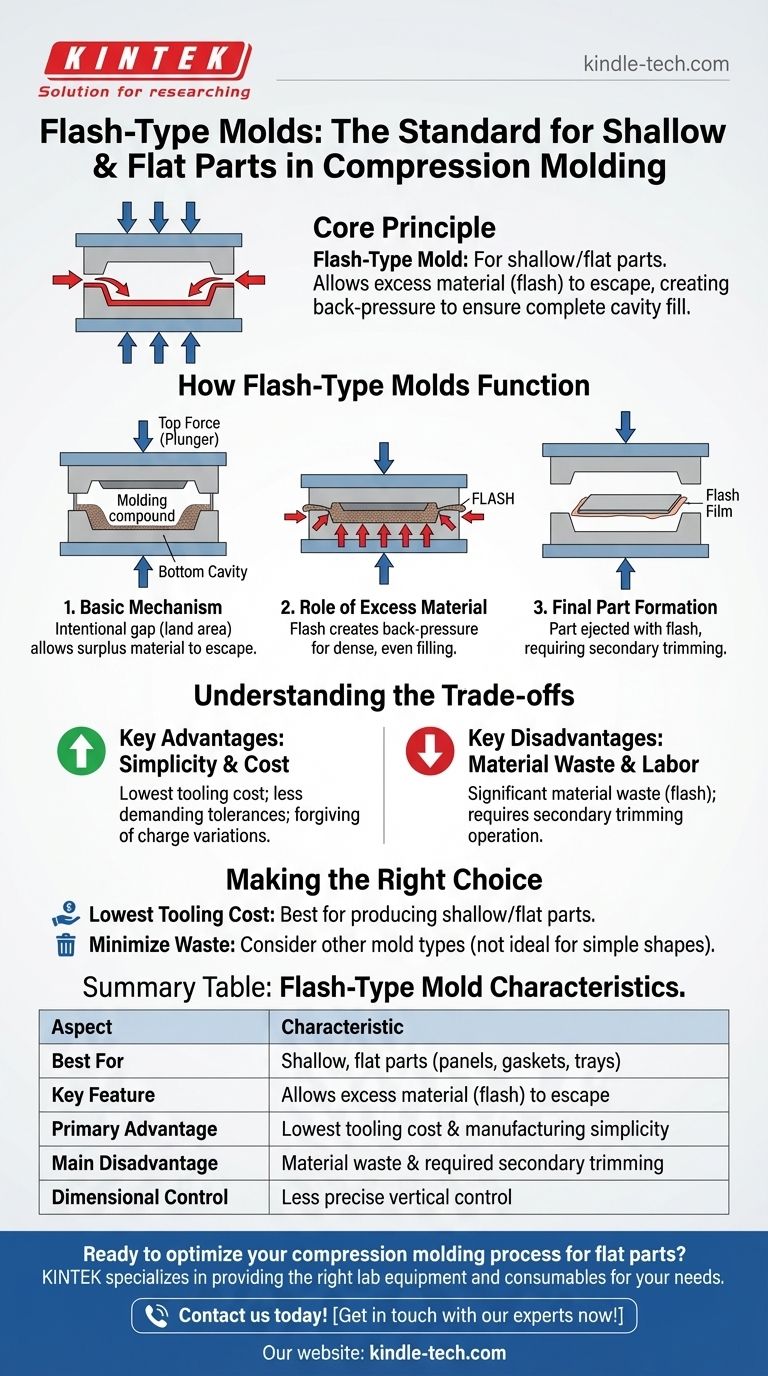
For shallow or flat parts, the standard choice in compression molding is the flash-type mold. This design is specifically engineered for components where precision on the vertical "shut-off" dimension is less critical than simplicity and cost-effectiveness. The defining characteristic of this mold is that it allows excess material, known as "flash," to be intentionally squeezed out as the mold closes.
The core principle is straightforward: a flash-type mold is an "open" system that uses excess material as a hydraulic medium to ensure the cavity fills completely. This makes it ideal for simpler, flatter components where the cost of post-processing (trimming the flash) is acceptable.
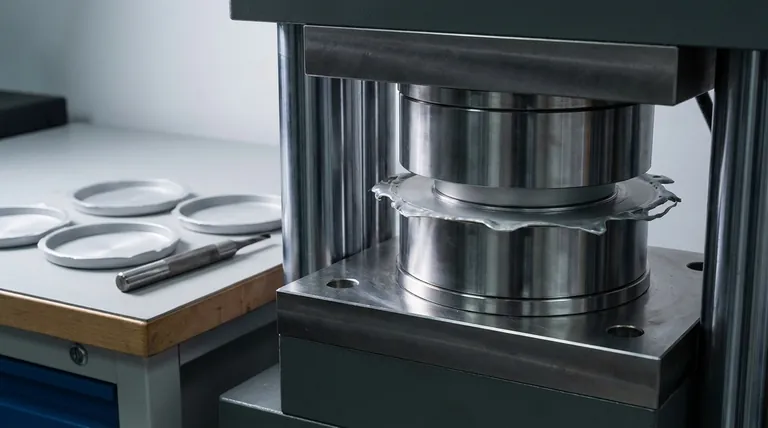

How Flash-Type Molds Function
The design and operation of a flash-type mold are fundamental to understanding its application in compression molding.
The Basic Mechanism
A flash-type mold consists of a top force (plunger) and a bottom cavity. The molding compound is placed into the cavity, and as the press closes, the plunger applies pressure.
The mating surfaces, often called the "land area," do not form a perfect seal. This intentional gap allows surplus material to escape as the mold fully closes.
The Role of Excess Material (Flash)
The "flash" is not merely waste; it is a functional part of the process. As the excess material is squeezed out, it creates back-pressure within the mold cavity.
This pressure ensures that the entire cavity is densely and evenly filled, which is critical for achieving a uniform part, especially over a large, flat surface area.
Final Part Formation
Once the material cures under heat and pressure, the mold is opened. The finished part is ejected along with the thin, attached film of flash around its perimeter. This flash must then be removed in a secondary trimming operation.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Choosing a flash-type mold involves accepting a clear set of advantages and disadvantages that make it suitable for specific applications.
Key Advantage: Simplicity and Cost
Flash-type molds are generally the simplest and least expensive to manufacture. The tolerances for the shut-off surfaces are less demanding compared to other mold types, reducing machining time and cost.
This design is also more forgiving of slight variations in the amount of material loaded into the mold (the "charge"), as the excess has a clear path to escape.
Key Disadvantage: Material Waste and Labor
The most significant drawback is the creation of flash, which is wasted material. This can be a considerable cost, especially with expensive molding compounds.
Furthermore, the flash must be trimmed off, which adds a secondary operation. This can involve manual labor or require automated trimming equipment, increasing the overall cost per part.
Impact on Part Quality
Because the final thickness of the part is determined by the amount of flash squeezed out, flash-type molds offer less precise control over the vertical dimension compared to more complex designs. This makes them unsuitable for high-precision components.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The decision to use a flash-type mold is driven entirely by the part's geometry and cost requirements.
- If your primary focus is producing shallow or flat parts at the lowest tooling cost: The flash-type mold is the definitive choice due to its manufacturing simplicity.
- If your primary focus is minimizing material waste and post-processing: You would need to consider more complex and expensive mold designs, such as semi-positive or positive molds, which are not ideal for simple, flat shapes.
Ultimately, for components like panels, gaskets, or trays, the flash-type mold provides the most practical balance of function and cost.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | Flash-Type Mold Characteristic |
|---|---|
| Best For | Shallow, flat parts (panels, gaskets, trays) |
| Key Feature | Allows excess material (flash) to escape |
| Primary Advantage | Lowest tooling cost and manufacturing simplicity |
| Main Disadvantage | Material waste and required secondary trimming |
| Dimensional Control | Less precise vertical control, ideal for simpler shapes |
Ready to optimize your compression molding process for flat parts?
At KINTEK, we specialize in providing the right lab equipment and consumables to support your material testing and production needs. Our expertise can help you select the most efficient molding solutions, ensuring cost-effectiveness and quality for your specific applications.
Contact us today to discuss how we can support your laboratory's goals and enhance your compression molding outcomes.
Get in touch with our experts now!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Polygon Press Mold for Lab
- Ball Press Mold for Lab
- Special Shape Press Mold for Lab
- Multi-Punch Rotary Tablet Press Mold Ring for Rotating Oval and Square Molds
- Assemble Lab Cylindrical Press Mold
People Also Ask
- How do ECAP molds and pressure equipment enhance FM steel? Master Microstructural Refinement & Grain Strength
- What is the function of a graphite mold during the vacuum hot pressing sintering process? Optimize Composite Performance
- What function do high-strength molds serve in MUE processing of FM steel? Unlock Superior Material Strength
- What is the opening sequence of a 3 plate mold? Master Automated De-gating for Precision Molding
- What are three-plate molds? Precision Injection Molding for Complex Parts
- What is the difference between injection mold and insert mold? A Guide to Multi-Material Parts
- What is the fundamental principle of the KBr pellet method? Master IR Spectroscopy with Plastic Deformation
- What are the parts of a mold assembly? A Guide to Injection Mold Components



















