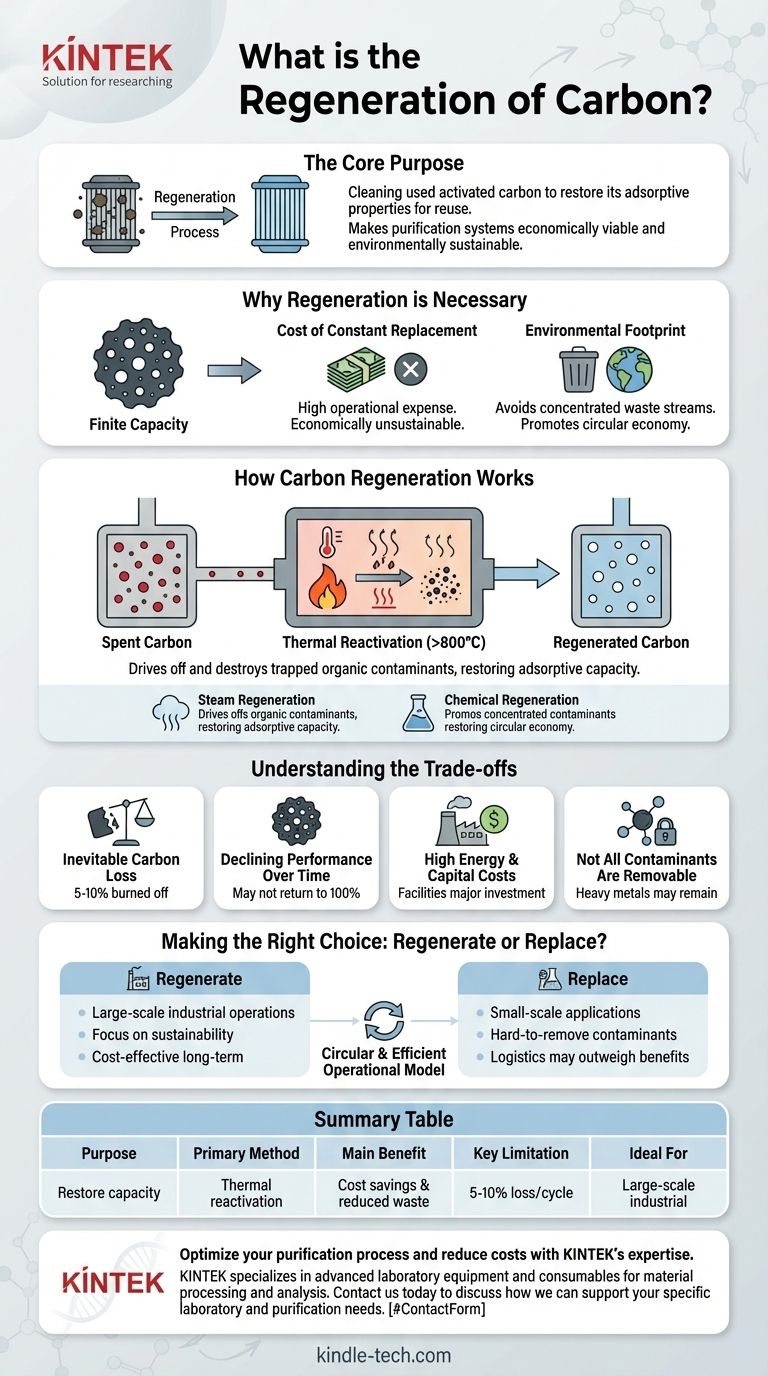
In simple terms, carbon regeneration is the process of cleaning used activated carbon to restore its adsorptive properties for reuse. It involves removing the contaminants that have become trapped in the carbon's pores, effectively "recharging" it so it can be used again in purification processes without destroying its underlying structure.
The core purpose of carbon regeneration is not just cleaning; it is a critical strategy for making purification systems economically viable and environmentally sustainable by breaking the costly cycle of constant replacement and disposal.

Why Regeneration is a Necessary Process
To understand the value of regeneration, you must first understand how activated carbon works and, more importantly, how it stops working.
The Finite Capacity of Activated Carbon
Think of activated carbon as a high-tech sponge with a vast internal network of microscopic pores. These pores provide an enormous surface area that traps and holds contaminant molecules—a process called adsorption.
However, this capacity is finite. Once the pores are filled with contaminants, the carbon is considered "exhausted" or "spent," and it can no longer effectively purify air or water.
The Cost of Constant Replacement
High-quality activated carbon is a significant operational expense. For industries that rely on large volumes for processes like water treatment, air purification, or chemical processing, continuously purchasing virgin carbon and disposing of the spent media is economically unsustainable.
The Environmental Footprint
Simply throwing away spent carbon is not a responsible solution. The used media is laden with the very contaminants it was used to remove, creating a concentrated stream of waste that requires proper disposal. Regeneration minimizes this waste and promotes a circular economy.
How Carbon Regeneration Works
The goal of regeneration is to reverse the adsorption process, forcing the trapped contaminants to leave the carbon's pores without damaging the carbon itself.
The Governing Principle: Reversal
The methods used to achieve this reversal apply energy or chemical reactions to break the bonds holding the contaminants to the carbon surface. The specific method depends on the type of carbon and the nature of the adsorbed materials.
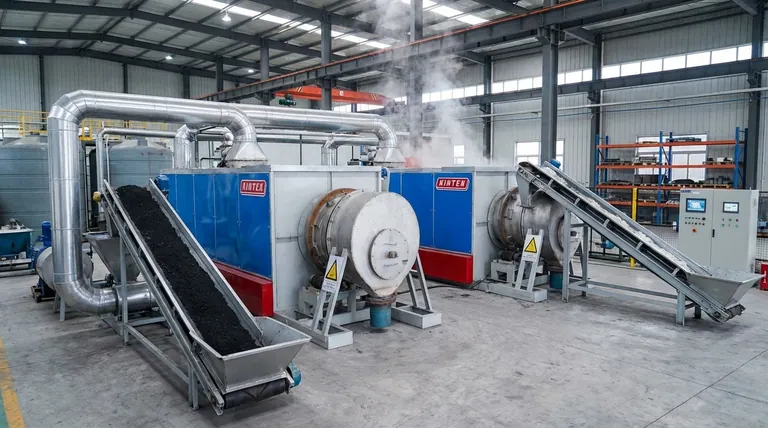
Thermal Reactivation
This is the most common and robust method. The spent carbon is heated to very high temperatures (typically over 800°C or 1500°F) in a controlled-atmosphere furnace or kiln.
This intense heat accomplishes two things: it drives off (volatilizes) the trapped organic contaminants, and it destroys and carbonizes them, effectively clearing out the pore structure and restoring the carbon's adsorptive capacity.
Other Regeneration Methods
While less common for large-scale industrial reactivation, other methods exist. Steam regeneration uses high-pressure steam to strip volatile organic compounds from the carbon. Chemical regeneration uses solvents or acids to wash away specific adsorbed substances.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Limitations
Regeneration is a powerful tool, but it is not a perfect process. Understanding its limitations is critical for making informed operational decisions.
Inevitable Carbon Loss
Each thermal regeneration cycle is aggressive. A small percentage of the activated carbon—typically 5% to 10%—is inevitably burned off or turned into fine dust. This lost volume must be replaced with virgin carbon to maintain the system's capacity.
Declining Performance Over Time
While regeneration restores the majority of the carbon's performance, it may not return to 100% of its original capacity. The effectiveness can slightly decrease with each subsequent cycle as some pores become permanently blocked.
High Energy and Capital Costs
Thermal reactivation facilities are a major investment. They require expensive kilns and sophisticated pollution control systems. The process itself is also very energy-intensive, which contributes to the overall operational cost.
Not All Contaminants Are Removable
Some substances, particularly heavy metals or certain polymers, can bond too strongly to the carbon or melt and foul the pore structure. These materials cannot be effectively removed through standard thermal reactivation.
Making the Right Choice: Regenerate or Replace?
The decision to regenerate used carbon or replace it with new material depends entirely on your operational scale, contaminant profile, and strategic goals.
- If your primary focus is large-scale industrial operations (e.g., municipal water treatment): Regeneration is almost always the most cost-effective and sustainable long-term strategy due to the sheer volume of material used.
- If your primary focus is on small-scale applications or hard-to-remove contaminants: The logistics and cost of regeneration may outweigh the benefits, making one-time replacement a more practical choice.
- If your primary focus is on environmental compliance and sustainability: Integrating a regeneration plan is a key component for minimizing your operational waste footprint and demonstrating responsible resource management.
Ultimately, understanding carbon regeneration allows you to shift from a linear, disposable mindset to a circular and far more efficient operational model.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | Key Takeaway |
|---|---|
| Purpose | Restores adsorptive capacity of spent activated carbon for reuse. |
| Primary Method | Thermal reactivation (heating to >800°C in a controlled furnace). |
| Main Benefit | Significant cost savings and reduced environmental waste vs. replacement. |
| Key Limitation | Inevitable 5-10% carbon loss per regeneration cycle. |
| Ideal For | Large-scale industrial applications (e.g., water treatment). |
Optimize your purification process and reduce costs with KINTEK's expertise.
Regenerating your spent activated carbon is a strategic move for economic and environmental sustainability. KINTEK specializes in the advanced laboratory equipment and consumables necessary for efficient material processing and analysis. Whether you are evaluating regeneration cycles or scaling your operations, our solutions support your goals for efficiency and responsible resource management.
Contact us today to discuss how we can support your specific laboratory and purification needs. #ContactForm
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Electric Rotary Kiln Small Rotary Furnace for Activated Carbon Regeneration
- Vertical Laboratory Tube Furnace
- 1200℃ Split Tube Furnace with Quartz Tube Laboratory Tubular Furnace
- Laboratory Rapid Thermal Processing (RTP) Quartz Tube Furnace
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
People Also Ask
- How do you carbonize charcoal? Master the 3-Step Pyrolysis Process for High-Purity Carbon
- Can you restore activated carbon? Understanding the Industrial Reactivation Process
- What temperature is needed for porcelain? A Guide to Cone 6 and Cone 10 Firing
- How to regenerate activated carbon? Master the 3-Stage Thermal Process for Cost Savings
- What is the temperature for activated carbon regeneration? Key Ranges from 220°C to 900°C



















