At its core, vulcanization is a chemical process used to transform soft, weak raw rubber into the durable, elastic material we rely on for countless applications. It enhances the mechanical properties and durability of both natural and synthetic rubbers, making them far more robust and versatile.
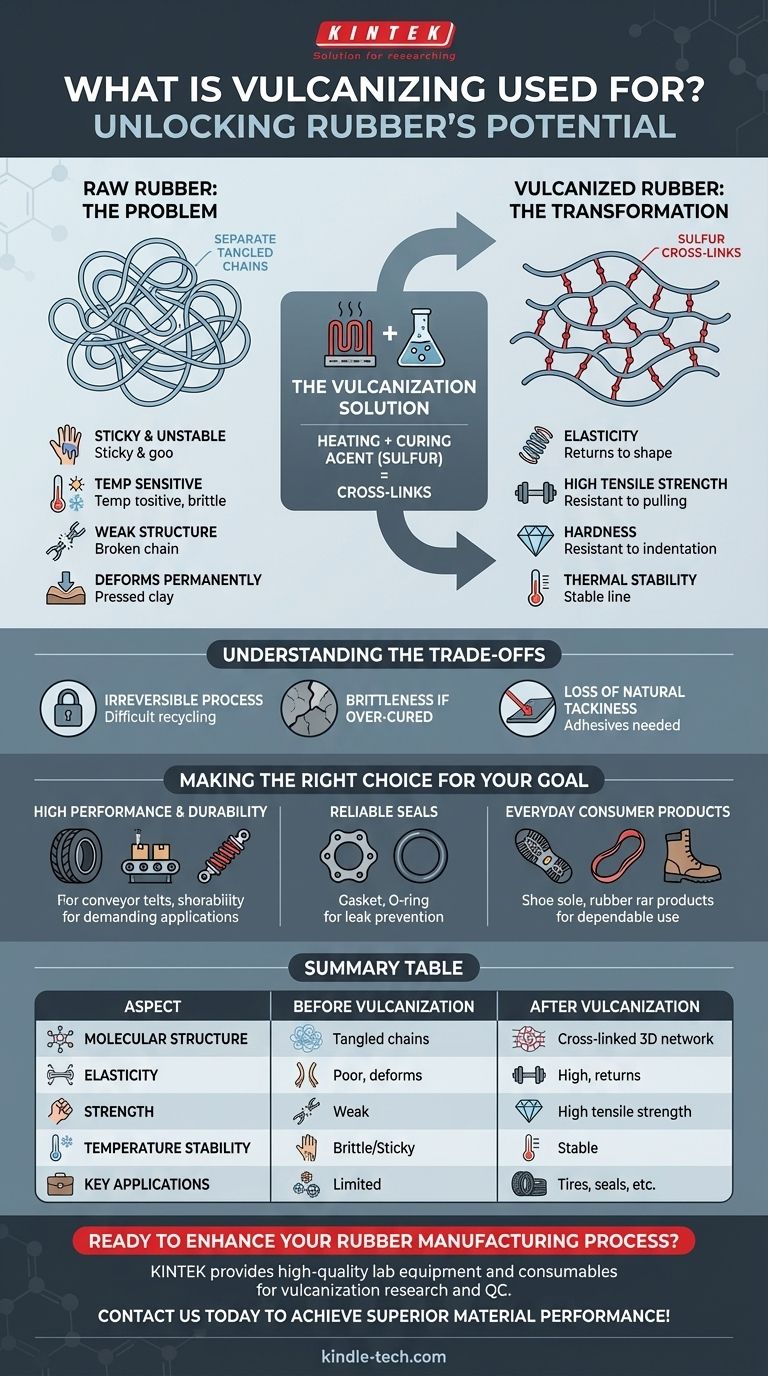
Vulcanization solves the inherent weakness of raw rubber by changing its molecular structure. It converts a collection of separate, tangled polymer chains into a single, unified molecular network, giving the material its signature strength, elasticity, and stability.

The Problem with Raw Rubber
Before vulcanization, raw rubber is a material with very limited practical use. Its natural state presents significant challenges for manufacturing and performance.
A Sticky and Unstable Material
Raw rubber is sticky to the touch and deforms permanently under pressure, much like a piece of clay. It is also highly sensitive to temperature, becoming a gooey, adhesive mess in the heat and turning hard and brittle in the cold.
Weak Molecular Structure
On a microscopic level, raw rubber consists of long, separate polymer chains (polyisoprene) that are simply tangled together. Because they are not connected, these chains can easily slide past one another when force is applied, which is why the material has poor elasticity and strength.
How Vulcanization Solves the Problem
The vulcanization process, famously perfected by Charles Goodyear in 1839, directly addresses the molecular weakness of raw rubber by reorganizing its internal structure.
Introducing Cross-Links
The key to vulcanization is the introduction of a curing agent, most commonly sulfur. When the rubber is heated with sulfur, the sulfur atoms form strong chemical bridges, or cross-links, between the individual polymer chains.
From Tangled Chains to a Cohesive Network
These cross-links act like rungs on a ladder, locking the polymer chains together into a single, cohesive three-dimensional network. The chains can no longer slide past each other freely.
This new structure allows the material to stretch under force, but the cross-links pull the chains back to their original position once the force is removed. This is the origin of rubber's powerful elasticity.
Key Properties Achieved
By creating this molecular network, vulcanization dramatically improves the material's properties:
- Elasticity: The ability to return to its original shape.
- Tensile Strength: Resistance to being pulled apart.
- Hardness: Resistance to indentation and abrasion.
- Thermal Stability: The ability to maintain properties over a wider range of temperatures.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While vulcanization is essential for making rubber useful, the process is not without its limitations and consequences.
An Irreversible Process
Vulcanization is a thermosetting process, meaning it is irreversible. Once the cross-links are formed, they cannot be easily broken. This makes recycling vulcanized rubber incredibly difficult, as it cannot be melted down and reformed like a thermoplastic.
Brittleness if Over-Cured
The degree of vulcanization is critical. While a certain number of cross-links creates elasticity, adding too many can make the material rigid and brittle. Engineers must precisely control the process to achieve the desired balance of properties.
Loss of Natural Tackiness
The process eliminates the natural stickiness of raw rubber. While this is desirable for a finished product, it means that adhesives or other surface treatments are required if the vulcanized rubber needs to be bonded to another material.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The properties imparted by vulcanization are directly responsible for rubber's widespread use. The application dictates the necessity and degree of the process.
- If your primary focus is high performance and durability: Vulcanization provides the necessary strength, resilience, and weather resistance for demanding applications like vehicle tires, conveyor belts, and shock absorbers.
- If your primary focus is creating reliable seals: The process creates a stable, elastic material ideal for gaskets, O-rings, and hoses that must prevent leaks while resisting heat and chemicals.
- If your primary focus is everyday consumer products: Vulcanization turns a fundamentally unstable raw material into the dependable, flexible products we use daily, such as shoe soles, rubber bands, and waterproof boots.
Ultimately, vulcanization is the molecular engineering that unlocks the true potential of rubber.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | Before Vulcanization | After Vulcanization |
|---|---|---|
| Molecular Structure | Separate, tangled chains | Cross-linked 3D network |
| Elasticity | Poor, deforms permanently | High, returns to shape |
| Strength | Weak and soft | High tensile strength |
| Temperature Stability | Brittle in cold, sticky in heat | Stable across a wide range |
| Key Applications | Limited practical use | Tires, seals, belts, shoe soles |
Ready to enhance your rubber manufacturing process? At KINTEK, we specialize in providing high-quality lab equipment and consumables to support your vulcanization research and quality control. Whether you're developing new rubber compounds or optimizing curing parameters, our solutions ensure precision and reliability. Contact us today to discover how KINTEK can help you achieve superior material performance!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Rubber Vulcanizer Vulcanizing Machine Plate Vulcanizing Press for Lab
- Automatic Heated Hydraulic Press Machine with Heated Plates for Laboratory Hot Press 25T 30T 50T
- Manual Heated Hydraulic Press Machine with Heated Plates for Laboratory Hot Press
- Heated Hydraulic Press Machine with Integrated Manual Heated Plates for Lab Use
- Automatic Laboratory Heat Press Machine
People Also Ask
- What are the ingredients used in rubber compounding? A Guide to the Essential Formula
- How are samples prepared for XRF analysis? Achieve Accurate and Reliable Results
- What is the purpose of a vulcanizing machine? Transform Rubber into High-Performance Parts
- What is the necessity of using a laboratory hydraulic pellet press for preparing solid catalysts? Maximize Catalyst Performance
- How to make compound rubber? Master the Sequence to Prevent Scorch and Ensure Quality



















