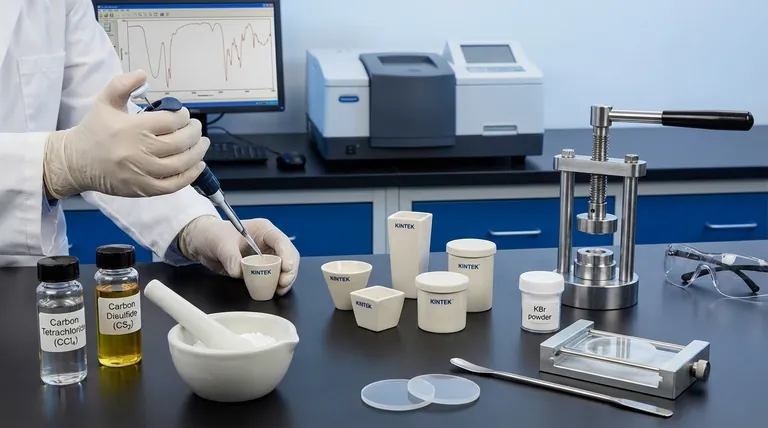
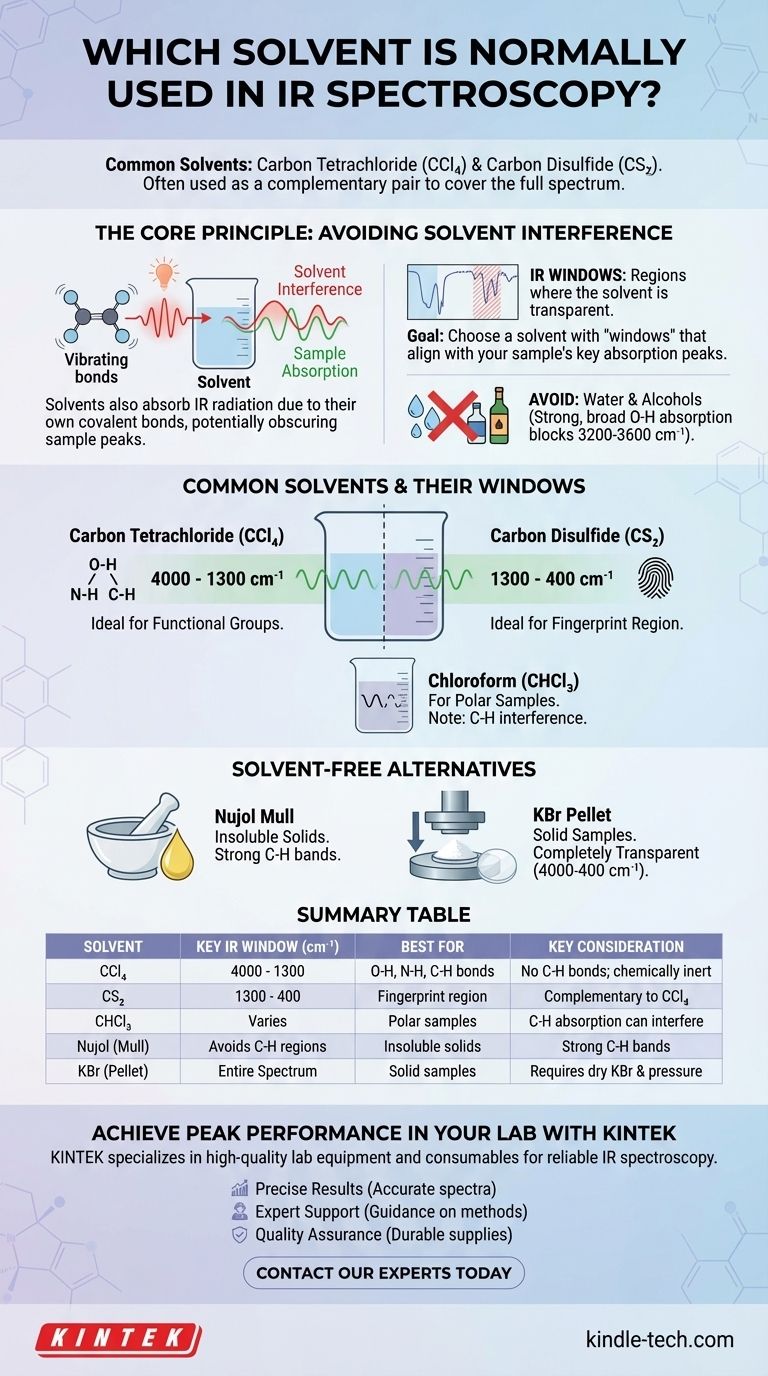
The most common solvents for IR spectroscopy are carbon tetrachloride (CCl₄) and carbon disulfide (CS₂). Because no single solvent is transparent across the entire infrared spectrum, these two are often used as a complementary pair to analyze different regions. The choice of solvent is critical, as the goal is to dissolve the sample without the solvent's own molecular vibrations obscuring the sample's absorption bands.
The fundamental principle of solvent selection in IR spectroscopy is to find a medium that dissolves your compound but is itself "invisible" in the spectral region you care about. Since no perfect solvent exists, the process involves strategically choosing a solvent with known transparent "windows" that align with the key absorption peaks of your sample.

The Core Principle: Avoiding Solvent Interference
Infrared spectroscopy works by measuring the vibrations of molecular bonds. The challenge is that the covalent bonds within any solvent molecule will also absorb IR radiation, creating their own spectral peaks that can interfere with or completely mask the peaks from your sample.
Why Solvents Absorb IR Radiation
Just like your sample, solvent molecules are made of atoms connected by covalent bonds. These bonds (like C-H, C-Cl, C=S) stretch and bend at specific frequencies when they absorb infrared light. This absorption is the source of interference.
The Concept of "IR Windows"
No solvent is transparent across the entire mid-IR range (4000 – 400 cm⁻¹). However, every solvent has regions where it absorbs only weakly or not at all. These areas are called "IR windows."
The goal is to choose a solvent whose windows match the absorption regions of the functional groups you want to study in your sample.
The Problem of Water and Alcohols
Solvents with -OH groups, such as water and ethanol, are almost never used for IR. The O-H bond produces an intensely strong and broad absorption band that completely obscures a vast and important region of the spectrum (roughly 3200-3600 cm⁻¹), making it impossible to see any sample peaks in that area.
Common Solvents and Their Windows
To obtain a full spectrum, chemists often run two scans of the same sample: one in a solvent that is clear in the high-frequency region, and another in a solvent that is clear in the low-frequency "fingerprint" region.
Carbon Tetrachloride (CCl₄)
This is the standard choice for the region from 4000 cm⁻¹ to 1300 cm⁻¹. Because it has no C-H bonds, it is transparent where C-H, N-H, and O-H stretching vibrations occur, making it ideal for analyzing these critical functional groups.
Carbon Disulfide (CS₂)
This is the complementary solvent to CCl₄. It is largely transparent in the fingerprint region from 1300 cm⁻¹ to 400 cm⁻¹. This allows for detailed analysis of the complex vibrations that give a molecule its unique spectral identity.
Chloroform (CHCl₃)
Chloroform is a more polar solvent and can be a good choice if your sample will not dissolve in CCl₄ or CS₂. However, its own C-H bond creates absorption bands (around 3000 cm⁻¹ and 1200 cm⁻¹) that can interfere with the analysis of C-H bonds in the sample.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Alternatives
Choosing a solvent is only one way to prepare a sample. If your compound is insoluble or if solvent interference is unavoidable, other standard techniques exist.
Chemical Inertness is Non-Negotiable
As the reference material notes, the solvent must not react with your sample. Using an acidic solvent for a basic sample, for example, would result in an ion-pair, and you would be analyzing the spectrum of a completely different chemical species than you intended.
The Nujol Mull: A Solvent-Free Alternative
When a sample is insoluble in all suitable IR solvents, a Nujol mull is the preferred technique. The solid sample is ground into a fine powder and mixed with a drop of Nujol (a mineral oil) to form a paste.
This paste is then pressed between two salt plates for analysis. Nujol itself consists of long-chain hydrocarbons, so it will show strong C-H absorption bands, but it is transparent elsewhere, allowing for analysis of most other functional groups.
The KBr Pellet
Another common solvent-free method is the KBr pellet. The solid sample is mixed with pure, dry potassium bromide (KBr) powder and pressed under high pressure to form a small, transparent disc. KBr is ionically bonded and does not absorb IR radiation, making it a completely transparent medium for analysis.
Making the Right Choice for Your Analysis
Your choice of sample preparation method depends entirely on the physical properties of your sample and the specific information you need from the spectrum.
- If your primary focus is on O-H, N-H, or C-H bonds (4000-1300 cm⁻¹): Use carbon tetrachloride (CCl₄) for its excellent transparency in this region.
- If your primary focus is on the fingerprint region (1300-400 cm⁻¹): Use carbon disulfide (CS₂) to get a clear view of the complex vibrations unique to your molecule.
- If your sample is insoluble in non-polar solvents: Consider a more polar option like chloroform, or bypass liquid solvents entirely and prepare a KBr pellet or a Nujol mull.
Ultimately, effective sample preparation is about ensuring the spectrum you record is that of your compound, not an artifact of your chosen medium.
Summary Table:
| Solvent | Key IR Window (cm⁻¹) | Best For | Key Consideration |
|---|---|---|---|
| Carbon Tetrachloride (CCl₄) | 4000 - 1300 | O-H, N-H, C-H bonds | No C-H bonds; chemically inert |
| Carbon Disulfide (CS₂) | 1300 - 400 | Fingerprint region | Complementary to CCl₄ |
| Chloroform (CHCl₃) | Varies (e.g., gaps around 3000 cm⁻¹) | Polar samples | C-H absorption can interfere |
| Nujol (Mull) | Avoids C-H regions | Insoluble solids | Strong C-H bands from Nujol |
| KBr (Pellet) | Entire spectrum (4000-400) | Solid samples | Requires dry KBr and high pressure |
Achieve Peak Performance in Your Lab
Navigating solvent selection is just one step toward precise material analysis. KINTEK specializes in providing the high-quality lab equipment and consumables you need for reliable IR spectroscopy and beyond.
Let us help you enhance your laboratory's capabilities:
- Precise Results: Ensure your sample preparation leads to accurate, interference-free spectra.
- Expert Support: Get guidance on the right tools and methods for your specific application.
- Quality Assurance: Trust in our durable, reliable supplies for consistent performance.
Ready to optimize your analytical processes? Contact our experts today to discuss how KINTEK can support your laboratory's unique needs in spectroscopy and material analysis.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Evaporation Crucible for Organic Matter
- Iridium Dioxide IrO2 for Water Electrolysis
- High Pressure Laboratory Autoclave Reactor for Hydrothermal Synthesis
- Customizable High Pressure Reactors for Advanced Scientific and Industrial Applications
- Reference Electrode Calomel Silver Chloride Mercury Sulfate for Laboratory Use
People Also Ask
- What precautions should be taken in a chemistry lab? Master the RAMP Framework for Ultimate Safety
- What is the delta 20 rule of evaporation? Master Safe and Effective Spraying
- What are the 5 factors that affect the rate of evaporation? Master the Process for Your Lab
- What are the analytical used in laboratory? Choose the Right Tool for Your Lab's Needs
- How is energy converted into biomass? Harnessing Nature's Solar Power for Renewable Energy





