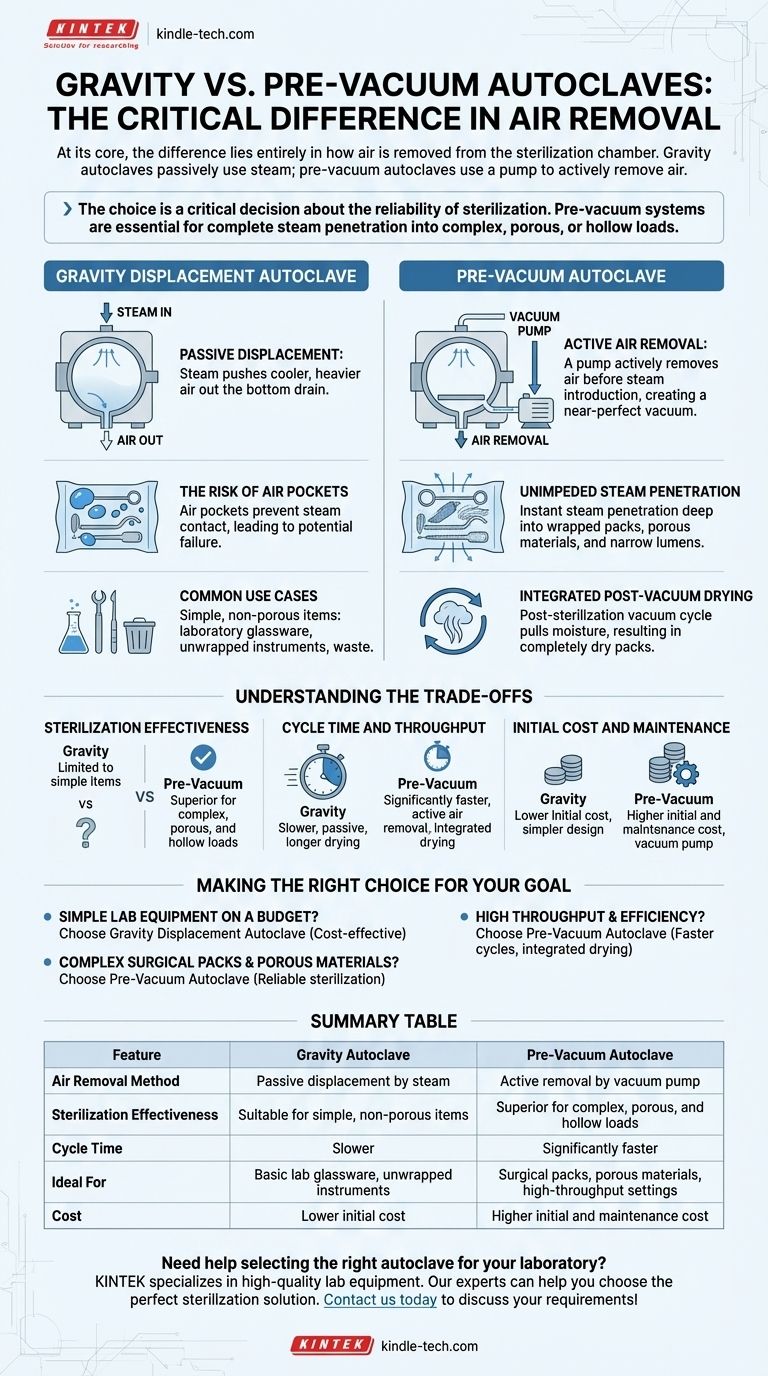
At its core, the difference between a gravity autoclave and a pre-vacuum autoclave lies entirely in how air is removed from the sterilization chamber. A gravity autoclave passively uses steam to push colder air out the bottom, while a pre-vacuum autoclave uses a pump to actively and forcefully remove air before steam is ever introduced. This single difference in air removal method dictates their speed, effectiveness, and the types of materials they can reliably sterilize.
The choice between gravity and pre-vacuum is not simply a matter of cost; it is a critical decision about the reliability of sterilization. Gravity autoclaves are sufficient for simple, non-porous items, but pre-vacuum systems are essential for ensuring complete steam penetration into complex, porous, or hollow loads.

How a Gravity Displacement Autoclave Works
A gravity displacement autoclave operates on a simple, reliable principle derived from basic physics. It is the most common type found in basic laboratory settings.
The Principle of Displacement
Steam is generated and piped into the chamber. Because steam is less dense than cool air, it fills the chamber from the top down.
This incoming steam gradually displaces the colder, heavier air, pushing it downward and out through a temperature-sensitive drain port at the bottom of the chamber. Sterilization time begins only after enough air has been displaced for the chamber to reach the target temperature.
The Risk of Air Pockets
The primary limitation of this passive method is the potential for trapped air. Air pockets can get stuck within complex instrument packs, porous textiles, or hollow tubes.
Since trapped air prevents steam from making direct contact with surfaces, these areas will not be sterilized, leading to a potential cycle failure.
Common Use Cases
Gravity autoclaves are best suited for sterilizing non-porous items with simple surfaces. This includes laboratory glassware, unwrapped metal instruments, waste, and some media solutions.
How a Pre-Vacuum Autoclave Works
Pre-vacuum (or prevac) autoclaves, also known as high-speed or Class B sterilizers, represent a more advanced approach. They are the standard in most medical and surgical settings.
The Power of Active Air Removal
Before steam is introduced, a vacuum pump actively removes the air from the chamber. This is often done in a series of pulses, alternating between vacuum and steam, to ensure all air is evacuated from even the most challenging loads.
Unimpeded Steam Penetration
By creating a near-perfect vacuum, the system ensures there is no residual air to act as a barrier. When steam is finally injected, it can instantly penetrate the entire load, reaching deep inside wrapped packs, porous materials, and long, narrow lumens.
Integrated Post-Vacuum Drying
Most pre-vacuum models also include a post-sterilization vacuum cycle. This final phase pulls moisture from the load, resulting in instrument packs that are completely dry and ready for storage or immediate use.
Understanding the Trade-offs
The choice between these two technologies involves clear trade-offs in performance, speed, and cost.
Sterilization Effectiveness
A pre-vacuum autoclave offers superior and more reliable sterilization for a wider range of materials, especially complex surgical kits and porous loads. Gravity systems are effective but limited to simpler items.
Cycle Time and Throughput
Pre-vacuum cycles are significantly faster. Active air removal and post-vacuum drying drastically reduce the total time compared to the slow, passive displacement and longer drying times required by gravity units.
Initial Cost and Maintenance
Gravity autoclaves have a lower initial purchase price due to their simpler design. Pre-vacuum systems are more expensive and require more maintenance due to the addition of a vacuum pump and more complex controls.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Your decision should be driven by the specific materials you need to sterilize and your operational requirements for speed and reliability.
- If your primary focus is sterilizing simple lab equipment like glassware or unwrapped metal tools on a budget: A gravity displacement autoclave is a cost-effective and perfectly suitable choice.
- If your primary focus is sterilizing complex surgical packs, porous materials, or hollow instruments: A pre-vacuum autoclave is the necessary standard for ensuring complete and reliable sterilization.
- If your primary focus is high throughput and efficiency in a clinical or production setting: The faster cycle times and integrated drying of a pre-vacuum system provide a clear advantage that justifies the higher cost.
Understanding this fundamental difference in air removal empowers you to select the precise sterilization technology that your application demands.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Gravity Autoclave | Pre-Vacuum Autoclave |
|---|---|---|
| Air Removal Method | Passive displacement by steam | Active removal by vacuum pump |
| Sterilization Effectiveness | Suitable for simple, non-porous items | Superior for complex, porous, and hollow loads |
| Cycle Time | Slower | Significantly faster |
| Ideal For | Basic lab glassware, unwrapped instruments | Surgical packs, porous materials, high-throughput settings |
| Cost | Lower initial cost | Higher initial and maintenance cost |
Need help selecting the right autoclave for your laboratory?
KINTEK specializes in providing high-quality lab equipment and consumables, including both gravity and pre-vacuum autoclaves. Our experts can help you choose the perfect sterilization solution based on your specific needs—whether you're processing simple glassware or complex surgical instruments.
Contact us today to discuss your requirements and ensure reliable, efficient sterilization for your laboratory!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Desktop Fast Laboratory Autoclave Sterilizer 35L 50L 90L for Lab Use
- Laboratory Sterilizer Lab Autoclave Vertical Pressure Steam Sterilizer for Liquid Crystal Display Automatic Type
- Laboratory Sterilizer Lab Autoclave Pulse Vacuum Lifting Sterilizer
- Benchtop Laboratory Vacuum Freeze Dryer
- Laboratory Test Sieves and Sieving Machines
People Also Ask
- What is cycle time as related to autoclaving? Master the Full Process for Effective Sterilization
- What is the normal temperature of an autoclave? Achieve Sterile Confidence with Precise Control
- What is the purpose of autoclaving in the laboratory? Ensure Sterile Safety & Integrity
- What are the advantages of using an autoclave in the lab? Achieve Unmatched Sterilization for Your Lab
- What is the size of the autoclave? Choose the Right Capacity for Your Lab



















