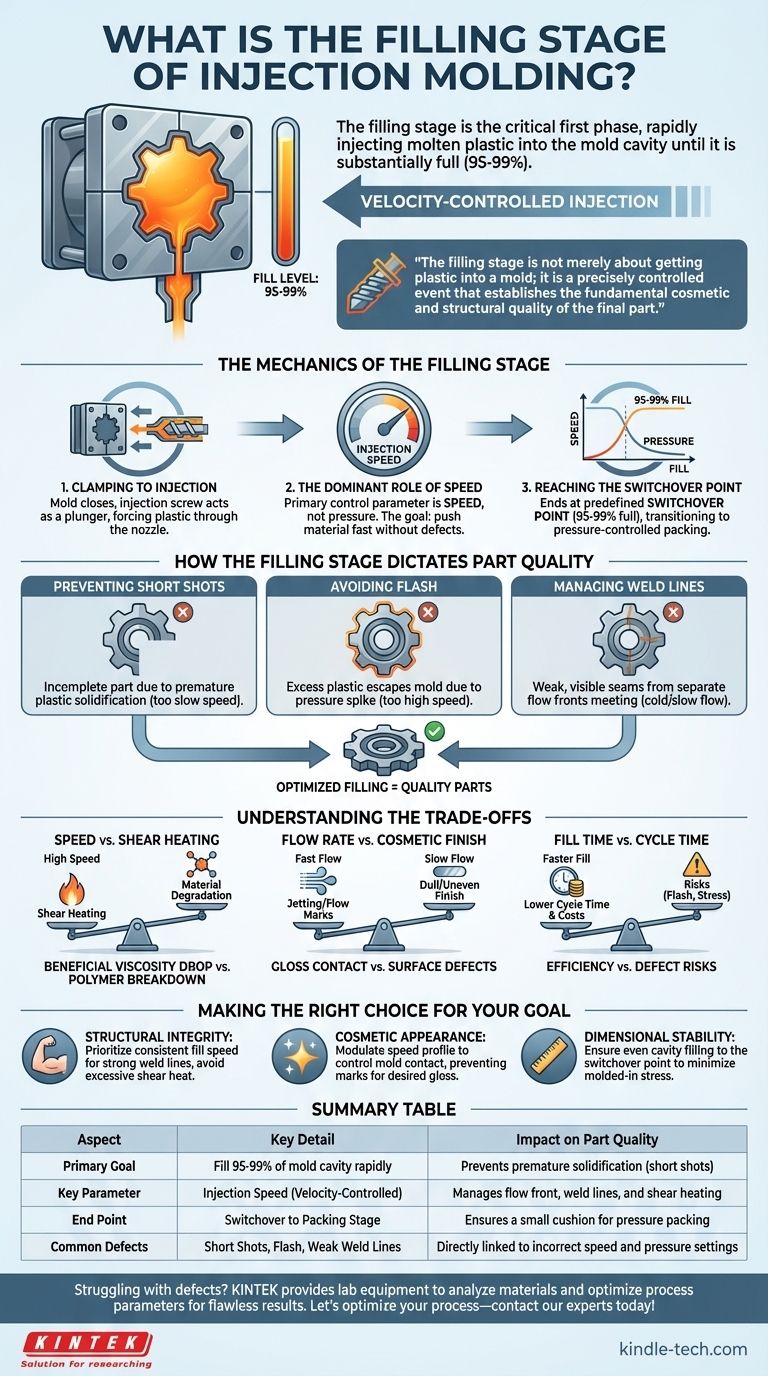
The filling stage is the critical first phase of the injection molding process. It begins the moment the two halves of the mold are clamped shut and involves rapidly injecting molten plastic material into the empty mold cavity. This high-speed, high-pressure event continues until the cavity is substantially full, typically between 95% and 99%.
The filling stage is not merely about getting plastic into a mold; it is a precisely controlled event that establishes the fundamental cosmetic and structural quality of the final part. The parameters set during these few seconds determine everything from surface finish to internal strength.
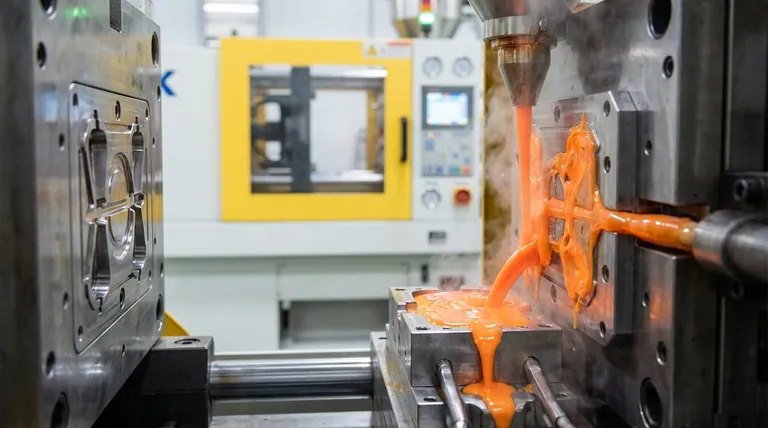

The Mechanics of the Filling Stage
To understand its importance, you must first understand the sequence of events. The filling stage is a dynamic process governed by speed, pressure, and temperature.
From Clamping to Injection
The cycle begins with the mold closing and being held together under immense force by the clamping unit. Once secure, the injection unit's screw moves forward like a plunger, forcing the accumulated molten plastic through the nozzle and into the mold's runner system.
The Dominant Role of Speed
During the filling stage, the primary control parameter is injection speed, not pressure. The goal is to push the material into the mold as quickly as possible without causing defects. This velocity-controlled approach ensures the entire cavity is filled before any section of the plastic can prematurely cool and solidify.
Reaching the Switchover Point
The filling stage ends at a predefined position known as the switchover point. This is the critical moment the machine transitions from the high-speed "filling" stage to the pressure-controlled "packing" stage. This switch typically occurs when the mold is 95% to 99% full, leaving a small cushion to be filled during the subsequent packing phase.
How the Filling Stage Dictates Part Quality
Nearly all common molding defects can be traced back to an improperly controlled filling stage. How the plastic enters and flows within the mold is paramount.
Preventing Short Shots
A short shot is an incomplete part, which occurs if the molten plastic solidifies before it has completely filled the mold cavity. This is often caused by an injection speed that is too slow, allowing the material to cool excessively as it travels.
Avoiding Flash
Flash is the opposite problem: a thin layer of excess plastic that escapes the mold cavity, typically at the parting line. This can happen if the injection speed is too high, creating a pressure spike that forces the mold halves apart slightly.
Managing Weld Lines
When the molten plastic flows around a core or enters from multiple gates, the separate flow fronts must meet and fuse. The point where they meet is called a weld line. A cold or slow-moving flow front results in a weak, often visible weld line, compromising the part's strength and appearance.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Optimizing the filling stage is a balancing act. Pushing for one objective can negatively impact another, requiring careful consideration of the material and part design.
Speed vs. Shear Heating
High injection speeds generate friction as the plastic flows, a phenomenon known as shear heating. This can be beneficial, as it lowers the plastic's viscosity and helps it fill thin sections. However, excessive shear can degrade the polymer, breaking down its molecular chains and weakening the final part.
Flow Rate vs. Cosmetic Finish
The speed at which the molten plastic contacts the mold surface directly impacts the part's gloss and finish. A fast injection can create a "jetting" effect, causing flow marks on the surface. Conversely, a fill that is too slow can lead to a dull or uneven finish.
Fill Time vs. Cycle Time
Naturally, a faster fill time reduces the overall cycle time, increasing production efficiency and lowering costs. However, this pursuit of speed must be balanced against the risk of creating defects like flash, high internal stresses, or material degradation.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The ideal filling strategy depends entirely on the specific requirements of the part.
- If your primary focus is structural integrity: Prioritize a consistent fill speed that ensures strong weld lines and avoids degrading the material with excessive shear heat.
- If your primary focus is cosmetic appearance: Modulate the injection speed profile to manage how the plastic contacts the mold wall, preventing flow marks and achieving the desired surface gloss.
- If your primary focus is dimensional stability: Ensure the cavity is filled evenly and consistently to the switchover point, minimizing molded-in stress that can cause warping later.
Ultimately, mastering the filling stage is the first and most essential step toward producing consistent, high-quality injection-molded parts.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | Key Detail | Impact on Part Quality |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Goal | Fill 95-99% of mold cavity rapidly | Prevents premature solidification (short shots) |
| Key Parameter | Injection Speed (Velocity-Controlled) | Manages flow front, weld lines, and shear heating |
| End Point | Switchover to Packing Stage | Ensures a small cushion of material remains for pressure packing |
| Common Defects | Short Shots, Flash, Weak Weld Lines | Directly linked to incorrect speed and pressure settings |
Struggling with molding defects like short shots or flash? The precision of your filling stage is critical. At KINTEK, we specialize in providing the high-performance lab equipment and consumables needed to analyze materials, optimize your process parameters, and achieve flawless results. Our expertise supports laboratories in perfecting injection molding for superior structural integrity and cosmetic finishes. Let's optimize your process—contact our experts today for a consultation!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Small Injection Molding Machine for Lab Use
- Double Plate Heating Press Mold for Lab
- Single Punch Electric Tablet Press Machine Laboratory Powder Tablet Punching TDP Tablet Press
- Lab Plastic PVC Calender Stretch Film Casting Machine for Film Testing
- Single Punch Electric Tablet Press Machine TDP Tablet Punching Machine
People Also Ask
- What is the manufacturing process of rubber molding? Injection, Compression, or Transfer Molding?
- What is the injection molding process? A Guide to High-Volume Part Production
- What is molding technique? A Guide to High-Volume, Complex Part Manufacturing
- What is a positive of injection moulding? Achieve High-Volume Production with Unmatched Efficiency
- What is the application of injection moulding machine? Powering Mass Production for Complex Parts



















