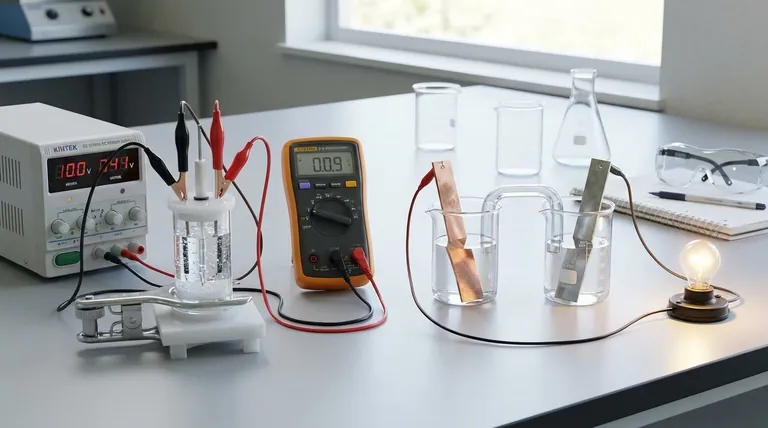
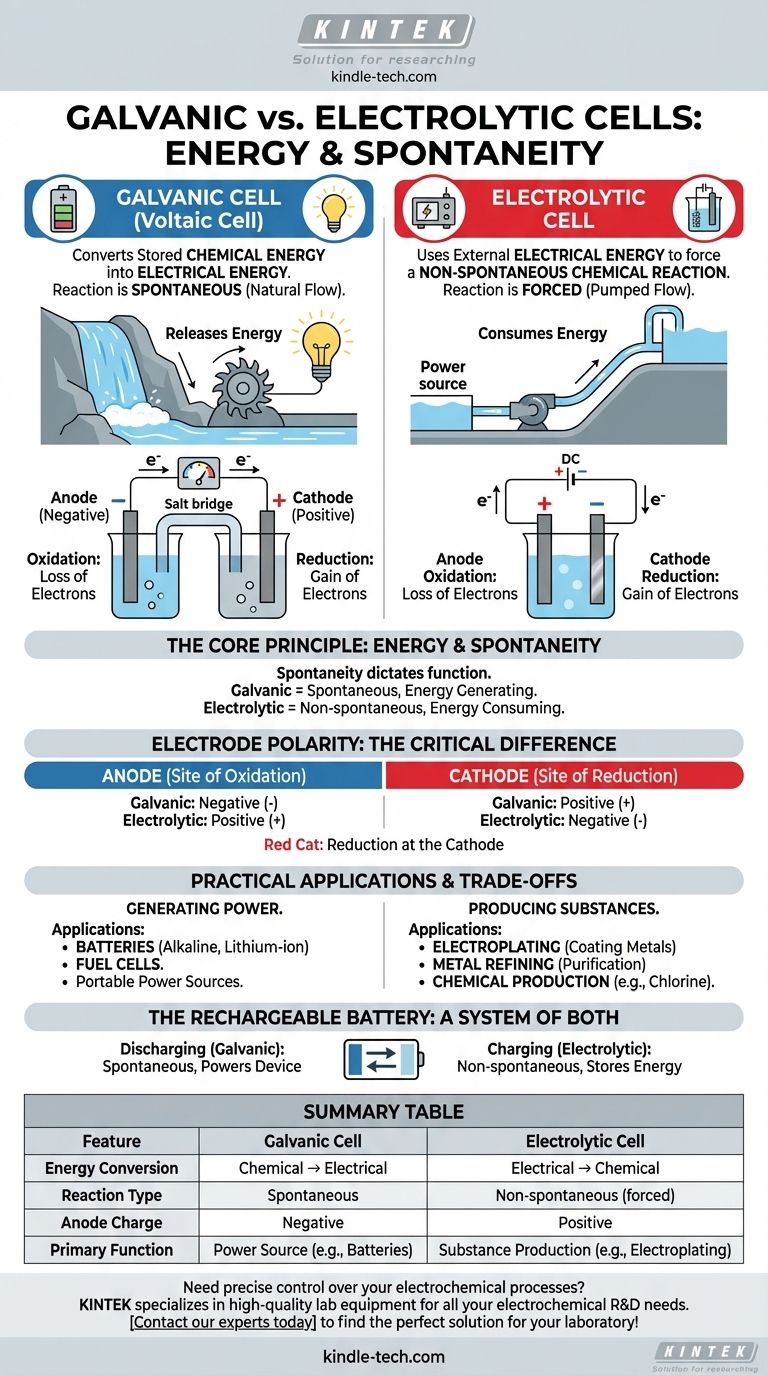
At their core, the difference between a galvanic and an electrolytic cell is the direction of energy conversion. A galvanic (or voltaic) cell converts stored chemical energy into electrical energy through a spontaneous reaction, like a battery powering a device. In contrast, an electrolytic cell uses external electrical energy to force a non-spontaneous chemical reaction to occur, such as in metal plating.
The fundamental distinction lies in spontaneity. Galvanic cells harness a chemical reaction that wants to happen on its own, releasing energy as electricity. Electrolytic cells use electricity to force a chemical reaction that would otherwise not happen.

The Core Principle: Energy and Spontaneity
The behavior of any electrochemical cell is governed by whether its internal redox reaction is spontaneous or non-spontaneous. This single principle dictates its function and structure.
Galvanic Cells: Generating Energy
In a galvanic cell, the chemical reaction is spontaneous. This means the reactants have higher potential energy than the products, and the reaction proceeds naturally, releasing energy.
This released energy drives electrons through an external circuit, creating an electric current. Think of it like a waterfall: the water naturally flows downhill, and we can place a turbine in its path to generate electricity.
Electrolytic Cells: Consuming Energy
In an electrolytic cell, the desired chemical reaction is non-spontaneous. The products are at a higher energy state than the reactants, so the reaction will not happen on its own.
To make it occur, we must supply energy from an external power source (like a battery or power supply). This external voltage forces electrons to move against their natural direction, driving the reaction. This is like using a pump to move water uphill.
How This Principle Defines Cell Components
While the fundamental definitions of the anode and cathode remain the same, their charge (polarity) is reversed between the two cell types. This is a common point of confusion but is a direct consequence of spontaneity.
The Anode: Always the Site of Oxidation
In both cell types, the anode is defined as the electrode where oxidation (the loss of electrons) takes place.
The Cathode: Always the Site of Reduction
Similarly, in both cell types, the cathode is the electrode where reduction (the gain of electrons) occurs. A simple mnemonic is "Red Cat" (Reduction at the Cathode).
The Critical Difference: Electrode Polarity
In a galvanic cell, the spontaneous oxidation at the anode releases a flow of electrons. This buildup of negative charge makes the anode negative and the cathode, which attracts the electrons, positive.
In an electrolytic cell, an external power source is used. Its positive terminal is connected to the anode, where it forcibly pulls electrons away from the chemical species, causing oxidation. Therefore, the anode is positive, and the cathode is negative.
Practical Applications and Trade-offs
The difference between generating and consuming energy leads to completely different real-world applications for these two types of cells.
Galvanic Cells in Practice: Portable Power
Galvanic cells are designed to be power sources. Their primary application is in batteries, from single-use alkaline batteries to rechargeable lithium-ion cells in your phone and car.
Fuel cells are another type of galvanic cell, continuously generating electricity as long as fuel (like hydrogen) is supplied.
Electrolytic Cells in Practice: Manufacturing and Refining
Electrolytic cells are industrial workhorses used to produce materials. Key applications include electroplating (coating an object with a thin metal layer) and the purification of metals like copper and aluminum.
They are also essential for producing key industrial chemicals, such as chlorine gas and sodium hydroxide from saltwater (brine).
The Rechargeable Battery: A System of Both
A rechargeable battery is the perfect illustration of both principles. When it is powering your device, it acts as a galvanic cell, running a spontaneous reaction. When you plug it in to charge, an external power source reverses the process, turning it into an electrolytic cell to drive a non-spontaneous reaction and restore the initial reactants.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Your understanding of which cell to consider depends entirely on whether you need to produce energy or produce a substance.
- If your primary focus is generating power from a chemical reaction: You are working with a galvanic cell, where a spontaneous process creates an electric current.
- If your primary focus is creating a substance using electricity: You are using an electrolytic cell, where an external voltage drives a non-spontaneous chemical change.
- If your primary focus is storing and reusing electrical energy: You are dealing with a rechargeable system that alternates between being an electrolytic cell (charging) and a galvanic cell (discharging).
Ultimately, these two cell types are two sides of the same electrochemical coin, defined by the direction of energy flow.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Galvanic Cell | Electrolytic Cell |
|---|---|---|
| Energy Conversion | Chemical → Electrical | Electrical → Chemical |
| Reaction Type | Spontaneous | Non-spontaneous (forced) |
| Anode Charge | Negative | Positive |
| Primary Function | Power Source (e.g., Batteries) | Substance Production (e.g., Electroplating) |
Need precise control over your electrochemical processes? The right lab equipment is crucial for accurate results, whether you're developing new battery materials or refining metal plating techniques. KINTEK specializes in high-quality lab equipment and consumables for all your electrochemical research and development needs. Contact our experts today to find the perfect solution for your laboratory!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Electrolytic Electrochemical Cell for Coating Evaluation
- Electrolytic Electrochemical Cell with Five-Port
- H-Type Double-Layer Optical Electrolytic Electrochemical Cell with Water Bath
- Electrolytic Electrochemical Cell Gas Diffusion Liquid Flow Reaction Cell
- Multifunctional Electrolytic Electrochemical Cell Water Bath Single Layer Double Layer
People Also Ask
- What are the design advantages of a three-electrode electrolytic cell? Achieve Precision in Photoelectrolysis
- What material is the body of the electrolysis cell made of? High Borosilicate Glass for Reliable Electrochemistry
- What are the advantages of using a three-electrode electrolytic cell? Achieve Precision in Stainless Steel Analysis
- How does a standard three-electrode electrolytic cell system evaluate AA 6061 coatings? Precision Corrosion Analysis
- How does a three-electrode electrolytic cell system control MnO2 nanosheet loading? Achieve Micro-Level Precision
- What is the significance of shortening the distance between the anode and cathode in a PEC reactor? Maximize Efficiency
- What is the function of an electrolytic cell in tritium enrichment? Boost Detection for Low-Level Analysis
- How should an all-quartz electrolytic cell and its components be maintained for long-term use? A Guide to Maximizing Equipment Lifespan







