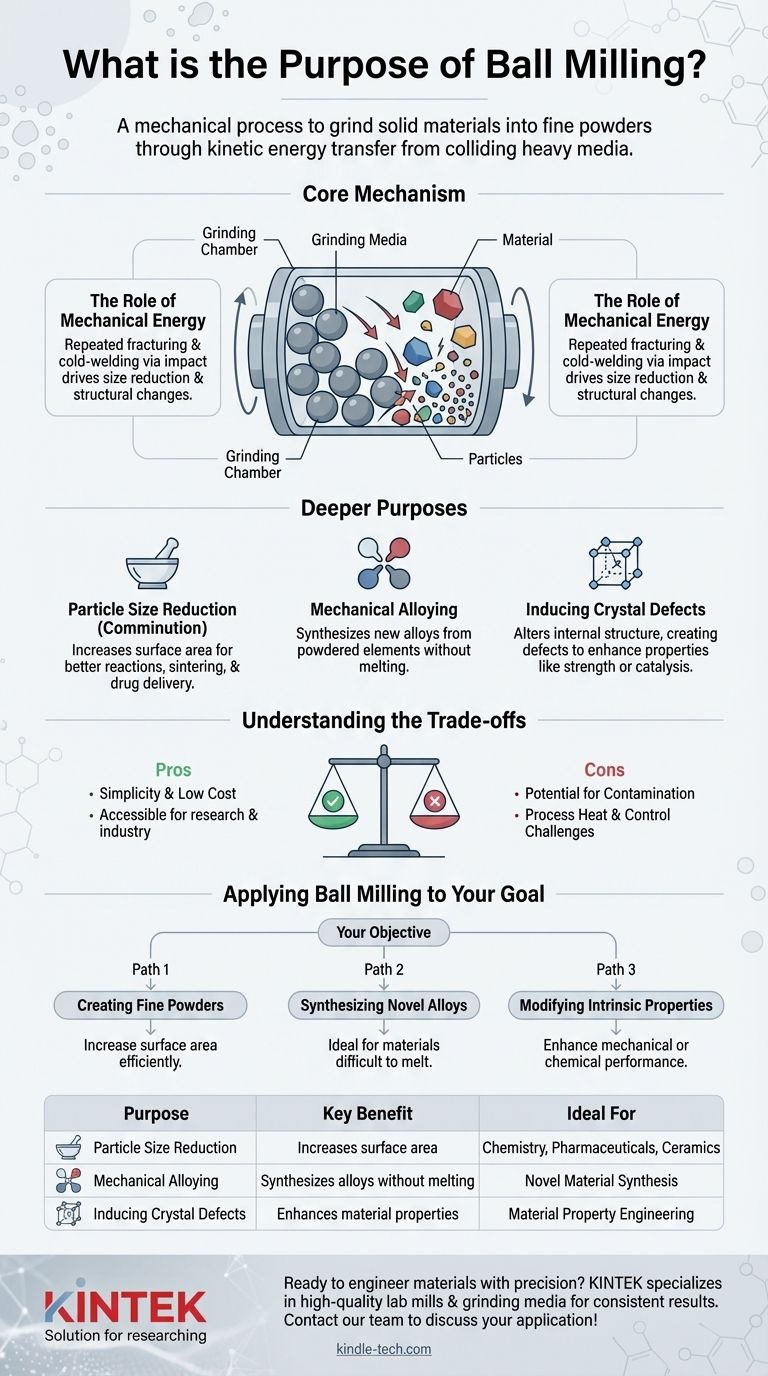
At its core, ball milling is a mechanical process used to grind solid materials into fine powders. It achieves this by placing the material into a rotating jar along with heavy grinding media (the "balls"), which repeatedly collide with the material, fracturing it into progressively smaller particles through the transfer of kinetic energy.
The true purpose of ball milling extends beyond simple particle size reduction. It is a powerful technique that uses intense mechanical energy to induce significant structural and chemical changes in materials, such as creating novel alloys or intentionally introducing crystal defects.
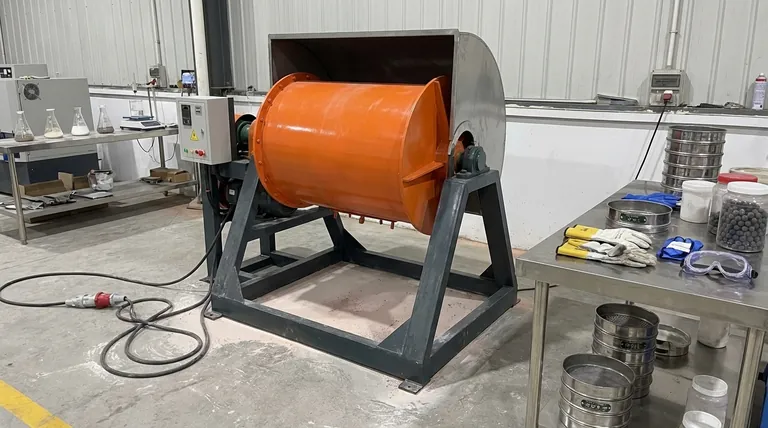

How Ball Milling Works: The Core Mechanism
The Grinding Chamber
A ball mill consists of a hollow cylindrical jar that is partially filled with the material to be ground and the grinding media. These media are typically hard, heavy balls made of steel, ceramic, or other durable materials.
The material of the jar and the balls is often chosen to be the same to minimize contamination from wear.
The Role of Mechanical Energy
As the jar rotates, the balls are lifted up the side of the jar and then cascade down, striking the material below. This high-energy impact is the primary force for grinding.
The repeated fracturing and cold-welding of particles between the colliding balls, and between the balls and the jar wall, is what drives the particle size reduction and other structural changes.
Beyond Grinding: The Deeper Purposes
Particle Size Reduction
The most common purpose of ball milling is comminution, or the reduction of particle size. Creating finer powders dramatically increases the material's surface area, which is critical for applications like improving reaction rates in chemistry, sintering in ceramics, and drug delivery in pharmaceuticals.
Mechanical Alloying
Ball milling is a key technique for mechanical alloying. This process allows for the synthesis of alloys from powdered elements without melting them. The intense collisions break apart particles and fuse them together, mixing the elements on an atomic level to form a new, homogenous alloy.
Inducing Crystal Defects
The severe mechanical stress applied during milling does not just break particles; it fundamentally alters their internal structure. This process intentionally creates crystal defects, such as dislocations and vacancies, within the material's lattice.
These defects can significantly change a material's properties, sometimes enhancing its strength, catalytic activity, or other desired characteristics.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Simplicity and Low Cost
A primary advantage of ball milling is that it is a relatively inexpensive and straightforward method. The equipment is not overly complex, and the process is easy to perform, making it highly accessible for both research and industrial applications.
Potential for Contamination
A significant drawback is the risk of contamination. As the balls and jar wear down from the constant collisions, small amounts of their material can be introduced into the sample powder. This must be carefully managed, especially when high purity is required.
Process Heat and Control
The process generates considerable heat, which can sometimes be undesirable. Furthermore, while it is excellent for size reduction, achieving a perfectly uniform final particle size can be challenging and may require long processing times.
Applying Ball Milling to Your Goal
Before choosing this method, it is crucial to align its capabilities with your specific objective.
- If your primary focus is creating fine powders: Ball milling is an excellent and cost-effective choice for increasing surface area and preparing materials for subsequent processes.
- If your primary focus is synthesizing novel alloys: The mechanical alloying capability is ideal for creating materials that are difficult or impossible to produce through traditional melting techniques.
- If your primary focus is modifying intrinsic properties: Use ball milling to intentionally introduce strain and crystal defects, which can be a powerful way to enhance a material's mechanical or chemical performance.
Ultimately, ball milling is a versatile and accessible tool for engineering materials far beyond simple grinding.
Summary Table:
| Purpose | Key Benefit | Ideal For |
|---|---|---|
| Particle Size Reduction | Increases surface area for reactions | Chemistry, Pharmaceuticals, Ceramics |
| Mechanical Alloying | Synthesizes alloys without melting | Novel Material Synthesis |
| Inducing Crystal Defects | Enhances material properties (strength, catalysis) | Material Property Engineering |
Ready to engineer your materials with precision? Ball milling is a powerful technique, but success depends on using the right equipment. KINTEK specializes in high-quality lab mills and grinding media designed for consistent, contaminant-minimized results. Whether you're developing novel alloys or creating fine powders, our experts can help you select the ideal solution for your laboratory's needs.
Contact our team today to discuss your application and discover how KINTEK can support your material science goals!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Stainless Steel Laboratory Ball Mill for Dry Powder and Liquid with Ceramic Polyurethane Lining
- Laboratory Ball Mill Jar Mill with Metal Alloy Grinding Jar and Balls
- Hybrid High Energy Vibratory Ball Mill for Lab Use
- Laboratory Single Horizontal Jar Mill
- Laboratory Planetary Ball Mill Rotating Ball Milling Machine
People Also Ask
- What is the key role of a planetary ball mill for IZO targets? Achieve Atomic-Level Uniformity in Material Preparation
- What is the difference between a ball mill and a sag mill? A Guide to Primary vs. Secondary Grinding
- What is the product size of a ball mill? Achieve Micron-Level Precision for Your Materials
- Why use ball milling for NMC cathode materials? Achieve Precision Particle Sizing for Composite Cathodes
- Why is a laboratory ball mill used in Co-Ni catalyst research? Optimize CO2 Conversion with Precise Milling



















