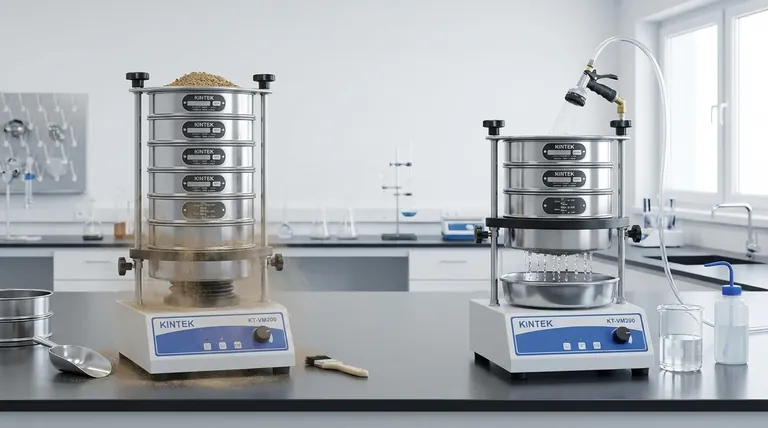
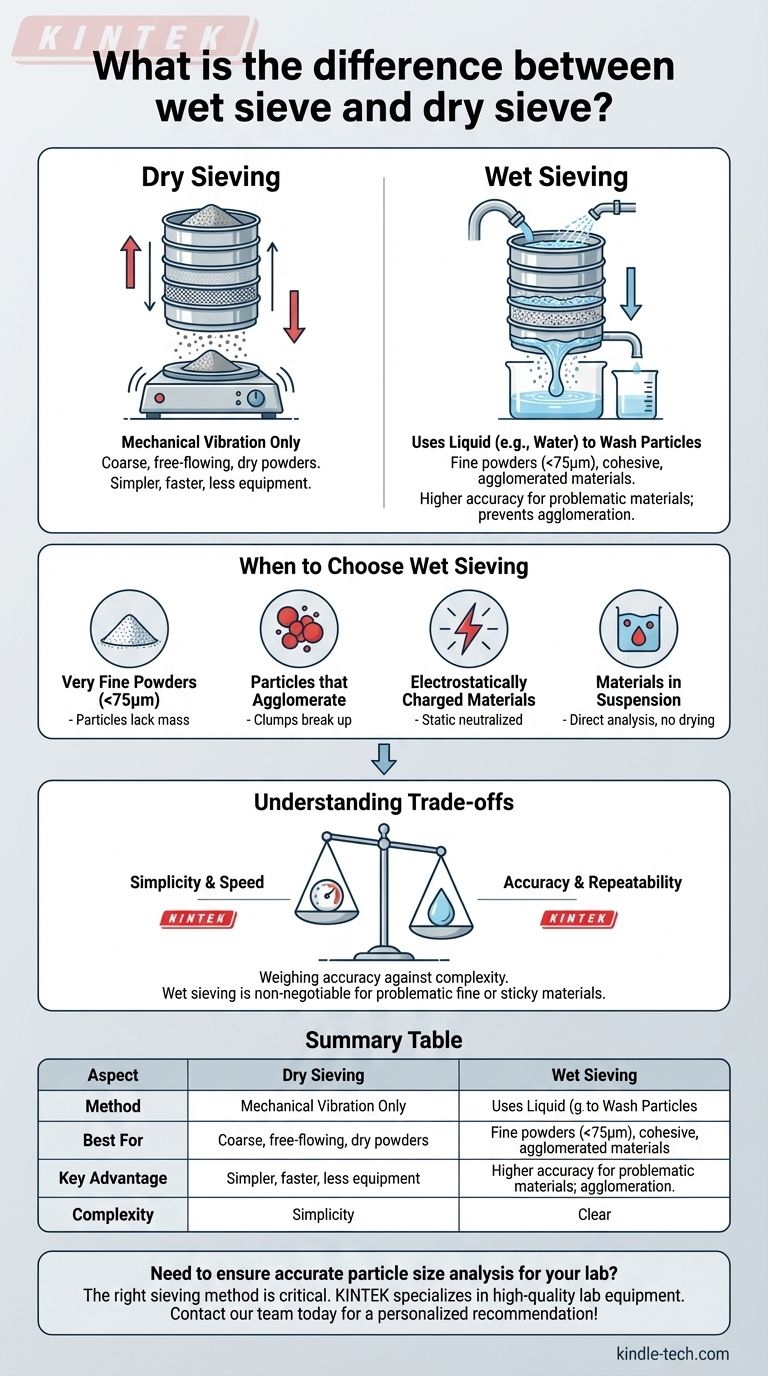
At its core, the difference is the medium used for separation. Dry sieve analysis relies on mechanical vibration alone to sort particles through a stack of screens, while wet sieve analysis introduces a liquid—typically water—to help wash fine, sticky, or agglomerated particles through the sieve mesh.
The decision between wet and dry sieving is not a matter of preference, but a necessary response to the physical properties of your sample. While dry sieving is the simpler default, wet sieving is the essential solution for fine or cohesive powders that would otherwise yield inaccurate results.

The Mechanics of Sieving
To understand when to use each method, you must first understand how they fundamentally work and the problems they are designed to solve.
Dry Sieving: The Standard Approach
Dry sieving is the most common method for particle size analysis. It involves placing a sample onto the top of a stack of sieves, each with a progressively smaller mesh opening.
The entire stack is then agitated by a mechanical shaker. Gravity and vibration cause the particles to move down through the stack until they are retained by a sieve with a mesh too small for them to pass through.
Wet Sieving: Overcoming Particle Resistance
Wet sieving is a more specialized technique used when dry methods fail. The process starts similarly, with a sample on a stack of sieves, but adds a critical element: a liquid.
A controlled spray of liquid (often water from a nozzle) is directed onto the sample. This liquid serves to wash the particles, break up clumps (agglomerates), and carry the finer material through the mesh openings. The process continues until the liquid running from the bottom of the stack is clear.
When to Choose Wet Sieving
Wet sieving is not an alternative but a necessary correction for materials that cannot be accurately measured when dry. It directly solves several common problems.
For Very Fine Powders
Particles below approximately 75 microns often lack the mass to easily overcome the resistance of the sieve mesh through gravity and vibration alone. The flow of water in wet sieving provides the additional force needed to carry these fine particles through the openings.
For Particles that Agglomerate
Fine materials can clump together due to moisture or intermolecular forces. These agglomerates behave like larger particles, preventing them from passing through the correct sieve and skewing the results toward a coarser distribution. The liquid in wet sieving deagglomerates these clumps, ensuring each particle is sized individually.
For Electrostatically Charged Materials
During the agitation of dry sieving, some powders can develop a static charge. This causes particles to cling to the sieve frame and wires, blinding the mesh and preventing an accurate separation. A liquid neutralizes these static forces, allowing the particles to move freely.
For Materials Already in Suspension
If your sample is already in a liquid form, such as a slurry or suspension, wet sieving is the most direct and logical method. It allows you to analyze the material in its native state without the need for drying, which could alter the particle characteristics.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Choosing the right method requires weighing the accuracy gains of wet sieving against its added complexity.
Simplicity and Speed
Dry sieving is faster, requires less equipment, and involves a simpler cleanup process. If a material can be sieved dry, it is almost always the more efficient method.
Accuracy and Repeatability
For problematic fine or sticky materials, wet sieving is non-negotiable for accuracy. It provides far more reliable and repeatable results by eliminating the issues of agglomeration and static charge that make dry sieving ineffective.
Equipment and Process Complexity
Wet sieving requires additional hardware like spray nozzles, pumps, and a system for collecting the liquid. The sample must also be carefully dried after sieving to get an accurate final weight for each fraction, adding time and a potential source of error to the process.
Sample Compatibility
A critical constraint is that the sieving liquid must not alter the sample. It cannot dissolve, react with, or cause the particles to swell. Selecting a compatible liquid is a prerequisite for any valid wet sieve analysis.
Making the Right Choice for Your Analysis
Your choice depends entirely on the physical characteristics of the material you are analyzing.
- If your primary focus is on coarse, free-flowing granules or powders: Dry sieving is the standard, most efficient, and most appropriate method.
- If your primary focus is on fine powders (<75 microns), cohesive materials, or samples that clump: Wet sieving is necessary to achieve accurate and repeatable particle size distribution.
- If your primary focus is on a material already in a slurry or liquid suspension: Wet sieving is the only direct and correct method for analysis.
Ultimately, selecting the right sieving method is the first step toward ensuring your particle size data is reliable and truly represents your material.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | Dry Sieving | Wet Sieving |
|---|---|---|
| Method | Mechanical vibration only | Uses liquid (e.g., water) to wash particles |
| Best For | Coarse, free-flowing, dry powders | Fine powders (<75µm), cohesive, or agglomerated materials |
| Key Advantage | Simpler, faster, less equipment | Higher accuracy for problematic materials; prevents agglomeration |
| Complexity | Lower | Higher (requires drying step, liquid handling) |
Need to ensure accurate particle size analysis for your lab?
The right sieving method is critical for reliable results. KINTEK specializes in high-quality lab equipment and consumables for all your particle analysis needs. Our experts can help you select the perfect sieving solution for your specific materials, whether you're working with fine powders, cohesive substances, or standard granules.
Contact our team today to discuss your application and get a personalized recommendation!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Test Sieves and Vibratory Sieve Shaker Machine
- Vibratory Sieve Shaker Machine Dry Three-Dimensional Vibrating Sieve
- Laboratory Vibratory Sieve Shaker Machine for Dry and Wet Three-Dimensional Sieving
- Three-dimensional electromagnetic sieving instrument
- Laboratory Vibratory Sieve Shaker Machine Slap Vibrating Sieve
People Also Ask
- Why is powder classification using standard sieves essential for SHS reactions? Unlock Superior Nitriding Results
- Why is a laboratory electromagnetic vibratory sieve shaker used? Optimize Walnut Shell Chemical Pretreatment
- What are the disadvantages of sieve machine? Key Limitations in Particle Size Analysis
- Why is a laboratory sieving system required for bentonite in coatings? Ensure Flawless Surface Performance
- How do high-precision sieving systems benefit zeolite preparation? Maximize Adsorption for Wastewater Treatment



















