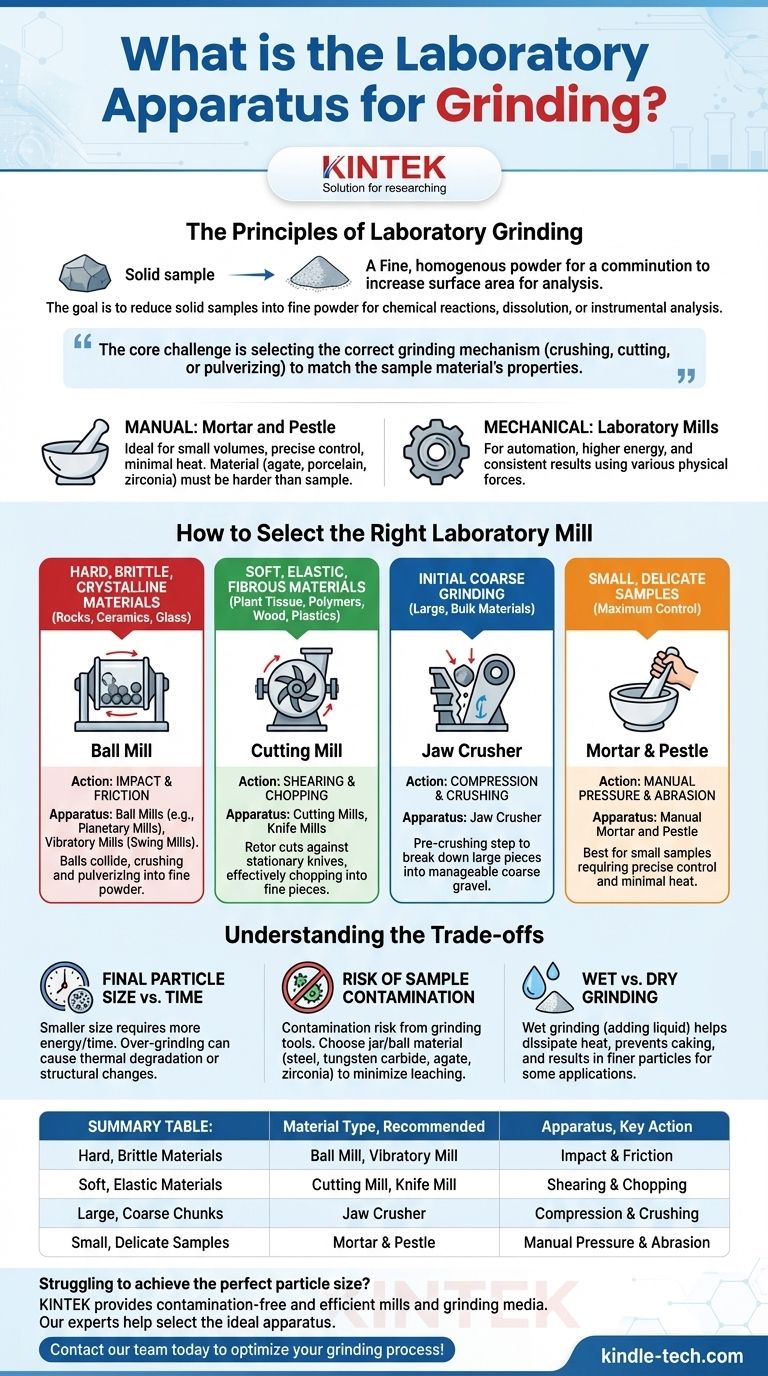
The primary laboratory apparatus for grinding is a mill, with the specific type—such as a ball mill, vibratory mill, or cutting mill—chosen based on the sample's properties and the desired final particle size. For simple, small-scale tasks, a manual mortar and pestle is also commonly used.
The core challenge is not simply finding a "grinder," but selecting the correct grinding mechanism. The choice depends entirely on matching the tool's action—whether it crushes, cuts, or pulverizes—to the physical characteristics of your sample material.

The Principles of Laboratory Grinding
Grinding, or comminution, is a critical step in sample preparation. The goal is to reduce the size of a solid sample to create a fine, homogenous powder. This increases the surface area, which is essential for subsequent chemical reactions, dissolution, or instrumental analysis.
Manual Grinding: The Mortar and Pestle
The most fundamental grinding tool is the mortar (the bowl) and pestle (the grinder). It works by applying pressure and abrasion to crush and mix a sample.
This method is ideal for small sample volumes where precise control is needed and automation is unnecessary. The material of the mortar and pestle (e.g., agate, porcelain, zirconia) is chosen to be harder than the sample to minimize contamination.
Mechanical Grinding: Laboratory Mills
For automation, higher energy, and more consistent results, laboratories rely on a variety of mechanical mills. These devices use different physical forces to achieve particle size reduction.
How to Select the Right Laboratory Mill
The type of mill you need is dictated by the properties of your starting material. Mills are not one-size-fits-all; using the wrong one can damage the sample or the equipment.
For Hard, Brittle, or Crystalline Materials
Materials like rocks, minerals, ceramics, and glass require high-energy impact and friction.
Ball mills (including planetary mills) are the standard choice. The sample is placed in a jar with grinding balls. As the jar rotates or moves in a planetary motion, the balls cascade and collide, crushing and pulverizing the material between them into a very fine powder.
For Medium-Hard and Fibrous Materials
Materials that are tough but not extremely hard are often processed with high-frequency motion.
Vibratory mills (or swing mills) use a powerful electromagnetic drive to vibrate the grinding jar, typically containing a puck and ring or several balls. The high-speed impacts rapidly pulverize the sample and are a common tool for preparing samples for X-ray fluorescence (XRF) analysis.
For Soft, Elastic, or Fibrous Materials
Materials like plant tissue, polymers, wood, and plastics do not shatter under impact; they deform or smear. These require a cutting or shearing action.
Cutting mills and knife mills operate like a high-speed blender. A rotor with sharp blades cuts the material against stationary knives, effectively chopping it into fine pieces rather than crushing it.
For Initial Coarse Grinding
When starting with large, bulk materials, a preliminary crushing step is often required before fine grinding.
A jaw crusher is used for this pre-crushing. Two jaws, one fixed and one moving, compress and break down large pieces of rock or other hard materials into a more manageable coarse gravel.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Choosing a grinding method involves balancing several key factors to ensure the final powder is suitable for your analysis.
Final Particle Size vs. Time
Achieving a smaller particle size requires more energy and a longer grinding time. Over-grinding can sometimes be detrimental, potentially causing thermal degradation of the sample or unwanted changes in its crystalline structure.
Risk of Sample Contamination
The grinding process inherently introduces a risk of contamination from the grinding tools themselves. The material of the grinding jars and balls (e.g., hardened steel, tungsten carbide, agate, zirconia) must be carefully selected to minimize leaching of unwanted elements into your sample.
Wet vs. Dry Grinding
Most grinding is done dry. However, for some applications, wet grinding (adding a liquid like water or ethanol) can help dissipate heat, prevent samples from caking, and result in a finer particle size. This decision depends entirely on the sample and the subsequent analysis.
Making the Right Choice for Your Sample
- If your primary focus is preparing hard, brittle materials (rocks, ceramics) for fine powder analysis: A planetary ball mill or vibratory swing mill is your most effective tool.
- If your primary focus is processing soft, organic, or elastic samples (plant tissue, polymers): A cutting or knife mill is essential to achieve proper size reduction without smearing.
- If your primary focus is breaking down large, coarse chunks of very hard material: A jaw crusher is the necessary first step before moving to a finer mill.
- If your primary focus is grinding a small, delicate sample with maximum control and minimal heat: A manual mortar and pestle offers the best solution.
Ultimately, successful sample preparation depends on correctly identifying your material's properties and selecting the grinding tool designed to handle them.
Summary Table:
| Material Type | Recommended Grinding Apparatus | Key Action |
|---|---|---|
| Hard, Brittle Materials (rocks, ceramics) | Ball Mill, Vibratory Mill | Impact & Friction |
| Soft, Elastic Materials (polymers, plant tissue) | Cutting Mill, Knife Mill | Shearing & Chopping |
| Large, Coarse Chunks | Jaw Crusher | Compression & Crushing |
| Small, Delicate Samples | Mortar & Pestle | Manual Pressure & Abrasion |
Struggling to achieve the perfect particle size for your analysis? KINTEK specializes in laboratory equipment and consumables, providing the right mills and grinding media to ensure your sample preparation is contamination-free and efficient. Our experts can help you select the ideal apparatus for your specific material and analytical goals. Contact our team today to optimize your grinding process!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Grinding Mill Mortar Grinder for Sample Preparation
- Laboratory Single Horizontal Jar Mill
- Laboratory Horizontal Planetary Ball Mill Milling Machine
- High Energy Vibratory Laboratory Ball Mill Double Tank Type
- High Energy Planetary Ball Mill Milling Machine for Laboratory
People Also Ask
- Why is an agate mortar and pestle preferred for grinding MAX phase? Ensure Sample Purity & Zero Contamination
- What is the primary purpose of using grinding tools like agate mortars? Optimize LTO Electrode Performance
- What is a mortar and pestle used for in a lab? A Guide to Precision Grinding and Mixing
- What are the different types of laboratory mills? Choose the Right Grinder for Your Sample Material
- What is the function of an Agate Mortar and Pestle in sodium battery preparation? Ensure Contaminant-Free Mixing



















