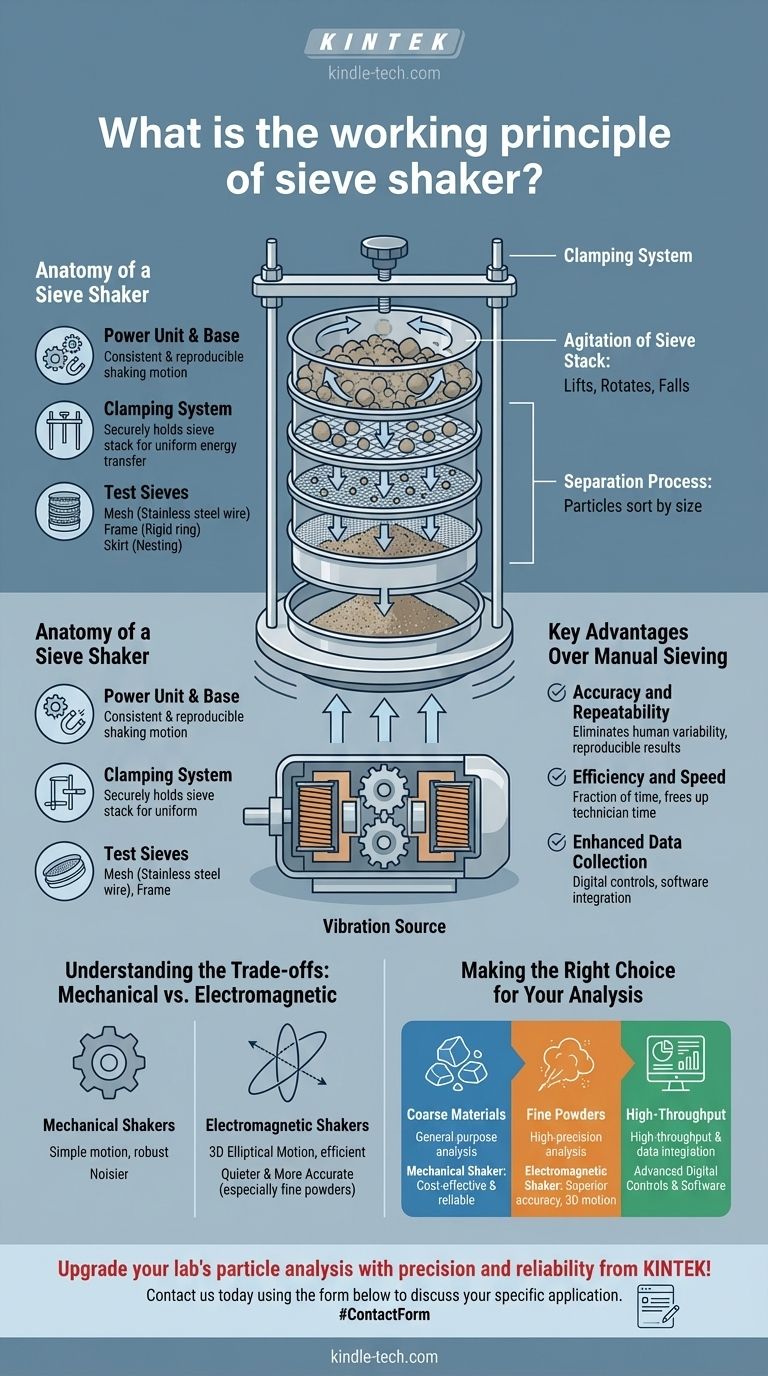
At its core, a sieve shaker automates particle separation through controlled vibration. It uses a motor or an electromagnetic drive to agitate a stacked column of test sieves, each with a specific mesh size. This motion causes particles to move across the mesh; particles smaller than the openings pass through to the sieve below, while larger particles are retained, effectively sorting the material by size.
The true purpose of a sieve shaker is not merely to shake particles, but to replace inconsistent manual methods with a highly repeatable, efficient, and accurate system for determining the particle size distribution of a granular material.

The Core Mechanism: From Vibration to Separation
A sieve shaker's operation is a straightforward process that combines mechanical force with the physical properties of the sieves themselves.
The Vibration Source
The process begins with the vibration source. This is typically one of two types: a standard electric motor that creates a mechanical shaking motion or a more advanced electromagnetic drive. This unit transfers energy to the base that holds the sieves.
The Agitation of the Sieve Stack
The energy from the source causes the entire stack of test sieves to vibrate in a specific, controlled pattern. This agitation lifts the material, rotates it, and causes it to fall back onto the sieve mesh repeatedly.
The Separation Process
This constant motion gives each particle numerous opportunities to find an opening it can pass through. The sieves are stacked in descending order of mesh size, with the largest openings at the top. As a result, the coarsest particles are captured on the top sieve, while progressively finer particles are captured on the lower sieves.
Anatomy of a Sieve Shaker
While the principle is simple, the components are engineered for precision and consistency.
The Power Unit and Base
This is the foundation of the machine, containing the motor or electromagnetic drive. It is designed to produce a consistent and reproducible shaking motion, which is critical for accurate test results.
The Clamping System
A secure clamping system is essential. It typically consists of rods and a top bar that hold the sieve stack inflexibly against the vibrating base, ensuring that the vibrational energy is transferred efficiently and uniformly through the entire stack.
The Test Sieves
The sieves are the most critical component. Each sieve consists of three parts:
- Mesh: A screen of woven stainless steel wire with precisely measured openings, ranging from several inches down to just a few microns.
- Frame: A rigid brass or stainless steel ring that holds the mesh taut and flat.
- Skirt: A small lip below the frame that allows the sieves to nest together securely without tipping.
Understanding the Trade-offs: Mechanical vs. Electromagnetic
The type of drive mechanism used has a significant impact on performance and application.
Mechanical Shakers
These shakers use a standard motor to create agitation. They are effective and robust, but their motion is often simpler. The mechanical components can also make them noisier during operation.
Electromagnetic Shakers
These advanced shakers use electromagnetic pulses to create a three-dimensional elliptical motion. This sophisticated movement is more efficient at separating particles, especially fine powders. With fewer moving parts, they are also significantly quieter and often considered more accurate.
Key Advantages Over Manual Sieving
Automating the sieving process provides several fundamental benefits for any quality control or research lab.
Accuracy and Repeatability
A sieve shaker eliminates the human variability inherent in hand sieving. The consistent motion ensures that results are reproducible from test to test and between different operators, which is vital for quality control.
Efficiency and Speed
An automated shaker can process a sample in a fraction of the time it would take to do so manually, freeing up valuable lab technician time for other tasks.
Enhanced Data Collection
Modern sieve shakers often include digital controls and software integration. This allows for sophisticated data collection and analysis, simplifying the process of creating a full particle size distribution curve.
Making the Right Choice for Your Analysis
Selecting the right equipment depends entirely on your specific analytical requirements.
- If your primary focus is general-purpose analysis of coarse materials: A standard mechanical shaker is often a cost-effective and reliable workhorse.
- If your primary focus is high-precision analysis of fine or difficult powders: An electromagnetic shaker with its 3D motion will deliver superior accuracy and quieter operation.
- If your primary focus is high-throughput testing and data integration: Prioritize a model with advanced digital controls and software for streamlined reporting.
Ultimately, using a sieve shaker ensures that your particle analysis is grounded in a reliable, consistent, and scientifically valid method.
Summary Table:
| Component | Function |
|---|---|
| Vibration Source | Motor or electromagnetic drive that creates controlled agitation. |
| Clamping System | Holds the sieve stack securely to transfer vibrational energy uniformly. |
| Test Sieves | Stacked sieves with precise mesh sizes to separate particles by size. |
| Separation Process | Vibration causes particles to pass through or be retained on sieves. |
Upgrade your lab's particle analysis with precision and reliability from KINTEK!
Tired of inconsistent manual sieving? Our range of sieve shakers, from robust mechanical models to high-precision electromagnetic systems, is engineered to deliver the accuracy, repeatability, and efficiency your laboratory demands. Whether you are analyzing coarse aggregates or fine powders, KINTEK has the right solution to streamline your workflow and ensure scientifically valid results.
Contact us today using the form below to discuss your specific application, and let our experts help you select the perfect equipment for your needs. #ContactForm
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Test Sieves and Vibratory Sieve Shaker Machine
- Laboratory Vibratory Sieve Shaker Machine for Dry and Wet Three-Dimensional Sieving
- Laboratory Vibratory Sieve Shaker Machine Slap Vibrating Sieve
- Laboratory Multifunctional Small Speed-Adjustable Horizontal Mechanical Shaker for Lab
- Vibratory Sieve Shaker Machine Dry Three-Dimensional Vibrating Sieve
People Also Ask
- What are the disadvantages of sieve machine? Key Limitations in Particle Size Analysis
- Why is a laboratory electromagnetic vibratory sieve shaker used? Optimize Walnut Shell Chemical Pretreatment
- Why is powder classification using standard sieves essential for SHS reactions? Unlock Superior Nitriding Results
- Why is a precision vibratory sieving system important for Pt/Pd alloy analysis? Ensure Data Integrity & XRD Accuracy
- Why is a standardized sieving system necessary for elephant grass research? Ensure Reliable Sample Consistency



















