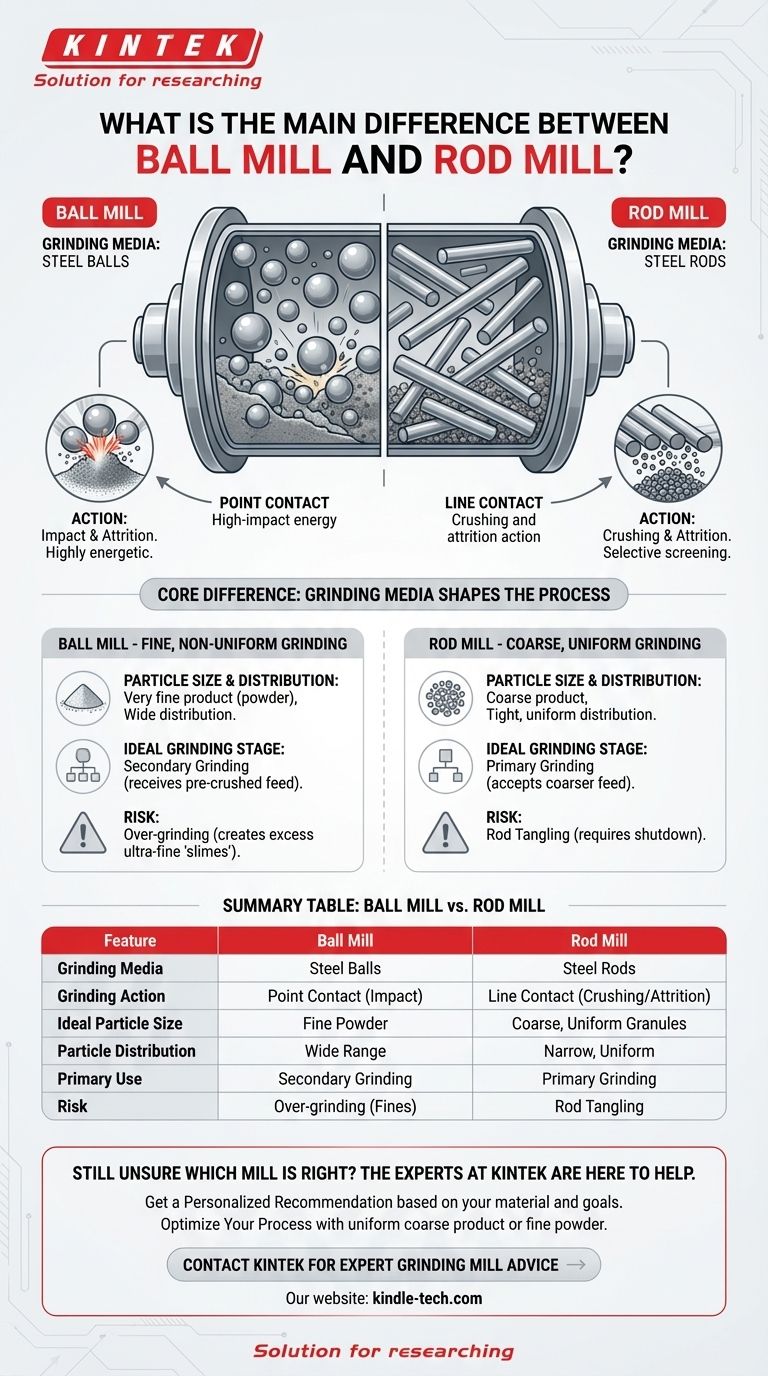
The defining difference between a ball mill and a rod mill lies in their grinding media. A ball mill uses steel balls to crush material, while a rod mill uses steel rods. This seemingly simple distinction creates significant differences in their internal grinding action, the final particle size they produce, and the applications for which they are best suited.
The choice between a rod mill and a ball mill is fundamentally a choice between coarse, uniform grinding and fine, non-uniform grinding. Rod mills excel at creating a consistent particle size with minimal fines, while ball mills are designed to reduce material to a very fine powder.

How Grinding Media Shapes the Process
The shape of the grinding medium—a sphere versus a cylinder—completely changes the physics inside the mill. This determines the efficiency, output, and ideal use case for each machine.
The Point Contact of a Ball Mill
In a ball mill, the grinding media are spheres. As the mill rotates, these balls cascade and tumble, creating countless points of high-impact contact.
This point contact is highly energetic and acts like a vast number of tiny hammer blows. It is exceptionally effective at pulverizing material into very fine particles.
Because the action is somewhat random and based on impact, ball mills tend to produce a wide distribution of particle sizes, including a significant amount of ultra-fine powder. The versatility of this method is why many specialized types exist, from small planetary and mixer mills to large horizontal rolling mills.
The Line Contact of a Rod Mill
In a rod mill, the grinding media are long steel rods. As the mill turns, these rods are lifted and then fall in a nearly parallel alignment, creating line contact with the material.
This line contact is a crushing and attrition action, not a high-impact one. The rods create a screening effect where larger particles at the feed end of the mill receive the most grinding energy, while smaller particles pass through the gaps between the rods.
This inherent classifying action is the rod mill's greatest strength. It naturally resists over-grinding and produces a product with a much narrower, more uniform particle size distribution.
Comparing the Output and Applications
The difference in grinding action directly translates to different outputs and roles within a processing circuit.
Particle Size and Distribution
A ball mill is the clear choice for producing a very fine product, often a powder. However, the particle size distribution will be wide.
A rod mill is used for producing a coarser product with a tight, uniform particle size distribution. It is highly effective at minimizing the creation of extreme fines (often called "slimes").
Ideal Feed and Grinding Stage
Rod mills are often used as the primary grinding mill. They can accept a coarser feed material and efficiently turn it into a consistent product ideal for the next stage of processing.
Ball mills are typically used as secondary grinding mills. They work best when fed a pre-crushed, relatively consistent material, which they then reduce to its final, fine specification.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Nuances
Choosing between these mills requires understanding their operational limitations and where they might fail.
The Risk of Over-Grinding
The primary trade-off with a ball mill is the risk of over-grinding. The intense, non-selective action can create an excess of ultra-fine particles. In processes like mineral flotation, these slimes can be detrimental to recovery rates.
The Risk of Rod Tangles
Rod mills have a critical operational risk: rod tangling. If the mill is operated incorrectly or the feed rate is inconsistent, the steel rods can become tangled into a mass, forcing a difficult and time-consuming shutdown to clear.
Mill Dimensions and Capacity
For both mill types, a general principle holds true: mill diameter dictates the grinding performance (the energy of the impact or crush), while mill length primarily affects capacity and residence time. This is why small-scale lab mills can effectively test formulations by matching the diameter of a full-size mill.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Your decision should be driven by the specific requirements of your final product and your overall process flow.
- If your primary focus is producing a coarse, uniform product with minimal fines: A rod mill is the superior choice due to its selective, line-contact grinding action.
- If your primary focus is achieving the finest possible particle size (a powder): A ball mill is the industry standard, offering high-impact grinding for maximum size reduction.
- If you are designing a multi-stage grinding circuit: Consider using a rod mill for the primary stage to prepare a consistent feed for a secondary ball mill, which then performs the fine grinding.
Ultimately, understanding the fundamental difference between point and line contact is the key to selecting the right mill for your specific size reduction goal.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Ball Mill | Rod Mill |
|---|---|---|
| Grinding Media | Steel Balls | Steel Rods |
| Grinding Action | Point Contact (Impact) | Line Contact (Crushing/Attrition) |
| Ideal Particle Size | Fine Powder | Coarse, Uniform Granules |
| Particle Distribution | Wide Range | Narrow, Uniform |
| Primary Use | Secondary Grinding | Primary Grinding |
| Risk | Over-grinding (Fines) | Rod Tangling |
Still Unsure Which Mill is Right for Your Process?
Selecting the correct grinding equipment is critical for achieving your target particle size and maximizing operational efficiency. The experts at KINTEK are here to help. We specialize in providing high-quality lab equipment and consumables, including mills tailored to your specific material and application.
- Get a Personalized Recommendation: Our technical team can analyze your material and grinding goals to recommend the ideal mill for your needs.
- Optimize Your Process: Ensure you get the uniform coarse product of a rod mill or the fine powder of a ball mill without the common operational pitfalls.
Contact us today via our form below to discuss your project and discover how KINTEK's solutions can enhance your laboratory's capabilities and results.
Contact KINTEK for Expert Grinding Mill Advice
Visual Guide
Related Products
- High Energy Planetary Ball Mill Machine for Laboratory Horizontal Tank Type
- Mini Planetary Ball Mill Machine for Laboratory Milling
- Liquid Nitrogen Cryogenic Grinder Mill Cryomill Airflow Ultrafine Pulverizer
- Single Punch Manual Tablet Press Machine TDP Tablet Punching Machine
- Warm Isostatic Press WIP Workstation 300Mpa for High Pressure Applications
People Also Ask
- What is the function of a high-energy planetary ball mill in the synthesis of iodo-vanadate-lead ceramic waste forms?
- How does a planetary ball mill enhance the electrocatalytic activity of La0.6Sr0.4CoO3-δ? Boost Your Catalyst Performance
- What is the role of a planetary ball mill in the preparation of NiCr-Al2O3-SrCO3 composite powders? Enhanced Homogeneity
- Why are high-intensity planetary ball mills preferred for reducing the crystallinity of lignocellulose?
- What is the specific role of a high-energy planetary ball mill in the synthesis of Ag-doped sulfide solid-state electrolytes?



















