In essence, electrolysis is the process of using electrical energy to drive a chemical reaction that would not happen on its own. An external power source applies a voltage across two electrodes submerged in a conductive solution or molten salt, called an electrolyte. This applied energy forces ions to migrate to oppositely charged electrodes, where they undergo decomposition through oxidation and reduction reactions.
An electrolytic cell is an engine for reversing chemical reactions. By applying external power, it forces electrons to flow against their natural tendency, compelling stable chemical compounds to break down into their constituent elements.
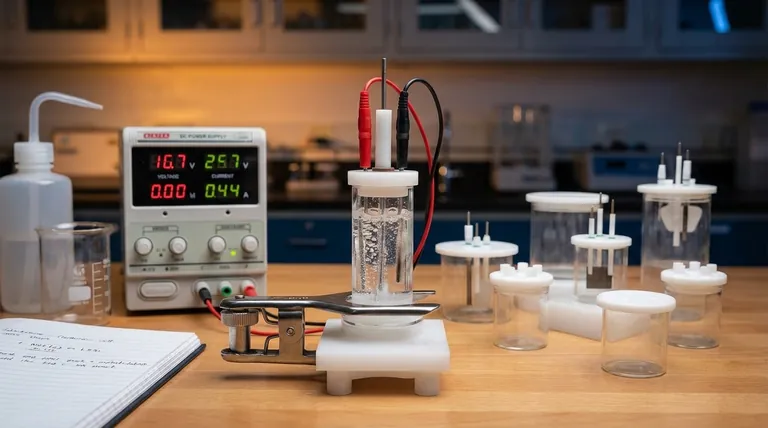

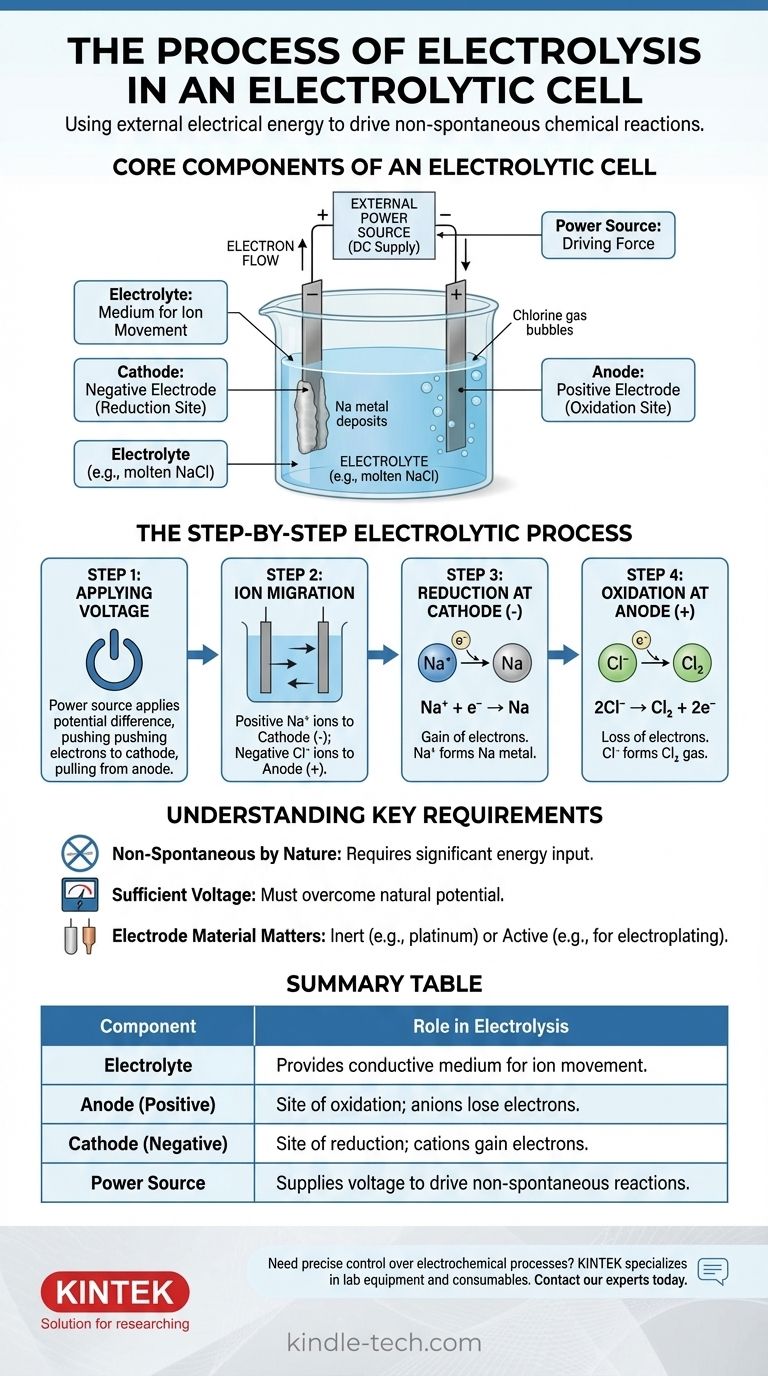
The Core Components of an Electrolytic Cell
To understand the process, you must first understand the function of each part. The system is a carefully orchestrated interplay between three key components.
The Electrolyte: A Medium for Ion Movement
The electrolyte is a substance containing free-moving ions, which makes it electrically conductive. It is typically a molten ionic compound, like sodium chloride (NaCl), or an aqueous solution containing dissolved ions.
The sole purpose of the electrolyte is to provide a medium through which charged ions can travel between the electrodes.
The Electrodes: Anode and Cathode
The electrodes are conductive materials (often metals or graphite) that are submerged in the electrolyte. They serve as the physical interface where the electrical circuit meets the chemical solution.
In an electrolytic cell, the polarity is defined by the external power source:
- The Anode is the positive electrode.
- The Cathode is the negative electrode.
The External Power Source: The Driving Force
This is typically a battery or DC power supply. Its job is to create a potential difference across the electrodes, forcing electrons to move in a direction they wouldn't spontaneously.
This external voltage is the "pump" that drives the entire non-spontaneous reaction, overcoming the natural chemical stability of the electrolyte.
The Step-by-Step Electrolytic Process
The process unfolds in a precise sequence once the power source is activated. We can illustrate this using the example of molten sodium chloride (NaCl).
Step 1: Applying the Voltage
An external voltage is applied. The power source pushes electrons toward one electrode, making it negatively charged (the cathode), and pulls electrons away from the other, making it positively charged (the anode).
Step 2: Ion Migration
Within the molten NaCl electrolyte, sodium exists as positive ions (cations, Na⁺) and chloride exists as negative ions (anions, Cl⁻).
Opposites attract: the positive Na⁺ cations are drawn toward the negative cathode, while the negative Cl⁻ anions are drawn toward the positive anode.
Step 3: Reduction at the Cathode (The Negative Electrode)
When the Na⁺ cations reach the negatively charged cathode, they each gain an electron supplied by the power source. This gain of electrons is a reduction reaction.
The Na⁺ ions are reduced to form neutral sodium metal (Na), which deposits on the cathode.
Step 4: Oxidation at the Anode (The Positive Electrode)
Simultaneously, when the Cl⁻ anions reach the positively charged anode, they each give up an electron to the electrode. This loss of electrons is an oxidation reaction.
The Cl⁻ ions are oxidized to form neutral chlorine atoms, which pair up to become chlorine gas (Cl₂) that bubbles away from the anode. The released electrons travel through the external circuit back to the power source, completing the circuit.
Understanding the Key Requirements
Electrolysis is powerful but operates under specific constraints. Ignoring these can lead to failed experiments or misunderstanding the results.
Non-Spontaneous by Nature
The core principle is that electrolysis drives a non-spontaneous reaction. The decomposition of salt into sodium metal and chlorine gas, for example, requires a significant input of energy. Without the external voltage, nothing would happen.
The Need for Sufficient Voltage
The external power source must supply a voltage high enough to overcome the natural potential of the chemical reaction. If the voltage is too low, it will not be strong enough to force the ion migration and electron transfer, and the reaction will not proceed.
Electrode Material Matters
For simple decomposition, inert electrodes (like platinum or carbon) are used. These materials facilitate the electron transfer without participating in the reaction themselves. In other applications, like electroplating, the anode can be an "active" electrode designed to be oxidized and dissolved into the electrolyte.
Applying This to Common Examples
The principles of electrolysis are universal, but the specific products depend entirely on the electrolyte used.
- If your goal is to produce pure metals: Use a molten salt of that metal as the electrolyte. The pure metal will be reduced and deposited at the cathode, as seen in the industrial production of sodium and aluminum.
- If your goal is to decompose water: Use water with a small amount of an acid or salt to improve conductivity. This process will produce hydrogen gas (H₂) at the cathode and oxygen gas (O₂) at the anode.
- If your goal is to electroplate an object: The object to be plated is set as the cathode. Metal ions from the electrolyte solution are reduced onto the object's surface, forming a thin, uniform metallic coating.
By controlling the flow of electrons, we can directly control and reverse chemical processes, a fundamental capability that underpins much of modern industry.
Summary Table:
| Component | Role in Electrolysis |
|---|---|
| Electrolyte | Provides conductive medium for ion movement (e.g., molten NaCl). |
| Anode (Positive) | Site of oxidation; anions lose electrons (e.g., Cl⁻ → Cl₂ gas). |
| Cathode (Negative) | Site of reduction; cations gain electrons (e.g., Na⁺ → Na metal). |
| Power Source | Supplies voltage to drive non-spontaneous reactions. |
Need precise control over electrochemical processes? KINTEK specializes in lab equipment and consumables for electrolysis, electroplating, and material synthesis. Our reliable power supplies, electrodes, and electrolyte solutions help you achieve consistent results—whether you're decomposing compounds, refining metals, or coating surfaces. Contact our experts today to discuss your laboratory's specific needs!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Quartz Electrolytic Electrochemical Cell for Electrochemical Experiments
- H-Type Double-Layer Optical Electrolytic Electrochemical Cell with Water Bath
- Electrolytic Electrochemical Cell Gas Diffusion Liquid Flow Reaction Cell
- Customizable CO2 Reduction Flow Cell for NRR ORR and CO2RR Research
- Li-Air Battery Case for Battery Lab Applications
People Also Ask
- How does electro deposition work? A Guide to Precision Coating with Electricity
- What procedures and observations are necessary during an experiment with a flat plate corrosion electrolytic cell? Master the 3-Phase Method
- How should an all-PTFE electrolytic cell be handled to prevent mechanical damage? Protect Your Investment and Data Integrity
- What are the key features of quartz that make it suitable for electrolytic cells? Discover the 4 Pillars of Superior Performance
- Which parameters must be strictly controlled using an all-PTFE electrolytic cell? Ensure Precision and Safety
- What is the mechanism of the Devanathan-Stachurski dual electrolytic cell? Explore Precise Hydrogen Permeation Testing
- What is the necessity of a non-woven fabric layer in a manganese electrolytic cell? Ensure High-Purity Metal Production
- What precautions should be taken regarding temperature when using an all-PTFE electrolytic cell? Ensure Safe & Accurate Experiments



















