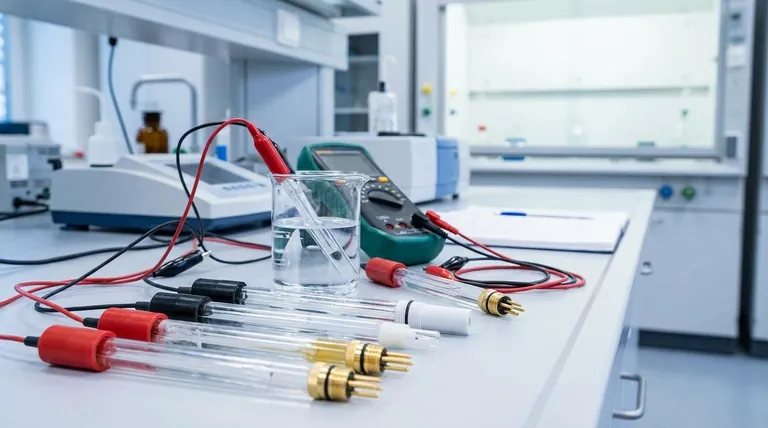
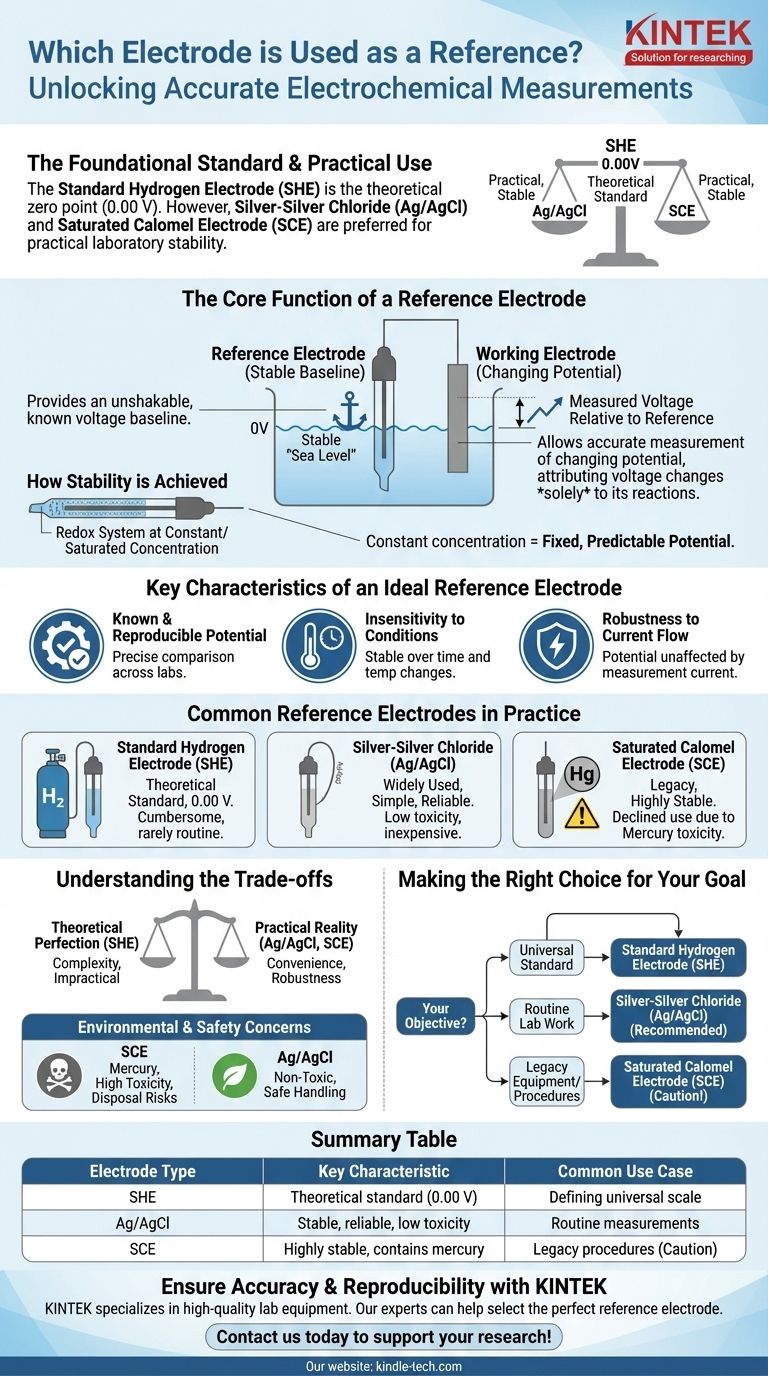
In electrochemistry, the foundational reference electrode is the Standard Hydrogen Electrode (SHE). By universal convention, its potential is defined as exactly 0.00 volts at all temperatures. However, for practical laboratory applications, electrodes like the Silver-Silver Chloride (Ag/AgCl) and Saturated Calomel Electrode (SCE) are far more common due to their ease of use and stable performance.
The core purpose of a reference electrode is not to participate in your experiment's primary reaction, but to provide an unshakable, known voltage baseline. It acts as a stable "zero point," allowing you to accurately measure the changing potential of the electrode you are actually studying.

The Core Function of a Reference Electrode
A reference electrode is a fundamental component of nearly any electrochemical measurement setup. Its role is to provide a fixed point against which another electrode's potential can be reliably determined.
Establishing a Stable Baseline
A reference electrode has a stable and well-known electrode potential. Think of it as the "sea level" for electrical potential in a chemical system.
You measure the "height," or potential, of your working electrode relative to this fixed, unchanging reference point.
Allowing Focus on the Working Electrode
By maintaining a constant potential, the reference electrode ensures that any voltage changes measured in the system can be attributed solely to the chemical reactions occurring at the working electrode.
This isolates the phenomenon you want to study, removing any doubt that your reference point is fluctuating.
How Stability is Achieved
This high stability is achieved by using a redox system where the components are held at a constant, typically saturated, concentration.
Because the concentrations of the reacting species inside the electrode do not change, the potential it produces remains fixed and predictable.
Key Characteristics of an Ideal Reference Electrode
While several types of reference electrodes exist, they all share a few critical characteristics that make them effective.
Known and Reproducible Potential
The electrode's potential must be precisely known and easily reproducible. This allows scientists in different labs to compare their results meaningfully.
Insensitivity to Conditions
An ideal reference electrode's potential should remain stable over time and with moderate changes in temperature.
Robustness to Current Flow
The electrode should be "well-poised," meaning its potential is not affected by the small amount of current that must flow through it for a measurement to be made. This ensures the act of measuring does not alter the result.
Common Reference Electrodes in Practice
While the SHE is the theoretical standard, other electrodes are used for day-to-day work due to practical considerations.
The Standard Hydrogen Electrode (SHE)
The SHE is the absolute standard against which all other electrode potentials are measured. It is the formal zero point of the electrochemical scale.
Despite its importance, it is cumbersome and rarely used in routine experiments because it requires a constant supply of pure hydrogen gas and a specially prepared platinum surface.
Silver-Silver Chloride (Ag/AgCl)
This is one of the most widely used reference electrodes today. It is valued for being simple, inexpensive, and reliable.
Its low toxicity gives it a significant advantage over older, mercury-based electrodes.
Saturated Calomel Electrode (SCE)
The SCE is another classic, highly stable reference electrode that was once extremely common.
Its use has declined significantly due to the fact that it contains mercury, a toxic heavy metal, making handling and disposal problematic.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Choosing a reference electrode involves balancing theoretical perfection against practical reality.
The Standard vs. The Practical
The SHE provides the theoretical foundation for electrochemistry, but its complexity makes it impractical for most applications. Electrodes like Ag/AgCl offer excellent stability in a much more convenient and robust package.
Environmental and Safety Concerns
The primary reason for the shift from the Saturated Calomel Electrode (SCE) to the Silver-Silver Chloride (Ag/AgCl) electrode is safety. The high toxicity of the mercury in the SCE presents significant handling and disposal risks that are absent with the Ag/AgCl electrode.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Your choice of reference electrode depends entirely on your objective, balancing the need for a universal standard against practical laboratory requirements.
- If your primary focus is establishing a universal standard: The Standard Hydrogen Electrode (SHE) is the definitive zero point against which all other potentials are measured.
- If your primary focus is routine laboratory work: The Silver-Silver Chloride (Ag/AgCl) electrode is the most common choice due to its stability, low cost, and non-toxic nature.
- If you are using legacy equipment or specific established procedures: You may encounter the Saturated Calomel Electrode (SCE), but you must remain mindful of its mercury content.
Ultimately, selecting the correct reference electrode is the first step toward ensuring your electrochemical measurements are both accurate and reproducible.
Summary Table:
| Electrode Type | Key Characteristic | Common Use Case |
|---|---|---|
| Standard Hydrogen Electrode (SHE) | Theoretical standard (0.00 V) | Defining the universal potential scale |
| Silver-Silver Chloride (Ag/AgCl) | Stable, reliable, low toxicity | Routine laboratory measurements |
| Saturated Calomel (SCE) | Highly stable, contains mercury | Legacy procedures (use with caution) |
Ensure the accuracy and reproducibility of your electrochemical experiments with the right reference electrode. KINTEK specializes in high-quality lab equipment and consumables, providing reliable solutions for all your laboratory needs. Our experts can help you select the perfect reference electrode for your specific application. Contact us today to discuss how we can support your research!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Reference Electrode Calomel Silver Chloride Mercury Sulfate for Laboratory Use
- Metal Disc Electrode Electrochemical Electrode
- Copper Sulfate Reference Electrode for Laboratory Use
- Glassy Carbon Electrochemical Electrode
- Graphite Disc Rod and Sheet Electrode Electrochemical Graphite Electrode
People Also Ask
- Why is a high-purity cobalt plate necessary for Co-Mo-Zr coatings? Ensure Superior Ternary Alloy Electrodeposition
- What are the common materials as electrodes? A Guide to Platinum, Gold, Carbon, and Copper
- In what scenarios should a gold plate electrode be dedicated to a single user or purpose? Ensure Patient Safety and Data Integrity
- What are the technical advantages of RVC foam for hydrogen evolution? Enhance Your 3D Electrode Performance
- What maintenance is required for a platinum mesh electrode? Essential Steps for Longevity and Accuracy
- What is the role of the Platinum electrode in Zircaloy-2 testing? Ensure High-Purity Electrochemical Results
- What should be done if a platinum mesh electrode changes shape or develops cracks? Stop Use Immediately to Protect Your Data
- How should an electrode holder be used during an experiment? A Guide to Ensuring Data Integrity



















