Media milling is a high-energy process designed to reduce the size of solid particles suspended in a liquid. It works by placing the material into a chamber filled with small grinding bodies, or "media," such as ceramic or glass beads. An agitator then churns this mixture, causing the media to collide with the material particles at high speed, breaking them down through repeated impact and grinding forces.
The core challenge in many industries is not just mixing ingredients, but breaking down solid particles to a sub-micron level to create a stable, homogenous dispersion. Media milling solves this by introducing grinding media to create a chaotic, high-intensity environment where thousands of micro-collisions per second efficiently fracture and deagglomerate particles.
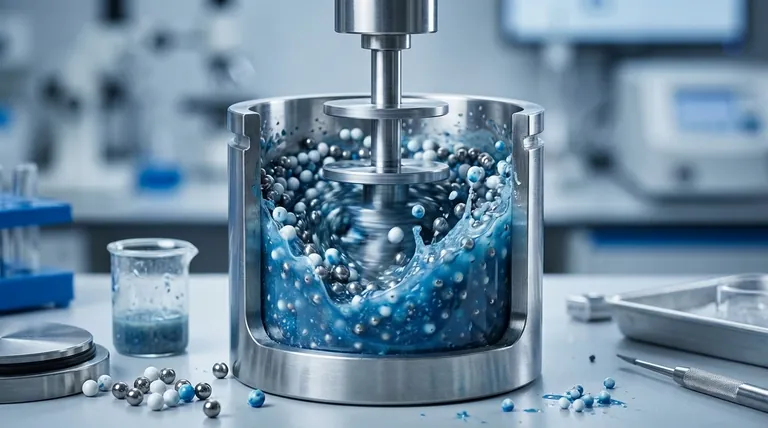

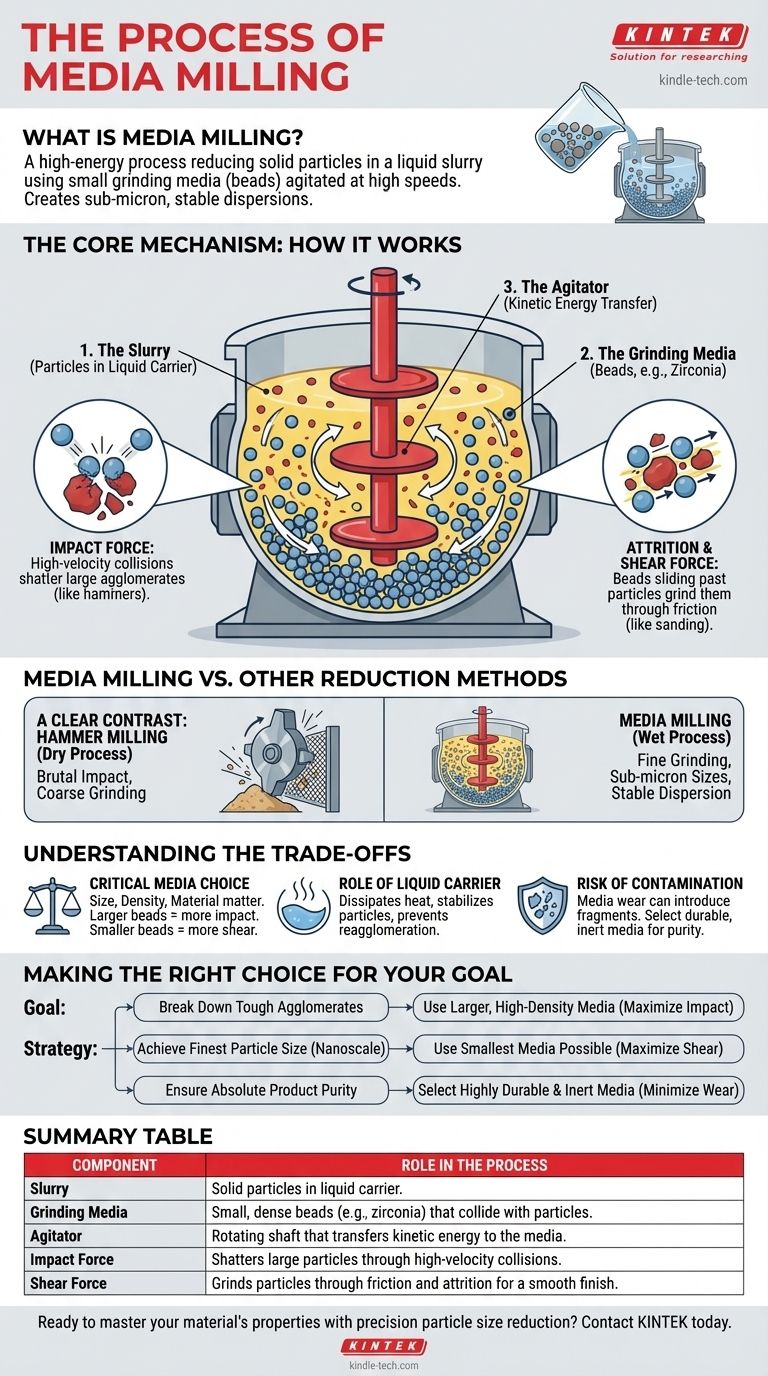
The Core Mechanism: How Media Milling Works
To understand the process, it's best to break it down into its essential components and the forces they generate. The entire system is designed to transfer kinetic energy from a motor into the grinding media as efficiently as possible.
The Three Key Components
A media mill consists of three primary elements working in concert:
- The Slurry: This is the material to be processed, consisting of the solid particles suspended in a liquid carrier.
- The Grinding Media: These are small, dense beads, typically made of highly durable materials like zirconium oxide, ceramic, or glass.
- The Agitator: This is a rotating shaft, often fitted with discs or pins, that transfers energy into the chamber.
Activating the Grinding Zone
When the mill is activated, the agitator spins at high speed. This movement forces the slurry and the grinding media into a state of intense, chaotic motion. The energy from the agitator is transferred directly to the countless beads within the chamber.
The Two Forces at Play
The particle size reduction occurs due to two distinct forces generated by the colliding media.
Impact Force
The high-velocity collisions between the grinding beads and the material particles create powerful impact forces. This action is like millions of microscopic hammers striking the particles, effectively shattering larger agglomerates and fracturing coarse primary particles.
Attrition and Shear Force
As the beads and particles are forced to slide past one another in the turbulent slurry, it creates immense shearing and attrition. This grinding action is particularly effective at reducing the size of already small particles and ensuring a smooth, homogenous final product.
Media Milling vs. Other Reduction Methods
It is critical to distinguish media milling from other techniques, as its purpose is unique. Its effectiveness lies in its ability to produce extremely fine particles in a liquid environment.
A Clear Contrast: Hammer Milling
A hammer mill is a dry milling process that uses rapidly rotating steel "hammers" to smash material through direct, brutal impact. The material is crushed until it is small enough to pass through a screen.
This method is excellent for coarse grinding of dry materials but lacks the finesse of media milling. Media milling is a wet process that uses the grinding media to achieve much finer, often sub-micron, particle sizes and create a stable dispersion, which is impossible with a hammer mill.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While powerful, the effectiveness of media milling depends on carefully controlling its variables. An incorrect setup can lead to inefficient processing or undesirable results.
The Critical Choice of Media
The size, density, and material of the grinding media are the most important variables. Larger, denser beads deliver higher impact forces, ideal for breaking down tough agglomerates. Smaller beads create more shear and have more contact points, which is better for achieving the finest possible particle sizes.
The Role of the Liquid Carrier
The liquid in the slurry does more than just carry the particles. It plays a crucial role in dissipating the intense heat generated during milling and helps stabilize the newly formed small particles, preventing them from clumping back together (a process known as reagglomeration).
The Inevitable Risk of Contamination
A primary trade-off is the potential for product contamination. Over time, the grinding media itself will wear down, and tiny fragments can enter the product. Choosing highly durable and chemically inert media, such as high-purity zirconium oxide, is essential for applications where purity is paramount, like in pharmaceuticals or electronics.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The optimal media milling strategy is defined entirely by your end goal. By adjusting the process variables, you can tailor the outcome to your specific application.
- If your primary focus is breaking down large, tough agglomerates: Use larger, high-density grinding media to maximize the impact forces within the mill.
- If your primary focus is achieving the finest possible particle size (nanoscale): Use the smallest grinding media possible to increase the number of shear events and surface contact points.
- If your primary focus is ensuring absolute product purity: Select a highly durable and inert media material, such as yttria-stabilized zirconia, to minimize wear and contamination.
Ultimately, mastering media milling is about controlling the energy and nature of these micro-collisions to precisely engineer your material's final properties.
Summary Table:
| Key Component | Role in the Process |
|---|---|
| Slurry | Solid particles suspended in a liquid carrier. |
| Grinding Media | Small, dense beads (e.g., zirconia) that collide with particles. |
| Agitator | Rotating shaft that transfers kinetic energy to the media. |
| Impact Force | Shatters large particles through high-velocity collisions. |
| Shear Force | Grinds particles through friction and attrition for a smooth finish. |
Ready to master your material's properties with precision particle size reduction? The experts at KINTEK are here to help. Whether you are developing pharmaceuticals, advanced ceramics, or specialty chemicals, our high-performance media mills and durable, contamination-free grinding media are engineered for your most demanding laboratory applications. Contact our team today to discuss your specific milling goals and discover the KINTEK solution for creating superior, stable dispersions.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Ball Mill Jar Mill with Metal Alloy Grinding Jar and Balls
- Laboratory Single Horizontal Jar Mill
- Laboratory Four-Body Horizontal Jar Mill
- Laboratory Horizontal Planetary Ball Mill Milling Machine
- Laboratory Grinding Mill Mortar Grinder for Sample Preparation
People Also Ask
- What industries use hammer mills? The Versatile Grinding Solution for Agriculture, Recycling, and More
- What is the primary role of grinding equipment in the pretreatment of copper concentrate for bioleaching?
- What is the role of laboratory-grade grinders and sieves in sample prep? Ensure High-Precision Corrosion Analysis
- What is the feed size of a ball mill? Optimize Your Grinding Process for Maximum Efficiency
- What is a mixer in biology? The Essential Tool for Homogeneous Samples
- What is the function of a high-energy ball mill in the synthesis of LPS? Unlock High Ionic Conductivity Today
- What types of gases, other than standard compressed air, can be used in jet milling? Enhance Precision and Safety
- What is the function of mechanical grinding equipment in AgI glass synthesis? Achieve Precise Material Homogeneity



















