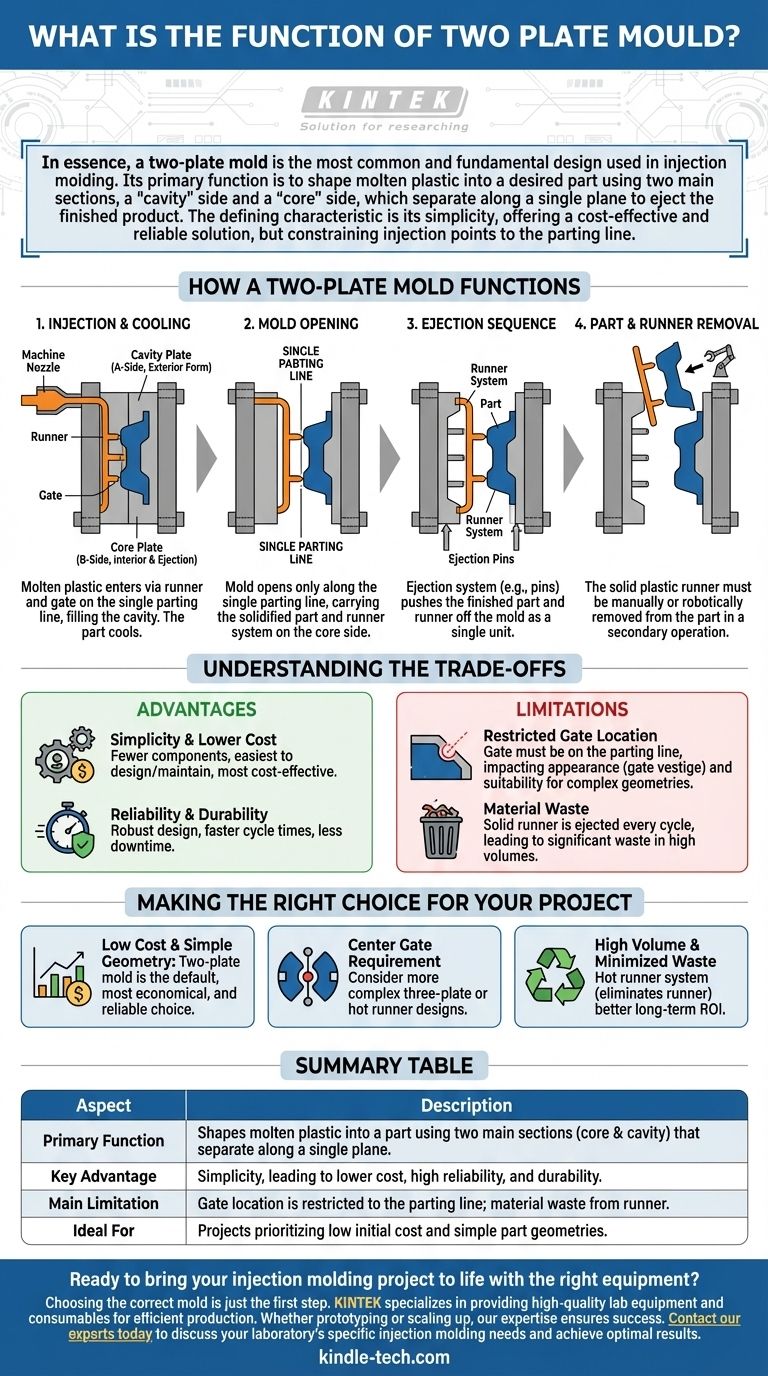
In essence, a two-plate mold is the most common and fundamental design used in injection molding. Its primary function is to shape molten plastic into a desired part using two main sections, a "cavity" side and a "core" side, which separate along a single plane to eject the finished product.
The defining characteristic of a two-plate mold is its simplicity. By using a single parting line where the mold opens, it offers a cost-effective and reliable solution, but this simplicity directly constrains where the plastic can be injected into the part.
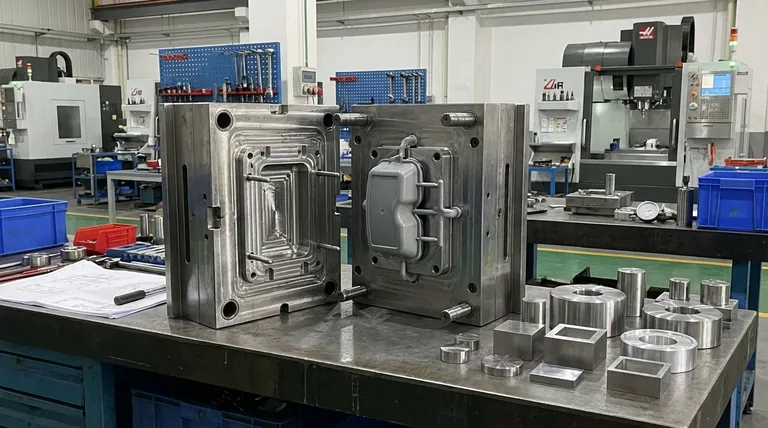

How a Two-Plate Mold Functions
A two-plate mold's operation is straightforward, revolving around its two main halves and the single surface where they meet.
The Two Main Sections: Core and Cavity
Every two-plate mold consists of two primary sections. The cavity plate (often called the A-side) typically forms the exterior, cosmetic surface of the part. The core plate (B-side) forms the interior geometry and houses the ejection system.
The Single Parting Line
This is the most critical concept. The parting line is the single plane where the core and cavity plates meet and separate. When the injection molding cycle is complete, the entire mold opens only along this line.
The Runner and Gate System
To get molten plastic into the part cavity, a channel system is machined into the mold. The runner is the main channel from the machine nozzle, and the gate is the small opening where plastic enters the actual part cavity.
In a two-plate mold, both the runner and the gate must be located directly on the parting line. This is a non-negotiable design constraint.
The Ejection Sequence
After the plastic part has cooled and solidified, the mold opens at the parting line. The finished part, along with the now-solid runner and gate, is held on the core side. An ejection system (typically using pins) then pushes the part and the attached runner system out of the mold as a single unit.
Understanding the Trade-offs
The simplicity of the two-plate mold is both its greatest strength and its primary source of limitations.
Advantage: Simplicity and Lower Cost
Fewer components and a simpler construction make two-plate molds the most cost-effective option to design, manufacture, and maintain. They are the workhorse of the injection molding industry for this reason.
Advantage: Reliability and Durability
With fewer moving parts compared to more complex designs, two-plate molds are extremely robust and reliable. This often leads to faster cycle times and less downtime for maintenance.
Limitation: Restricted Gate Location
Because the gate must be on the parting line, you can only inject plastic into the part's outer edge. This can impact the part's final appearance (leaving a "gate vestige" or mark) and can be unsuitable for complex geometries that require a more central fill point.
Limitation: Material Waste
The runner system is ejected with the part in every cycle. This solid plastic runner must be manually or robotically removed from the part in a secondary operation. This runner material is often waste, which can become a significant cost in high-volume production.
Making the Right Choice for Your Project
Choosing the right mold type depends entirely on your part design, budget, and production volume.
- If your primary focus is low initial cost and simple part geometry: The two-plate mold is the default, most economical, and most reliable choice.
- If your part requires a gate in the center for cosmetic or structural reasons: You must consider a more complex three-plate or hot runner mold design.
- If you are running very high volumes where minimizing material waste is critical: A hot runner system, which eliminates the runner entirely, often provides a better long-term return on investment.
Ultimately, recognizing the two-plate mold's reliance on a single parting line is the key to leveraging its cost-effective power for the right applications.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | Description |
|---|---|
| Primary Function | Shapes molten plastic into a part using two main sections (core & cavity) that separate along a single plane. |
| Key Advantage | Simplicity, leading to lower cost, high reliability, and durability. |
| Main Limitation | Gate location is restricted to the parting line, which can impact part aesthetics and lead to material waste from the runner system. |
| Ideal For | Projects prioritizing low initial cost and featuring simple part geometries. |
Ready to bring your injection molding project to life with the right equipment?
Choosing the correct mold is just the first step. KINTEK specializes in providing the high-quality lab equipment and consumables necessary for efficient and reliable production. Whether you're prototyping with a simple two-plate mold or scaling up with more complex systems, our expertise ensures you have the right tools for success.
Contact our experts today to discuss how we can support your laboratory's specific injection molding needs and help you achieve optimal results.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Special Heat Press Mold for Lab Use
- Cylindrical Press Mold for Lab Applications
- Polygon Press Mold for Lab
- Assemble Square Lab Press Mold for Laboratory Applications
- Special Shape Press Mold for Lab
People Also Ask
- What is the role of high-strength graphite molds in vacuum hot pressing Beryllium? Enhance Densification & Precision
- What roles do graphite molds play during vacuum hot pressing? Optimize Alloy Powder Densification & Precision
- What are the advantages of using high-strength graphite molds in the hot press sintering of Ti6Al4V-based composites?
- What are the primary functions of graphite dies in sintering? Optimize Nano-AlN Sintering Efficiency
- How do graphite molds function within the vacuum hot pressing process for ZnS? Optimize Densification & Optical Clarity















