinder rotates, it carries the media and material up the side until gravity overcomes the centrifugal force. The media then cascades and tumbles back down, grinding the material through impact and attrition. This process is analogous to a large industrial rock tumbler.
The energy input is relatively low and inefficient, as most of it is used to rotate the heavy drum itself, not to directly move the media.
How an Attritor Mill Works: Forced Agitation
An attritor mill consists of a stationary, often jacketed, tank filled with grinding media and the material slurry.
Instead of rotating the entire tank, a central shaft with attached arms rotates at high speed within the tank. This agitator directly and forcefully stirs the media, creating intense shear forces and countless high-energy impacts throughout the entire volume.
This method is similar to using a high-speed kitchen mixer in a bowl full of marbles. The energy is transferred directly to the media, making the process much more energetic and efficient.
Impact on Grinding Performance
The mechanical difference directly translates into significant performance differences in speed, final particle size, and energy consumption.
Speed and Throughput
Attritor mills are significantly faster than ball mills, often by an order of magnitude or more.
Because the attritor's agitator puts all the media into constant, energetic motion, grinding occurs much more rapidly. A process that might take 24 hours in a ball mill could potentially be completed in just 1-2 hours in an attritor.
Final Particle Size
Attritor mills can achieve much finer particle sizes, often reaching into the sub-micron or nanometer range.
The high-energy, high-shear environment is exceptionally effective at breaking down particles to their smallest components. While ball mills are excellent for reducing materials to the micron level, they often lack the energy intensity required for true nano-milling.
Energy Consumption and Heat
Attritor mills are more energy-efficient. The energy from the motor is transferred directly to the agitating shaft and media, not wasted on rotating a heavy drum.
However, this high energy input generates significant heat. For this reason, attritor tanks are almost always jacketed to allow for water cooling, a critical consideration for temperature-sensitive materials.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Neither mill is universally superior. The correct choice depends entirely on your process goals, material properties, and operational constraints.
Ball Mills: Simplicity and Scale
The primary advantages of ball mills are their mechanical simplicity and their ability to scale to very large production volumes. Horizontal rolling mills can have capacities of several hundred liters.
Their main drawback is their slow speed and relative inefficiency. They are best suited for large-volume bulk grinding where achieving nano-scale particle sizes is not the primary objective.
Attritor Mills: Intensity and Control
The attritor's key advantage is its process intensity, which enables rapid grinding and the production of ultra-fine dispersions.
The trade-off is greater mechanical complexity, a higher initial capital cost, and the near-universal need for a cooling system. They excel in applications involving high-value materials, difficult-to-grind substances, and the development of nano-materials.
Process Type (Wet vs. Dry)
While both types of mills can be used for wet or dry grinding, their strengths differ.
Ball mills work well in both dry and wet conditions. Attritors, however, are particularly effective for wet grinding, where the liquid slurry helps dissipate heat and facilitates the creation of a stable, fine-particle dispersion.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Select your milling technology based on your specific process outcome.
- If your primary focus is large-volume production and cost-effective bulk size reduction: A ball mill is almost always the correct choice for its scalability and simplicity.
- If your primary focus is achieving nano-sized particles or creating high-performance dispersions: An attritor mill's high-energy environment is necessary to reach these targets.
- If your primary focus is rapid product development and formulation testing: An attritor offers a significant speed advantage, allowing for more iteration cycles in less time.
- If your primary focus is processing temperature-sensitive materials: A ball mill may be simpler, but a jacketed attritor offers superior control over process temperature.
Ultimately, understanding that a ball mill uses passive tumbling while an attritor uses active agitation is the key to selecting the ideal technology for your needs.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Ball Mill | Attritor Mill |
|---|---|---|
| Core Mechanism | Rotating drum (tumbling action) | Stationary tank with rotating agitator |
| Energy Transfer | Low-intensity, gravity-driven | High-intensity, direct agitation |
| Grinding Speed | Slower | Significantly faster |
| Final Particle Size | Micron level | Sub-micron / Nanometer level |
| Best For | Large-volume, cost-effective bulk grinding | Ultra-fine particles, nano-dispersions, R&D speed |
Still unsure which mill is right for your lab's specific materials and goals? The experts at KINTEK are here to help. We specialize in lab equipment and consumables, providing solutions for all your laboratory needs. We can help you analyze your process requirements to select the perfect milling technology—whether it's a ball mill for large-scale production or an attritor for high-intensity nano-grinding—ensuring you achieve optimal efficiency and results. Contact our team today for a personalized consultation!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Stainless Steel Laboratory Ball Mill for Dry Powder and Liquid with Ceramic Polyurethane Lining
- Laboratory Ball Mill Jar Mill with Metal Alloy Grinding Jar and Balls
- Laboratory Single Horizontal Jar Mill
- Laboratory Horizontal Planetary Ball Mill Milling Machine
- Laboratory Planetary Ball Mill Rotating Ball Milling Machine
People Also Ask
- What role does a planetary ball mill play in eggshell fertilizer production? Unlock Superior Chemical Reactivity
- What is the function of ball milling equipment in NZSSP electrolyte preparation? Optimize NASICON Solid-State Synthesis
- What is the purpose of ball milling? A Versatile Tool for Material Synthesis and Modification
- What are the disadvantages of a ball mill? High Energy Use, Noise, and Contamination Risks
- What is the difference between a ball mill and a sag mill? A Guide to Primary vs. Secondary Grinding



















