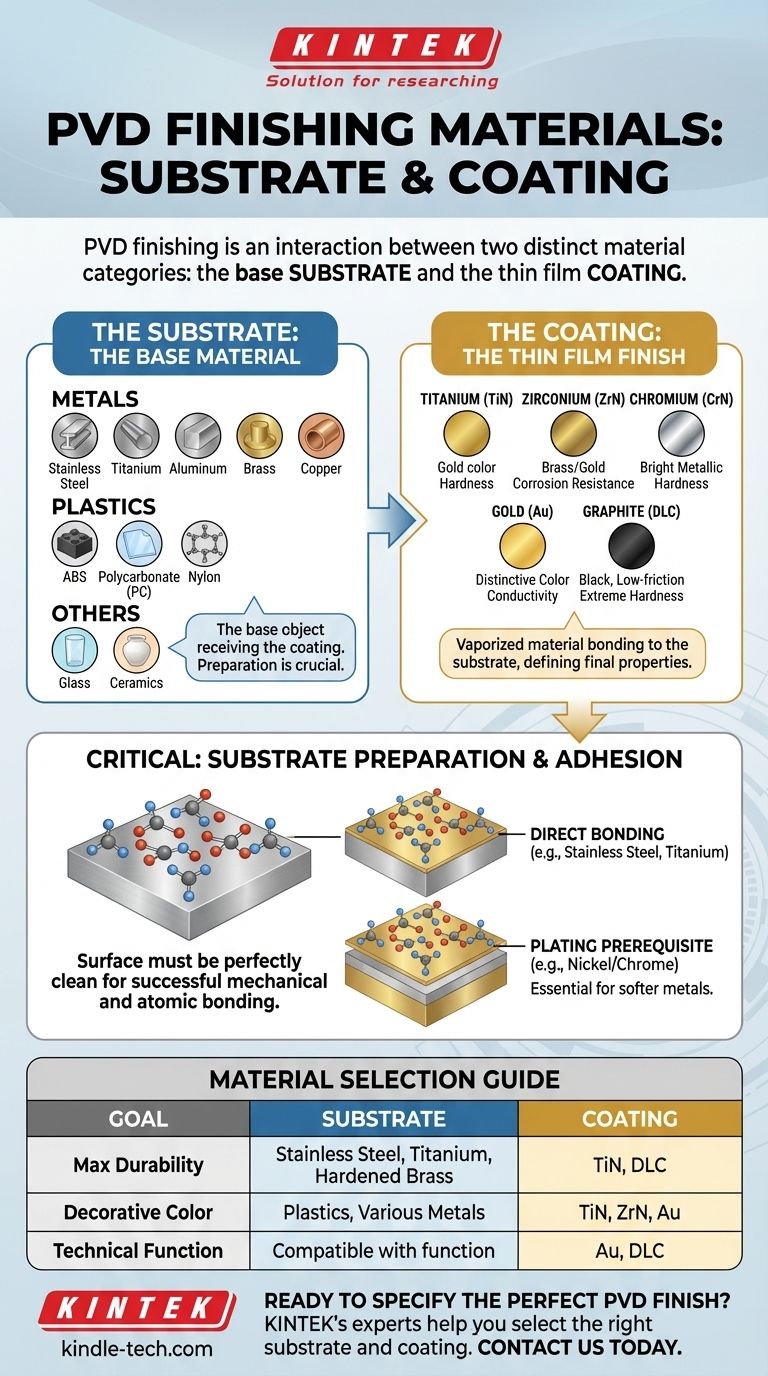
In PVD finishing, the materials can be broken down into two distinct categories: the substrate, which is the base object being coated, and the coating material, which forms the thin, durable film on the surface. Common substrates include stainless steel, titanium, brass, and even plastics, while popular coating materials are compounds of titanium, zirconium, gold, and graphite. The success of the process depends entirely on the interaction between these two material groups.
The versatility of PVD allows for coating a vast range of materials, but the key to a successful finish lies not just in the coating itself, but in the selection and meticulous preparation of the underlying substrate.

The Two Sides of PVD: Substrates and Coatings
Physical Vapor Deposition is a process of transference. One material is vaporized and then deposited onto another. Understanding both of these components is essential to understanding the process.
The Substrate: The Base Material
The substrate is the component or part that receives the coating. The PVD film is exceptionally thin, so the properties of the substrate are critical to the final product's performance.
A wide variety of materials can serve as substrates. Common choices include:
- Metals: Stainless steel, titanium, aluminum, zinc alloys, brass, and copper.
- Plastics: ABS, polycarbonate (PC), nylon, and other polymers are often coated to achieve a metallic finish for decorative or functional purposes.
- Other Materials: Glass and ceramics can also be effectively coated using PVD.
The Coating: The Thin Film Finish
The coating material is what is vaporized in a vacuum and bonded to the substrate, creating the surface finish. These materials are chosen for specific properties like color, hardness, or corrosion resistance.
The most common PVD coating materials are:
- Titanium (Ti): Often used in its nitride form (TiN), providing a hard, gold-colored finish known for exceptional durability.
- Zirconium (Zr): Zirconium Nitride (ZrN) offers superior corrosion resistance and a light brass or gold-like color.
- Chromium (Cr): Chromium Nitride (CrN) is extremely hard, corrosion-resistant, and provides the classic, bright metallic look of chrome.
- Gold (Au): Used for its distinctive color in decorative applications (like jewelry and watches) and for its conductivity in aerospace and electronics.
- Graphite & other Carbon forms: Used to create Diamond-Like Carbon (DLC) coatings, which are exceptionally hard, low-friction, and typically black in color.
- Aluminum (Al) & Copper (Cu): Also used, often in combination with other elements, to achieve specific colors and functional properties.
Why Substrate Preparation is Critical
The PVD coating is only as good as the surface it's applied to. A weak foundation will inevitably lead to a failed finish, regardless of the quality of the coating material.
The Foundation for Adhesion
The bond between the coating and the substrate is mechanical and atomic. The substrate surface must be perfectly clean, smooth, and free of any contaminants. Any imperfection will be a point of failure.
Metals: The Ideal Canvas
Stainless steel and titanium are excellent substrates for PVD because the coating can be deposited directly onto their surfaces with strong adhesion. Their inherent hardness also provides a rigid foundation for the thin PVD film.
Plating as a Prerequisite
Softer metals like brass or zinc alloys often lack the ideal surface chemistry for a direct PVD bond. For these materials, an intermediate layer of nickel and/or chromium plating is typically applied first. PVD adheres exceptionally well to chrome plating, creating a highly durable final product.
Coating on Plastics and Other Materials
When coating plastics, the goal is often metallization—giving a plastic part a metallic appearance. This requires specialized pre-treatment steps to ensure the vaporized metal will adhere to the polymer surface.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While PVD is a highly versatile technology, it is not a magical solution. Understanding its limitations is crucial for project success.
It's Not a "One-Size-Fits-All" Process
The choice of substrate dictates the required preparation steps, which in turn affects the complexity, cost, and timeline of the project. A direct-to-steel application is far more straightforward than a multi-step process for metallizing a plastic part.
The Myth of "Indestructible"
PVD coatings are extremely hard, but they are also extremely thin—often just a few microns. If the substrate beneath the coating is soft, a significant impact can dent the substrate, causing the hard PVD film above it to crack or flake. The overall durability is a function of the coating and substrate system.
Cost vs. Performance
High-performance combinations, such as a DLC coating on a titanium watch case, involve more complex and costly processes than a simple decorative titanium nitride finish on a pre-plated zinc faucet handle. The material choices for both substrate and coating directly influence the final cost.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
To select the right materials, you must first define your primary objective.
- If your primary focus is maximum durability and wear resistance: Use a hard coating like Titanium Nitride (TiN) or Diamond-Like Carbon (DLC) on a robust metal substrate like stainless steel, titanium, or properly chrome-plated brass.
- If your primary focus is a specific decorative color or metallic finish: Your choice of substrates is wider, including plastics, but success depends on meticulous pre-treatment to ensure proper adhesion and a flawless final appearance.
- If your primary focus is a technical function (e.g., conductivity): The coating material (like gold) is non-negotiable and chosen for its physical properties, meaning the substrate must be selected to support that function without compromise.
Ultimately, understanding the profound interplay between the substrate and the coating is the key to leveraging PVD to its full potential.
Summary Table:
| Material Category | Common Examples | Key Characteristics |
|---|---|---|
| Substrates | Stainless Steel, Titanium, Brass, Plastics (ABS, PC) | The base material; determines preparation needs and final durability. |
| Coating Materials | Titanium Nitride (TiN), Zirconium Nitride (ZrN), Diamond-Like Carbon (DLC), Gold | Vaporized to create a thin, hard, decorative, or functional film on the substrate. |
Ready to specify the perfect PVD finish for your components? The ideal material combination is critical for achieving durability, appearance, and performance. KINTEK specializes in precision lab equipment and consumables for surface science and coating development. Our experts can help you select the right substrate and coating process for your specific application. Contact our team today to discuss your project requirements and discover how our solutions can enhance your product's quality and longevity.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- RF PECVD System Radio Frequency Plasma-Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition RF PECVD
- High-Purity Titanium Foil and Sheet for Industrial Applications
- Vacuum Cold Trap Direct Cold Trap Chiller
- Vacuum Cold Trap Chiller Indirect Cold Trap Chiller
- High Purity Zinc Foil for Battery Lab Applications
People Also Ask
- What is the principle of plasma enhanced chemical vapor deposition? Achieve Low-Temperature Thin Film Deposition
- Why does PECVD commonly use RF power input? For Precise Low-Temperature Thin Film Deposition
- What are the applications of PECVD? Essential for Semiconductors, MEMS, and Solar Cells
- How does RF power create plasma? Achieve Stable, High-Density Plasma for Your Applications
- What are the benefits of PECVD? Achieve Superior Low-Temperature Thin Film Deposition



















