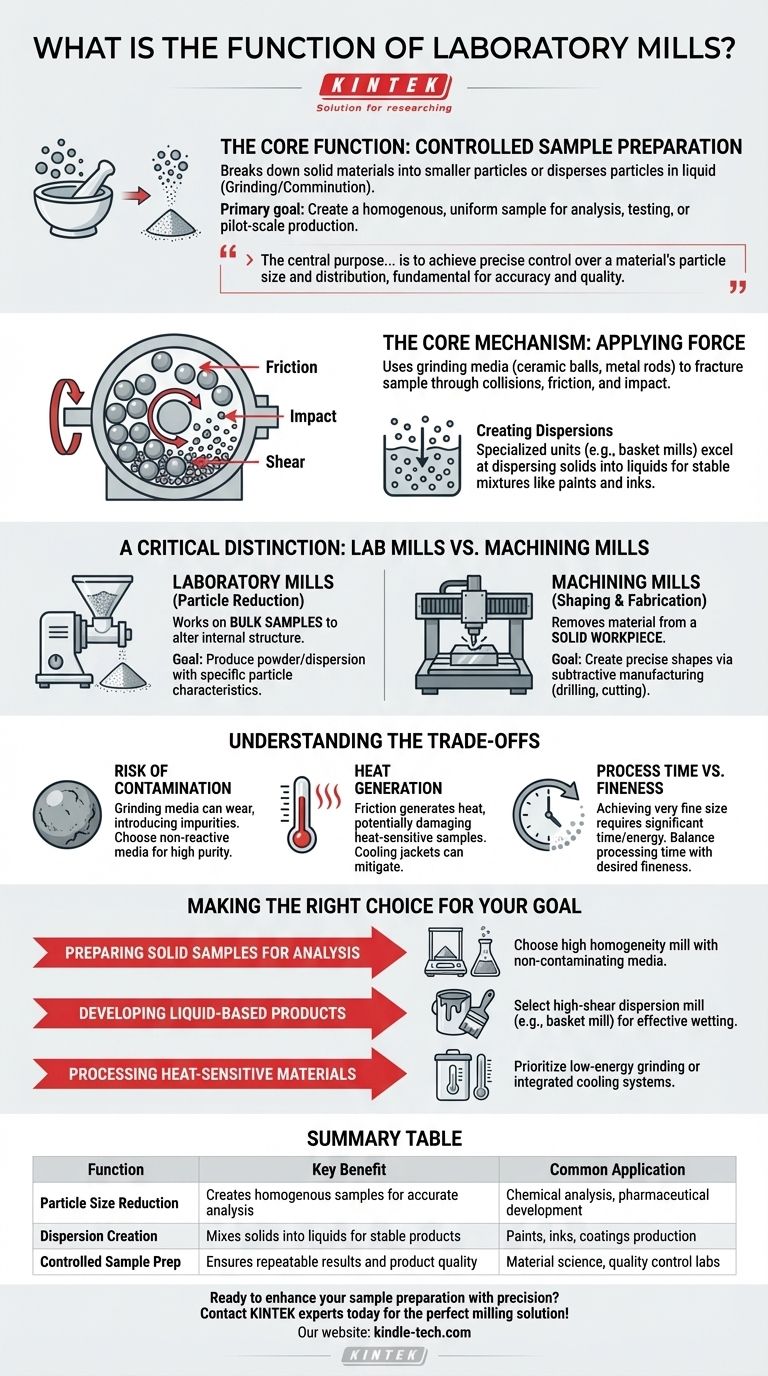
At its core, a laboratory mill is a device designed to break down solid materials into smaller particles or to disperse particles within a liquid. This process of size reduction, known as grinding or comminution, is achieved by applying mechanical force through friction, impact, or shear. The primary function is to create a homogenous, uniform sample suitable for analysis, testing, or pilot-scale production.
The central purpose of a laboratory mill is not just to break things, but to achieve precise control over a material's particle size and distribution. This control is fundamental to ensuring the accuracy of scientific analysis and the quality of product development.

The Primary Goal: Controlled Sample Preparation
The effectiveness of many scientific and industrial processes hinges on the physical characteristics of the starting materials. Laboratory mills provide the necessary control over these characteristics.
Why Particle Size Matters
Reducing particle size increases the surface area of a material. This can dramatically affect its properties, such as accelerating chemical reaction rates, improving the solubility of a compound, or defining the texture and stability of a final product like paint or a pharmaceutical tablet.
The Core Mechanism: Applying Force
Lab mills use a grinding medium—such as ceramic balls, metal rods, or flint pebbles—to create friction and impact forces. As the mill's chamber rotates or agitates, this media collides with the sample material, fracturing it into progressively smaller pieces.
Beyond Grinding: Creating Dispersions
Some specialized units, like basket mills, are designed less for dry grinding and more for creating stable mixtures. They excel at dispersing solid pigments or particles into a liquid base, which is a critical step in producing materials like inks, paints, adhesives, and other chemical coatings.
A Critical Distinction: Lab Mills vs. Machining Mills
The term "mill" can be a source of confusion, as it is also used to describe a common machine tool. It is essential to understand the difference in their function.
Laboratory Mills: For Particle Reduction
These devices work on a bulk sample to alter its internal structure. The goal is to produce a powder or a liquid dispersion with specific particle characteristics. The overall shape of the starting material is irrelevant; the focus is on what happens at the microscopic level.
Machining Mills: For Shaping and Fabrication
A vertical mill or milling machine is a tool used for fabrication. It removes material from a solid workpiece (like a block of metal or plastic) to create a precise shape or feature through tasks like drilling, cutting, and boring. This is a subtractive manufacturing process, not a sample preparation one.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While essential, using a laboratory mill involves considerations that can impact the quality of your results. Understanding these trade-offs is key to proper use.
The Risk of Contamination
The grinding media is not indestructible. Over time, it can wear down, introducing small amounts of its own material into your sample. This is a critical concern in high-purity applications, and selecting an appropriate, non-reactive media (like zirconia or agate) is crucial.
Heat Generation from Friction
The intense friction and impact inside a mill generate significant heat. This can be detrimental to heat-sensitive samples, potentially causing them to melt, decompose, or undergo unwanted chemical changes. Some advanced mills incorporate cooling jackets to mitigate this effect.
Process Time vs. Desired Fineness
Achieving an extremely fine particle size is not instantaneous. It requires significant time and energy input. There is always a trade-off between the processing time you can afford and the final particle size your application requires.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The ideal milling process depends entirely on your end objective.
- If your primary focus is preparing a solid sample for chemical analysis: Choose a mill that provides high homogeneity and offers grinding media that will not contaminate your sample.
- If your primary focus is developing a liquid-based product like paint or ink: Select a high-shear dispersion mill, such as a basket mill, designed to effectively wet and distribute particles in a liquid matrix.
- If your primary focus is processing a heat-sensitive or fragile material: Prioritize a mill that allows for low-energy grinding or has an integrated cooling system to prevent sample degradation.
Ultimately, selecting the right laboratory mill is about gaining precise control over your material's physical properties to ensure repeatable and reliable results.
Summary Table:
| Function | Key Benefit | Common Application |
|---|---|---|
| Particle Size Reduction | Creates homogenous samples for accurate analysis | Chemical analysis, pharmaceutical development |
| Dispersion Creation | Mixes solids into liquids for stable products | Paints, inks, coatings production |
| Controlled Sample Prep | Ensures repeatable results and product quality | Material science, quality control labs |
Ready to enhance your sample preparation with precision? The right laboratory mill is critical for achieving accurate, repeatable results in your research or quality control processes. At KINTEK, we specialize in providing high-quality lab equipment and consumables tailored to your specific application—whether you're in pharmaceuticals, chemicals, or material science. Contact our experts today to find the perfect milling solution for your laboratory's needs and ensure your materials meet the highest standards of quality and consistency.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Single Horizontal Jar Mill
- High Energy Vibratory Laboratory Ball Mill Double Tank Type
- High Energy Planetary Ball Mill Milling Machine for Laboratory
- High-Energy Omnidirectional Planetary Ball Mill Milling Machine for Laboratory
- High-Energy Omnidirectional Planetary Ball Mill Machine for Laboratory
People Also Ask
- What role does a high-frequency ultrasonic homogenizer play in PEO? Achieve Superior Coating Uniformity and Stability
- What is the function of an agate mortar and pestle in solid-state battery preparation? Ensure High Purity Mixing
- What are the limitations of ball milling method? Understand the trade-offs of mechanical grinding
- How does the argon atmosphere protection in a ball mill affect the final quality of CuCr50 alloy powder? Explained
- Can you make flour with a hammer mill? Yes, for Coarse, Whole-Grain Flour & Animal Feed
- What is the primary function of an Agate Mortar in Mesoporous Rutile TiO2 preparation? Ensure Ultra-Pure Sample Grinding
- Why are mechanical grinding or high-shear mixing processes necessary? Achieve Uniform Zinc Anode Protective Layers
- What is the use of a micro pulverizer? Achieve Fine Grinding for Food, Pharma & Chemicals



















