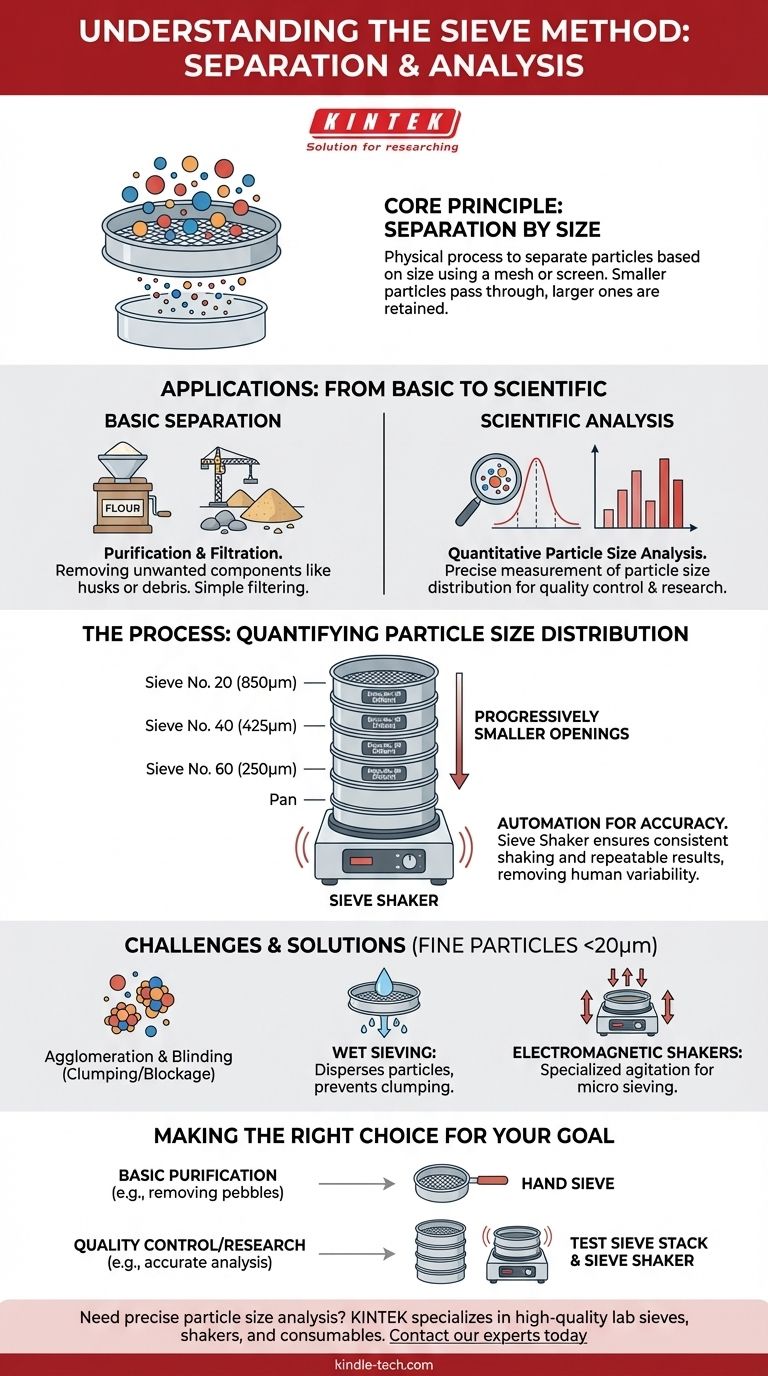
At its core, the sieve method is a physical process used to separate particles based on their size. It involves passing a granular material through a mesh or screen with uniform apertures, allowing smaller particles to pass through while retaining larger ones.
The sieve method is far more than a simple separation tool. While its basic function is to sort particles, its most critical application in science and industry is for quantitative particle size analysis—a precise measurement technique essential for quality control, research, and production across numerous fields.

The Fundamental Principle: Separation by Size
Everyday Separation
The most familiar use of sieving is for basic purification. In a flour mill, sieves remove larger impurities like husks and stones from wheat grains. On construction sites, they are used to separate fine sand from larger pebbles and debris.
In these cases, the goal is simple: to get rid of unwanted components that are a different size from the desired material. The sieve acts as a basic filter.
The Core Mechanism
The process relies on a sieve, which is essentially a screen or mesh with openings of a specific, uniform size. When a mixture of particles is placed on the sieve and agitated, particles smaller than the openings fall through, while those larger than the openings are left behind.
From Separation to Scientific Analysis
The true power of the sieve method is unlocked when it moves from simple separation to precise measurement. This is known as particle size analysis.
Quantifying Particle Size Distribution
In many industries, the exact distribution of particle sizes within a material is critical to its performance. It's not enough to know that a powder is "fine"; you must know how fine it is and the proportion of particles at each size.
To achieve this, a stack of test sieves is used. The sieve with the largest openings is placed on top, followed by sieves with progressively smaller openings. The sample is placed in the top sieve, and the entire stack is agitated.
Afterward, the material retained on each sieve is weighed. This data reveals the particle size distribution of the sample, a crucial quality control metric.
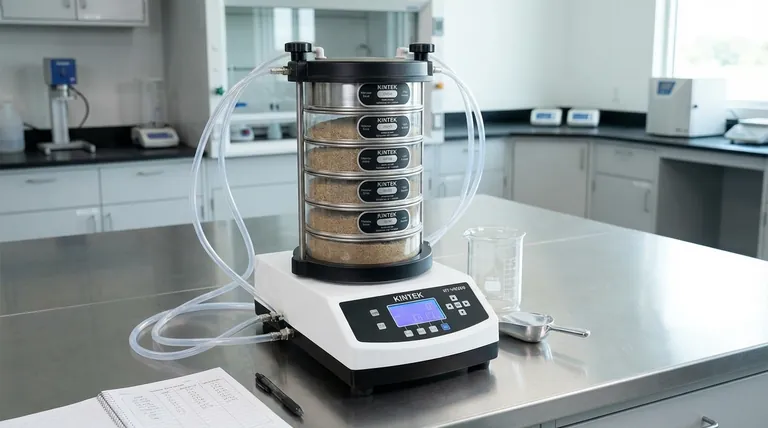
The Role of the Sieve Shaker
For accurate and repeatable results, this process is automated using a sieve shaker. This device holds the sieve stack and applies a consistent shaking or tapping motion for a set amount of time.
This removes human variability and ensures that different samples are tested under identical conditions, which is essential for quality assurance in fields like metallurgy, pharmaceuticals, geology, and chemical manufacturing.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Limitations
While powerful, the sieve method is not without its challenges, particularly when dealing with very fine materials.
The Challenge of Fine Particles
Sieving particles smaller than approximately 20 micrometers (µm) becomes very difficult. These fine powders can agglomerate (clump together) or cause blinding, where individual particles block the sieve openings and prevent other particles from passing through.
Specialized equipment, such as an electromagnetic sieve shaker, can perform "micro" sieving down to 5 µm by using a different type of agitation to keep the particles dispersed.
Wet vs. Dry Sieving
To overcome agglomeration and blinding, wet sieve analysis can be used. A liquid (usually water) is added to the sample to help disperse the particles and wash them through the mesh.
This method is highly effective, but it can only be used if the material itself is not soluble or otherwise affected by the liquid. The choice between wet and dry sieving depends entirely on the properties of the material being analyzed.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Your application of the sieve method depends entirely on what you need to achieve.
- If your primary focus is basic purification: A simple hand sieve is sufficient for tasks like removing pebbles from soil or sifting flour.
- If your primary focus is quality control or research: You need a calibrated set of test sieves and a mechanical sieve shaker to ensure accurate and repeatable particle size analysis.
Ultimately, the sieve method is a foundational technique that scales from simple household tasks to the most demanding industrial and scientific standards.
Summary Table:
| Application | Goal | Key Equipment |
|---|---|---|
| Basic Separation | Purification; remove unwanted large/small particles | Hand sieve |
| Particle Size Analysis | Quantitative measurement of particle size distribution | Test sieve stack, Sieve shaker |
| Fine Particle Analysis (< 20µm) | Analyzing challenging, fine powders | Electromagnetic sieve shaker, Wet sieving setup |
Need precise particle size analysis for your lab? The right sieve equipment is critical for accurate quality control and reproducible results. KINTEK specializes in high-quality lab sieves, shakers, and consumables to meet your specific separation and analysis needs. Contact our experts today to find the perfect sieving solution for your application!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Test Sieves and Vibratory Sieve Shaker Machine
- Three-dimensional electromagnetic sieving instrument
- Laboratory Wet Three-Dimensional Vibratory Sieve Shaker Machine
- Laboratory Vibratory Sieve Shaker Machine Slap Vibrating Sieve
- Custom PTFE Teflon Parts Manufacturer for PTFE Mesh F4 Sieve
People Also Ask
- What function does a sieving system perform during HPS powder pretreatment? Ensure Uniform Particle Size Distribution
- What are the disadvantages of sieve machine? Key Limitations in Particle Size Analysis
- Why is a precision vibratory sieving system important for Pt/Pd alloy analysis? Ensure Data Integrity & XRD Accuracy
- How do high-precision sieving systems benefit zeolite preparation? Maximize Adsorption for Wastewater Treatment
- Why is a laboratory sieving system required for bentonite in coatings? Ensure Flawless Surface Performance



















