At its most effective, a planetary ball mill can reduce materials down to the sub-micron level, with many models capable of achieving final particle sizes in the nanometer range (typically below 100 nm). This process of creating nano-scale particles through high-energy milling is a primary application for this technology.
The ultimate particle size is not a single number but a result of the system's high energy input. The key takeaway is that planetary ball mills achieve fine grinding by creating intense impact and frictional forces, far exceeding those of a standard ball mill.

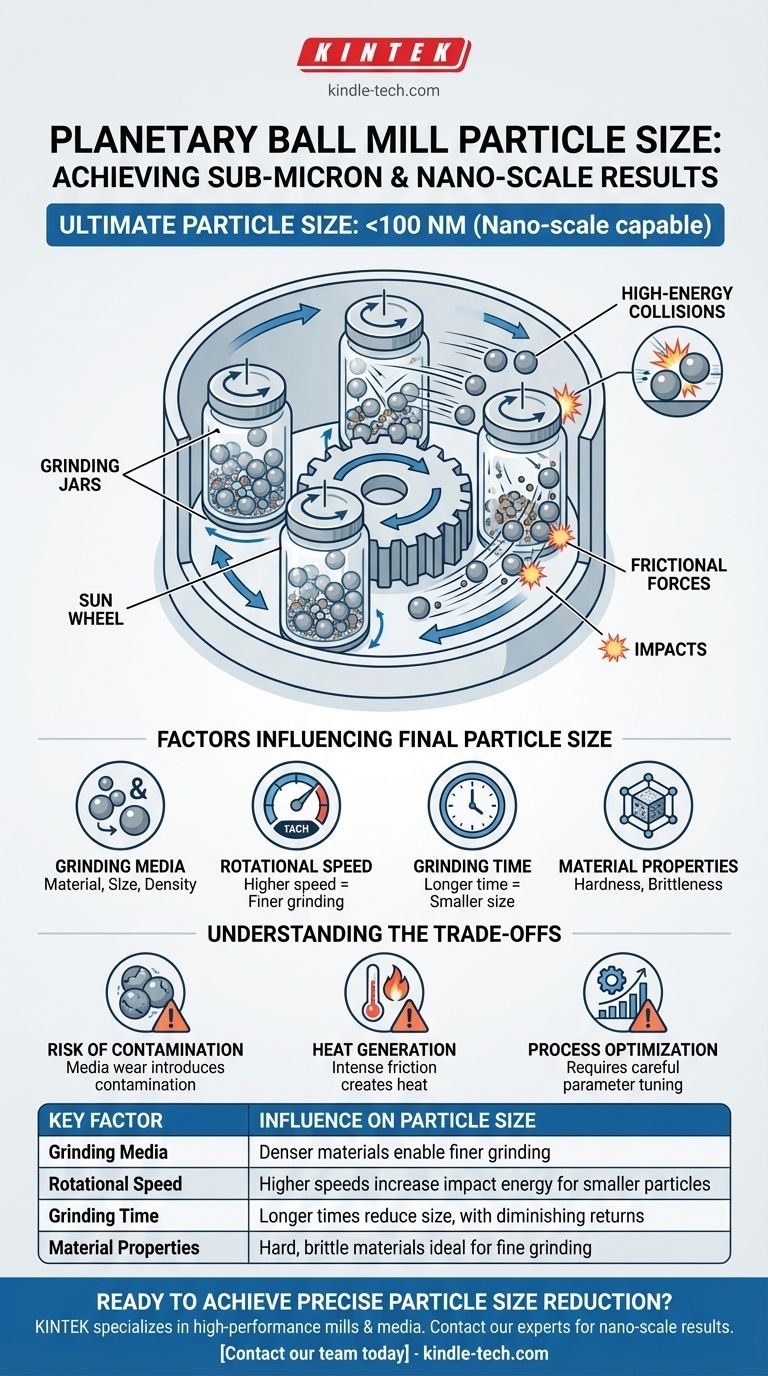
How Planetary Ball Mills Achieve Fine Grinding
A planetary ball mill's effectiveness comes from its unique and powerful mechanical action. It is not simply a container that tumbles; it is a system designed for high-energy transfer.
The Planetary Motion Principle
The grinding jars are arranged on a rotating "sun wheel." These jars simultaneously rotate on their own axes, but in the opposite direction of the main wheel.
This compound motion results in extremely high acceleration forces on the grinding media (the balls) and the sample material inside the jar.
High-Energy Collisions
The opposing rotations cause the grinding balls to detach from the inner wall of the jar and fly across its diameter, striking the opposite wall with significant force. This creates a constant state of high-frequency, high-energy impacts.
These impacts are the primary mechanism for pulverizing hard, brittle, and fibrous materials down to very fine powders.
The Role of Frictional Forces
In addition to impacts, intense frictional forces and shearing occur. The balls roll against each other and the inner wall of the jar, grinding the material trapped between them.
This combination of impact and friction is what enables the comminution process to reach the nanometer scale.
Factors Influencing Final Particle Size
You cannot simply turn on a planetary mill and expect a specific result. The final particle size is a function of several interdependent parameters that you must control.
Grinding Media and Jar Material
The material, size, and density of the grinding balls are critical. Denser materials like tungsten carbide provide higher impact energy than stainless steel or zirconia. A higher ball-to-powder ratio also increases grinding efficiency.
Rotational Speed
Higher rotational speeds increase the centrifugal forces and the energy of the impacts, leading to faster and finer grinding. However, there is an optimal speed beyond which grinding efficiency can decrease.
Grinding Time
Longer processing times generally lead to smaller particle sizes. However, the rate of size reduction diminishes over time, and excessive grinding can lead to unwanted material changes or contamination.
Material Properties
The starting material's hardness, brittleness, and toughness fundamentally dictate how it will respond to the milling process. Hard and brittle materials are ideal candidates for significant size reduction.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While powerful, planetary ball mills are not without their operational challenges. Understanding these limitations is crucial for successful application.
Risk of Contamination
The high-energy environment inevitably causes wear on the grinding jars and balls. This wear introduces small amounts of contamination into your sample.
Choosing grinding media made of the same material as your sample (if possible) or using extremely hard materials like silicon nitride can mitigate this, but it is a factor that must always be considered, especially for high-purity applications.
Heat Generation
The intense friction and impact generate significant heat. This can be detrimental to heat-sensitive materials, potentially causing phase changes, melting, or degradation. Some systems offer cooling jackets to manage this temperature increase.
Process Optimization is Not Trivial
Achieving a specific, repeatable particle size distribution requires careful and systematic optimization of all parameters (speed, time, ball size, etc.). This can be a time-consuming process of trial and error for new materials.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Use the capabilities of the planetary ball mill to match your specific material processing objective.
- If your primary focus is achieving nano-scale particles (<100 nm): A planetary ball mill is a strong candidate, but you must carefully control parameters and consider potential contamination from the grinding media.
- If your primary focus is grinding hard, brittle materials: The high-impact energy of a planetary mill makes it one of the most effective tools for pulverizing materials like ceramics, minerals, and alloys.
- If your primary focus is maintaining absolute sample purity: Be aware that contamination from media wear is a significant risk. You must select your grinding media carefully or consider a non-contact method.
Understanding these core principles allows you to effectively harness the power of a planetary ball mill for your specific material goal.
Summary Table:
| Key Factor | Influence on Particle Size |
|---|---|
| Grinding Media | Denser materials (e.g., tungsten carbide) enable finer grinding. |
| Rotational Speed | Higher speeds increase impact energy for smaller particles. |
| Grinding Time | Longer times reduce size, but with diminishing returns. |
| Material Properties | Hard, brittle materials are ideal for fine grinding. |
Ready to achieve precise particle size reduction in your lab? KINTEK specializes in high-performance planetary ball mills and grinding consumables. Our experts can help you select the right equipment and media to optimize your process for nano-scale results, whether you're working with ceramics, alloys, or other advanced materials. Contact our team today to discuss your specific application and ensure you get the fineness and purity you require.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Planetary Ball Mill Rotating Ball Milling Machine
- High-Energy Omnidirectional Planetary Ball Mill Milling Machine for Laboratory
- High-Energy Omnidirectional Planetary Ball Mill Machine for Laboratory
- High Energy Planetary Ball Mill Milling Machine for Laboratory
- High Energy Planetary Ball Mill Milling Machine for Laboratory
People Also Ask
- What is the principle of planetary ball mill? Achieve Rapid, High-Energy Grinding for Your Materials
- What are the effects of ball milling? A Deep Dive into Mechanical Alloying and Material Transformation
- What is the difference between a ball mill and a planetary mill? Choose the Right Grinding Tool for Your Lab
- How does a planetary mill work? Harnessing High-Energy Impact for Nano-Grinding
- What size are planetary mill particles? Achieve Nanoscale Precision for Your Materials



















