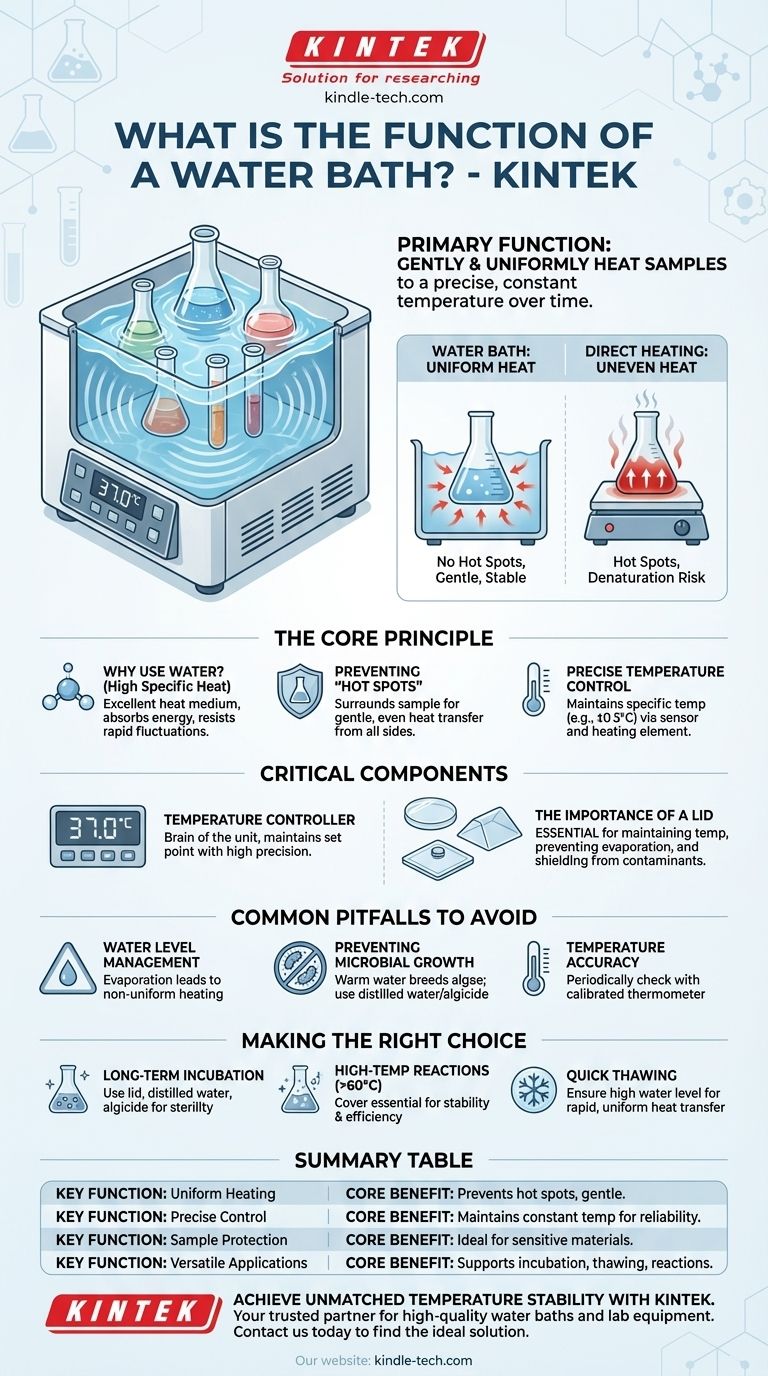
In a laboratory setting, a water bath serves one primary function: to gently and uniformly heat samples to a constant, precise temperature over a long period. It works by submerging vessels, like test tubes or flasks, in a container of heated water. This use of water as a medium ensures that no part of the sample is overheated or subjected to the harsh "hot spots" common with direct heating methods.
The true value of a water bath isn't just about heating; it's the control and uniformity it provides. It acts as a thermal buffer, protecting sensitive biological and chemical samples from the rapid, uneven temperature fluctuations of a hot plate or open flame.

The Core Principle: Uniform and Gentle Heat Transfer
A water bath's design is simple, but its effectiveness relies on the physical properties of water and a controlled system. This combination is what makes it an indispensable tool for countless scientific procedures.
Why Use Water?
Water is an excellent medium for transferring heat. It has a high specific heat capacity, meaning it can absorb a lot of heat energy before its own temperature rises significantly.
This property creates a stable thermal environment. Once the bath reaches the target temperature, it resists rapid fluctuations, providing a steady state for the immersed samples.
Preventing "Hot Spots"
When you place a beaker directly on a hot plate, the glass at the bottom becomes much hotter than the rest of the liquid. This creates "hot spots" that can denature sensitive enzymes, kill living cells, or ruin delicate chemical reactions.
A water bath completely avoids this. The water surrounds the sample vessel, delivering heat gently and evenly from all sides at once.
Precise Temperature Control
Modern water baths use a thermostat and heating element to maintain a specific temperature with high accuracy, often within a fraction of a degree. Some advanced models also include a circulating pump to ensure the temperature is identical throughout the entire basin.
Critical Components for Optimal Performance
While the concept is straightforward, certain components are vital for maintaining the stability and integrity of an experiment. The choice of accessories directly impacts the quality of your results.
The Temperature Controller
This is the brain of the unit. It measures the water temperature via a sensor and cycles the heating element on and off to maintain the set point. Digital controllers offer the highest precision.
The Importance of a Lid or Cover
A cover is not merely an accessory; it is often essential for proper function. It serves several critical purposes that directly impact experimental conditions.
Lids are crucial for maintaining temperature, especially when operating the bath at temperatures above 60°C. They trap heat and prevent heat loss to the surrounding air.
They also prevent evaporation, which can change the concentration of solutions in open sample containers and lower the water level in the bath itself.
Finally, a cover acts as a shield to prevent outside contaminants like dust or airborne microbes from falling into the bath and your samples. Different lid designs—such as clear, gabled, or hinged—accommodate different types of glassware and experimental needs.
Common Pitfalls to Avoid
To achieve reliable and repeatable results, users must be aware of common operational mistakes that can compromise the stability of the water bath environment.
Water Level Management
Evaporation, especially during long, high-temperature incubations, will lower the water level. If the level drops below the sample in your vessel, heating will become non-uniform and the temperature will not be accurate.
Preventing Microbial Growth
Warm, standing water is an ideal breeding ground for algae and bacteria. This contamination can be a disaster for sterile applications. Using distilled water and adding a commercial algicide can prevent unwanted growth.
Temperature Accuracy
Never assume the display temperature is perfectly accurate. It's good practice to periodically check the water temperature with a calibrated thermometer, especially for highly sensitive applications, to ensure the unit is performing correctly.
Making the Right Choice for Your Experiment
Your specific goal dictates how you should use the water bath and its accessories to ensure the best outcome.
- If your primary focus is long-term incubation of sensitive cells: Use a properly fitted lid to prevent evaporation and contamination, and use distilled water with an algicide to maintain sterility.
- If your primary focus is running high-temperature reactions (above 60°C): A cover is essential to maintain thermal stability, reduce energy consumption, and reach the set point efficiently.
- If your primary focus is quickly thawing frozen reagents: Ensure the water level is high enough to submerge the frozen portion of the sample vessel for rapid and uniform heat transfer.
Ultimately, mastering the use of a water bath is about leveraging its unique stability to achieve reliable and repeatable experimental results.
Summary Table:
| Key Function | Core Benefit |
|---|---|
| Uniform Heating | Prevents hot spots, ensuring gentle heat transfer from all sides. |
| Precise Temperature Control | Maintains a constant temperature (often within ±0.5°C) for reliable results. |
| Sample Protection | Ideal for sensitive biological and chemical materials that degrade with direct heat. |
| Versatile Applications | Supports incubation, thawing, chemical reactions, and more. |
Achieve Unmatched Temperature Stability in Your Lab
Does your research demand precise, gentle heating without the risk of hot spots? The right water bath is critical for protecting your sensitive samples and ensuring experimental integrity.
KINTEK is your trusted partner for all laboratory equipment needs. We specialize in supplying high-quality water baths and consumables designed for reliability and precision. Our experts can help you select the perfect model with the right accessories—like precise digital controllers and essential lids—to maintain temperature stability and prevent contamination.
Let KINTEK enhance your lab's capabilities. Contact us today to find the ideal heating solution for your specific applications, from cell culture to chemical synthesis.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- High Temperature Constant Temperature Heating Circulator Water Bath Chiller Circulator for Reaction Bath
- 10L Heating Chilling Circulator Cooling Water Bath Circulator for High and Low Temperature Constant Temperature Reaction
- 50L Heating Chilling Circulator Cooling Water Bath Circulator for High and Low Temperature Constant Temperature Reaction
- 30L Heating Chilling Circulator Cooling Water Bath Circulator for High and Low Temperature Constant Temperature Reaction
- 20L Heating Chilling Circulator Cooling Water Bath Circulator for High and Low Temperature Constant Temperature Reaction
People Also Ask
- What is the working temperature range of a high-temperature oil bath? Optimize Your High-Heat Lab Processes
- How does a thermostatic water bath function in ODS steel corrosion tests? Ensure Precise Bio-Simulation Accuracy
- Why do manganese electrolysis processes require a thermostatic water bath? Master Thermal Control for High-Purity Metal
- What is the function of a constant temperature water bath? Ensure Reliable Dental Resin Conversion Rates
- Why is a constant temperature water bath necessary for evaluating corrosion inhibitors? Ensure Precise Thermal Control



















