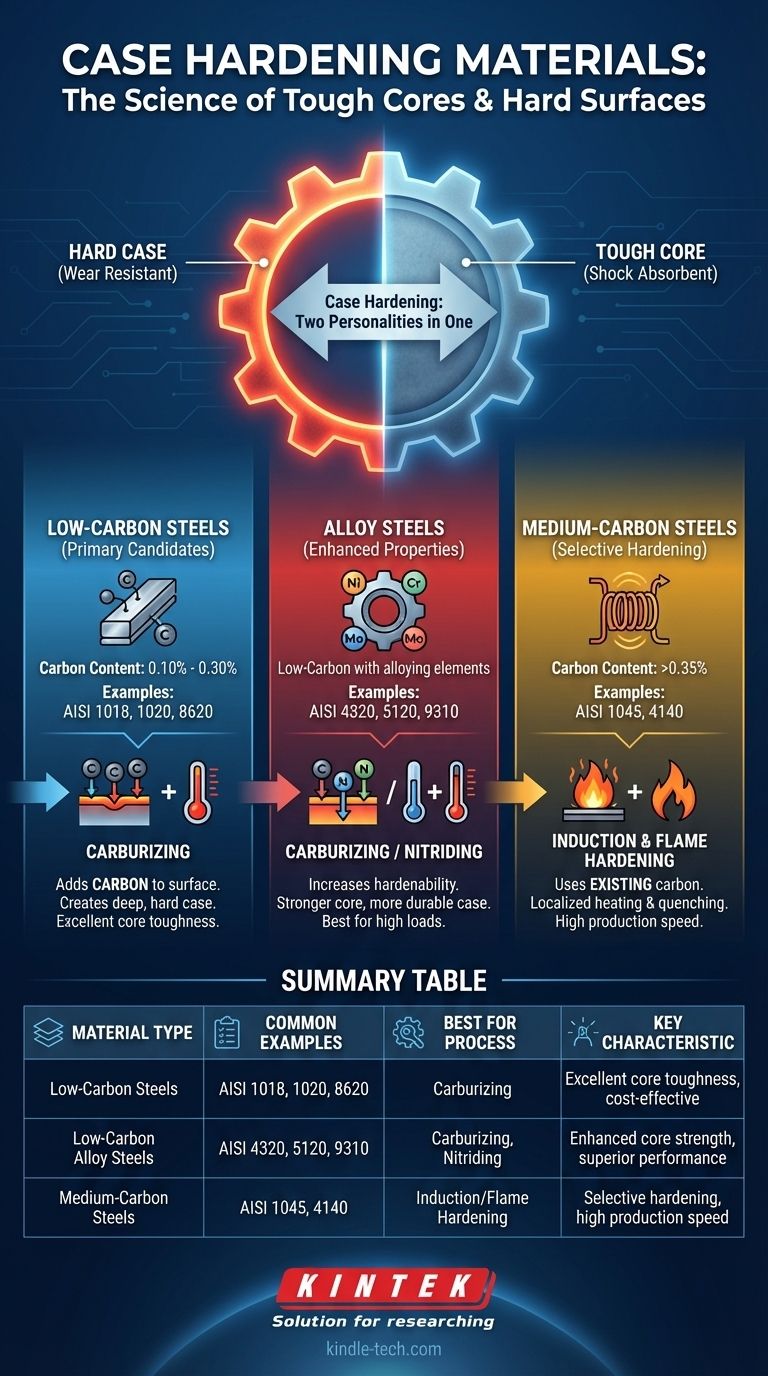
The materials best suited for case hardening are primarily low-carbon steels and certain alloy steels. These materials are selected because their core chemistry—low in carbon—provides innate toughness, while their surfaces can be chemically altered to absorb elements like carbon or nitrogen, which is essential for creating a hard, wear-resistant outer layer.
The fundamental purpose of case hardening is to create a component with two distinct personalities: an exceptionally hard, wear-resistant surface ("the case") fused to a softer, more ductile core that can absorb shock and resist fracture.

The Core Principle: A Hard Case and a Tough Core
The genius of case hardening is that it allows a single piece of metal to have properties that are typically mutually exclusive.
The Best of Both Worlds
Materials that are extremely hard are often brittle. Conversely, materials that are tough and ductile are usually soft.
Case hardening resolves this conflict. By infusing the outer layer of a tough, low-carbon steel with hardening elements, you create a component ideal for applications like gears, bearings, and camshafts, which require a durable surface and a resilient core.
It's a Chemical Transformation
Most case hardening methods are diffusion processes. This involves heating the steel in an environment rich in carbon (carburizing) or nitrogen (nitriding).
At high temperatures, the steel's crystal structure opens up, allowing these elements to seep into the surface. When the part is later quenched (rapidly cooled), this newly enriched surface layer becomes extremely hard, while the low-carbon core remains tough.
Material Suitability: A Deeper Look
The choice of material is directly tied to the specific case hardening process you intend to use.
Low-Carbon Steels (The Primary Candidates)
These are the workhorses of case hardening, especially for carburizing. They typically have a carbon content between 0.10% and 0.30%.
Common examples include AISI 1018, 1020, and 8620. Their low internal carbon content ensures they remain soft and tough after heat treatment, perfectly complementing the hard case.
Alloy Steels (For Enhanced Properties)
For more demanding applications, low-carbon alloy steels are used. These contain other elements like nickel, chromium, and molybdenum.
Steels like AISI 4320, 5120, and 9310 are designed for case hardening. The alloys increase the "hardenability" of both the case and the core, resulting in a stronger core and a more durable case, ideal for high-load gears and bearings.
What About Medium and High-Carbon Steels?
Steels with higher carbon content (above 0.35%) are generally not case hardened using diffusion methods like carburizing.
These steels already have enough carbon to be hardened through their entire cross-section via simple heating and quenching. This process is known as through-hardening. Some surface hardening methods, however, are used on these materials.
Matching the Material to the Process
Different processes work best with different steel families.
Carburizing
This is the most common method. It adds carbon to the surface of low-carbon and low-carbon alloy steels. It creates a deep, hard case that is excellent for resisting wear and fatigue.
Nitriding
This process adds nitrogen to the surface. It is performed at lower temperatures, which significantly reduces part distortion.
Nitriding is best suited for alloy steels that contain nitride-forming elements like aluminum, chromium, and molybdenum. These elements form extremely hard nitride compounds in the surface layer.
Induction & Flame Hardening
These methods are fundamentally different. They do not add elements to the surface. Instead, they use intense, localized heat to rapidly raise the surface temperature of a part, followed by an immediate quench.
This process requires a steel that already has sufficient carbon to harden—typically medium-carbon steels like AISI 1045 or 4140. It creates a "case" by transforming the existing surface structure, not by changing its chemistry.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Choosing a material and process involves balancing competing factors.
Distortion and Dimensional Control
High-temperature processes like carburizing can cause significant part distortion, often requiring post-treatment grinding.
Nitriding, being a lower-temperature process, results in minimal distortion, making it ideal for finished parts with tight tolerances. Induction hardening offers excellent control over which areas are hardened, also helping to manage distortion.
Cost vs. Performance
Simple carburizing of a plain low-carbon steel is often the most cost-effective solution for general-purpose applications.
Nitriding and using high-end alloy steels are more expensive but deliver superior performance, especially in terms of fatigue life and dimensional stability.
Case Depth
Carburizing can produce a relatively deep case (over 1mm), which is beneficial for parts under high contact stress. Nitriding typically produces a shallower but harder case.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Your final decision should be driven by the specific demands of the component.
- If your primary focus is high impact strength and cost-effectiveness: Carburizing a low-carbon steel like 1020 or an alloy steel like 8620 is the standard choice.
- If your primary focus is extreme wear resistance and minimal distortion: Nitriding a chromium-molybdenum alloy steel is the superior technical solution.
- If your primary focus is selective hardening and high production speed: Induction or flame hardening a medium-carbon steel like 1045 or 4140 is highly efficient.
Ultimately, selecting the right material is about defining the precise balance of wear resistance, core toughness, and manufacturing precision that your application demands.
Summary Table:
| Material Type | Common Examples | Best For Process | Key Characteristic |
|---|---|---|---|
| Low-Carbon Steels | AISI 1018, 1020, 8620 | Carburizing | Excellent core toughness, cost-effective |
| Low-Carbon Alloy Steels | AISI 4320, 5120, 9310 | Carburizing, Nitriding | Enhanced core strength, superior performance |
| Medium-Carbon Steels | AISI 1045, 4140 | Induction/Flame Hardening | Selective hardening, high production speed |
Ready to optimize your heat treatment process with the right materials? KINTEK specializes in providing high-quality lab equipment and consumables for metallurgical testing and heat treatment applications. Whether you're developing new case hardening protocols or ensuring material quality, our solutions help you achieve precise, reliable results. Contact our experts today to discuss how we can support your laboratory's specific needs in material science and heat treatment.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Teflon Parts Manufacturer for PTFE Mesh F4 Sieve
- Glassy Carbon Sheet RVC for Electrochemical Experiments
- Heated Hydraulic Press Machine with Heated Plates Split Manual Laboratory Hot Press
- Automatic High Temperature Heated Hydraulic Press Machine with Heated Plates for Lab
- 24T 30T 60T Heated Hydraulic Press Machine with Heated Plates for Laboratory Hot Press
People Also Ask
- What is the difference between PPF and coating? Armor vs. Slick Shell for Your Car
- Why is PTFE wire used for hanging metal specimens in biodiesel corrosion tests? Ensure Pure Experimental Results
- What is the function of PTFE reaction kettle bodies in micro-CSTR systems? Enhance Chemical Stability & Flow
- Why are PTFE laboratory consumables required when testing stainless steel against organic acids? Ensure Data Integrity
- What are the advantages of using PTFE molds for epoxy resin flame retardant samples? Ensure High-Purity Material Testing



















