At its core, insulation in an ultra-low temperature (ULT) freezer serves one primary function: to create a highly effective thermal barrier. Its job is to minimize the transfer of heat from the outside environment into the freezer's cold interior, thereby protecting valuable samples and significantly reducing the workload on the mechanical cooling system.
The role of insulation goes far beyond simply "keeping the cold in." A better way to understand it is as the freezer's first and most critical line of defense, actively working to "keep the heat out." This defensive function is the foundation of a ULT freezer's stability, reliability, and energy efficiency.

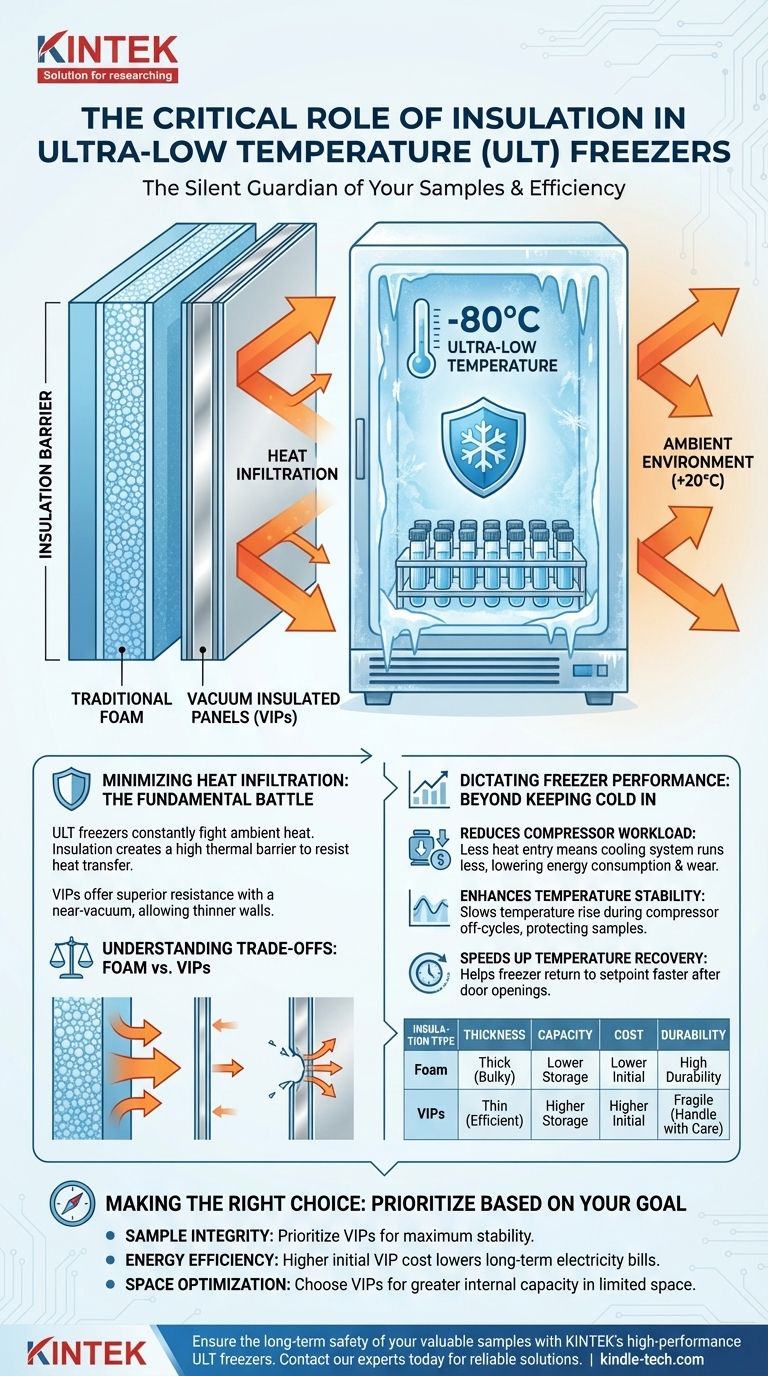
The Fundamental Battle: Keeping Heat Out
An ultra-low temperature freezer, maintaining -80°C, is in a constant battle with the ambient heat of the room it's in. Insulation is its primary defense system in this fight.
Minimizing Heat Infiltration
Heat naturally moves from a warmer area to a colder one. The massive temperature difference between the room (e.g., +20°C) and the freezer's interior (e.g., -80°C) creates immense thermal pressure.
Insulation's purpose is to slow this infiltration to a crawl. By resisting heat transfer, it ensures that the internal environment remains stable and protected from external temperature fluctuations.
The Role of Advanced Materials
To achieve this, ULT freezers rely on specialized materials. Traditional polyurethane foam is common, but modern freezers often use Vacuum Insulated Panels (VIPs).
VIPs create a near-vacuum between two layers of material, drastically reducing heat transfer because there are very few air molecules to conduct the heat. This technology allows for much thinner walls compared to foam, increasing internal storage capacity.
More Than Just the Walls
Effective insulation isn't limited to the main cabinet. Critical points of potential heat entry are the doors.
High-quality, multi-point gaskets and tightly sealed inner doors are essential components of the overall insulation system. Any failure in these seals creates a thermal "leak," compromising the entire unit.
How Insulation Dictates Freezer Performance
The quality of a freezer's insulation has a direct and measurable impact on its most important performance characteristics, from energy use to sample safety.
Reducing Compressor Workload
The cooling system, typically a cascade refrigeration system, is designed to actively pump out any heat that gets inside. The better the insulation, the less heat gets in.
This directly translates to the compressors running less frequently and for shorter durations. The result is lower energy consumption, less wear on mechanical parts, and a quieter freezer.
Enhancing Temperature Stability
All freezers experience minor temperature fluctuations as the compressor cycles on and off. In a poorly insulated unit, the internal temperature will rise quickly when the compressor is off.
Superior insulation slows this temperature rise dramatically. This creates a much more stable environment, which is critical for the long-term viability of sensitive biological samples.
Speeding Up Temperature Recovery
Every time the freezer door is opened, a large volume of warm, moist air rushes in. The cooling system must work hard to remove this heat and return to its setpoint.
A well-insulated freezer helps win this race faster. By preventing ambient heat from continuing to leak in through the cabinet walls, it allows the refrigeration system to focus solely on removing the heat introduced by the door opening.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While better insulation is always desirable, its implementation involves key engineering and cost considerations.
Insulation Thickness vs. Storage Capacity
Traditional foam insulation is effective but bulky. To achieve ultra-low temperatures, the foam walls must be very thick, which reduces the internal storage volume for a given external footprint.
This is the primary reason manufacturers have moved toward thinner, more efficient VIP technology.
The Cost and Fragility of VIPs
Vacuum Insulated Panels offer superior thermal resistance in a thin profile, but they come at a higher initial cost.
They are also fragile. If a panel is punctured or its seal is compromised, the vacuum is lost, and its insulating capability drops dramatically. This makes proper handling and care of the freezer essential.
Frost: The Unwanted Insulator
Breaches in door seals or gaskets don't just let in heat; they let in moisture. This moisture freezes onto interior surfaces and cooling coils, creating frost.
Excessive frost acts as an unwanted insulator, forcing the cooling system to work harder to cool the chamber and eventually requiring a manual defrost.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Understanding the role of insulation allows you to evaluate a ULT freezer based on your specific priorities.
- If your primary focus is long-term sample integrity: Prioritize freezers with the best possible insulation, like VIPs, to ensure maximum temperature stability and the fewest fluctuations.
- If your primary focus is energy efficiency and operational cost: Recognize that a higher initial investment in a freezer with superior insulation will directly lower electricity bills for the life of the unit.
- If your primary focus is maximizing storage in a limited lab space: Seek out models that use thin-profile VIPs to provide the greatest internal capacity without increasing the freezer's external footprint.
Ultimately, the insulation is the silent guardian that makes everything else in a ULT freezer possible.
Summary Table:
| Insulation Function | Impact on Freezer Performance |
|---|---|
| Creates a thermal barrier | Minimizes heat infiltration from the environment |
| Uses advanced materials (e.g., VIPs) | Enhances temperature stability for sensitive samples |
| Reduces compressor workload | Lowers energy consumption and operational costs |
| Improves temperature recovery | Maintains setpoint faster after door openings |
Ensure the long-term safety of your valuable samples and optimize your lab's energy efficiency. The insulation system is the heart of a reliable ultra-low temperature freezer. At KINTEK, we specialize in providing high-performance lab equipment, including ULT freezers with advanced insulation technologies like Vacuum Insulated Panels (VIPs), designed to meet the rigorous demands of modern laboratories.
Contact our experts today to find the perfect freezer solution for your specific needs and discover how we can support your research with reliable, energy-efficient equipment.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 158L Precision Vertical Ultra Low Freezer for Laboratory Applications
- 508L Advanced Vertical Ultra Low Temperature Freezer for Critical Laboratory Storage
- 808L Precision Laboratory Vertical Ultra Low Temperature Freezer
- 208L Advanced Precision Laboratory Ultra Low Temperature Freezer for Cold Storage
- 608L Essential Laboratory Ultra Low Temperature Freezer For Critical Sample Preservation
People Also Ask
- What is the purpose of ultra-low temperature (ULT) freezers? Preserve Critical Biological Samples
- How is temperature controlled in ultra low temperature freezers? A Guide to Stable -80°C Storage
- What are the different types of ultra-low temperature freezers available? Choose the Right ULT Freezer for Your Lab
- How do ultra-low temperature freezers work? Unlocking the Secrets of -86°C Sample Preservation
- How should frost be removed from Ultra-Low Temperature Freezers? Protect Your Samples and Equipment



















