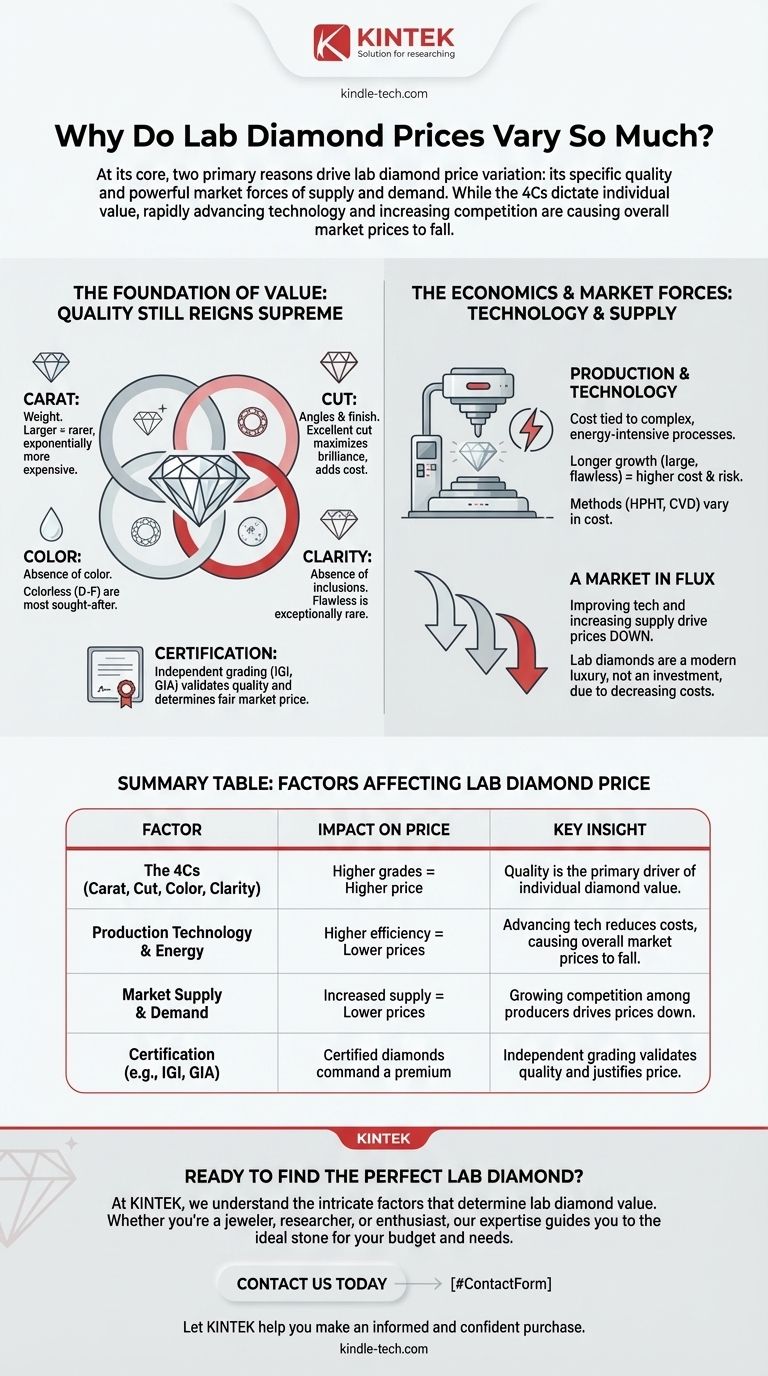
At its core, the price of a lab-grown diamond varies for two primary reasons: its specific quality and the powerful market forces of supply and demand. Just like natural diamonds, the value of an individual lab diamond is dictated by its "4Cs"—carat, cut, color, and clarity. However, the overall price landscape for all lab diamonds is currently defined by rapidly advancing technology and increasing competition, which are causing prices to fall.
While a diamond's individual quality sets its price relative to other stones, the most significant factor influencing the wide price variance you see today is a rapidly evolving market. Technological advancements are making it cheaper and faster to grow high-quality diamonds, leading to a consistent downward trend in overall prices.
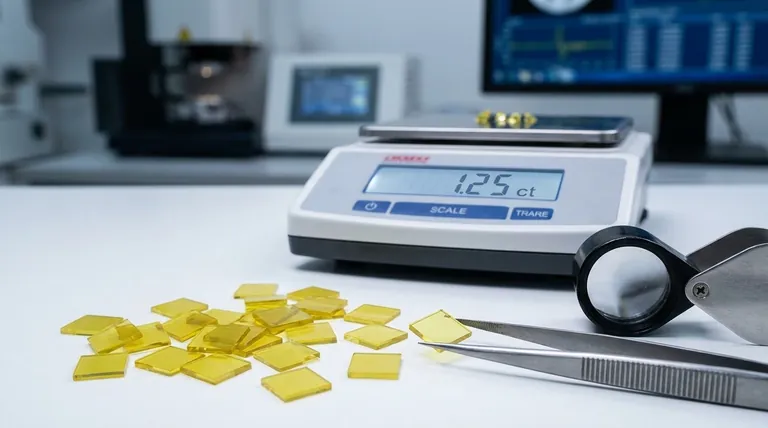

The Foundation of Value: Quality Still Reigns Supreme
Even in a technologically driven market, the fundamental principles of diamond valuation still apply. The primary driver of price difference between two specific lab diamonds is their gemological quality.
The 4Cs: The Universal Standard
The "4Cs" are the globally accepted standards for assessing a diamond's quality and value. A lab diamond with superior grades will always command a higher price than one with lower grades, all else being equal.
- Carat: This is a measure of weight. Larger diamonds are rarer and more difficult to grow successfully, making them exponentially more expensive.
- Cut: This refers to the quality of the diamond's angles, facets, and finish. An excellent cut maximizes brilliance and fire, requiring significant skill and adding to the diamond's cost.
- Color: This grades the absence of color. Colorless diamonds (D-F grades) are the most sought-after and expensive.
- Clarity: This measures the absence of internal inclusions or external blemishes. Flawless diamonds are exceptionally rare and costly to produce.
The Role of Certification
An independent grading report from a reputable gemological lab like IGI or GIA provides an objective assessment of the 4Cs. This certification validates a diamond's quality and is a critical factor in determining its fair market price.
The Economics of Creation: Production and Technology
Unlike mined diamonds, the cost of a lab diamond is directly tied to the complex, energy-intensive process of its creation.
The Cost of Time and Energy
Growing a large, high-quality lab diamond is not instantaneous. It requires sophisticated HPHT (High Pressure/High Temp) or CVD (Chemical Vapor Deposition) machinery to run continuously for weeks or even months.
This process consumes enormous amounts of energy and carries a high risk of failure. The longer a diamond grows, the higher the operational cost and the greater the chance of an imperfect result, making large, flawless stones significantly more expensive to produce.
The Impact of Growth Methods
The two primary methods, HPHT and CVD, can produce diamonds of varying qualities and costs. The specific "recipe," technology, and any necessary post-growth treatments to improve a diamond's color or clarity all contribute to its final production cost.
Understanding the Trade-offs: A Market in Flux
The single biggest reason for price shifts over time is the dynamic nature of the lab diamond market itself. What a diamond cost two years ago has little bearing on its price today.
Improving Technology Drives Prices Down
The technology behind diamond growth is constantly improving. As producers become more efficient, they can create better quality diamonds faster and with lower failure rates. This reduction in production cost is passed on to the consumer.
Increasing Supply and Competition
The lab diamond industry is expanding rapidly, with more producers entering the market. This increased supply and fierce competition exert strong downward pressure on prices as suppliers vie for customers. Over the past few years, wholesale prices have dropped dramatically due to this trend.
What This Means for Future Value
Because lab diamonds are a product of technology with no supply constraints, their prices will likely continue to decrease over time. They should be viewed as a modern, affordable luxury good, not a financial investment. Their value is in their beauty and the significant cost savings they offer compared to natural diamonds of similar quality, not in their potential for resale.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Navigating the market is about aligning your purchase with your personal priorities.
- If your primary focus is maximizing size and quality for your budget: A lab-grown diamond is an outstanding choice, allowing you to acquire a much larger and higher-quality stone than a natural diamond for the same cost.
- If your primary focus is long-term investment or resale value: You should understand that the value of lab diamonds is expected to depreciate as technology improves. A natural diamond holds its value more traditionally.
- If your primary focus is finding a fair price on a beautiful stone: Concentrate on the 4Cs and the diamond's certification. Compare similarly graded diamonds from several retailers to ensure you are paying the current market rate.
By understanding these factors, you can confidently navigate the market and select a diamond that perfectly aligns with your priorities and budget.
Summary Table:
| Factor | Impact on Price | Key Insight |
|---|---|---|
| The 4Cs (Carat, Cut, Color, Clarity) | Higher grades = Higher price | Quality is the primary driver of individual diamond value. |
| Production Technology & Energy | Higher efficiency = Lower prices | Advancing tech reduces costs, causing overall market prices to fall. |
| Market Supply & Demand | Increased supply = Lower prices | Growing competition among producers drives prices down. |
| Certification (e.g., IGI, GIA) | Certified diamonds command a premium | Independent grading validates quality and justifies price. |
Ready to find the perfect lab diamond for your needs?
At KINTEK, we understand the intricate factors that determine lab diamond value. Whether you're a jeweler, researcher, or enthusiast, our expertise in high-quality materials and precision equipment can guide you to the ideal stone for your specific requirements and budget.
Contact us today using the form below to discuss your project and benefit from our industry knowledge. Let KINTEK help you make an informed and confident purchase.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- CVD Diamond for Thermal Management Applications
- CVD Diamond Dressing Tools for Precision Applications
- Laboratory CVD Boron Doped Diamond Materials
- Cylindrical Resonator MPCVD Machine System Reactor for Microwave Plasma Chemical Vapor Deposition and Lab Diamond Growth
- CVD Diamond Domes for Industrial and Scientific Applications
People Also Ask
- Can diamond be made artificially? Yes, with Identical Quality to Natural Diamonds
- Why is Microwave Plasma Chemical Vapor Deposition (MW-PCVD) preferred for BDD? Achieve Ultra-Pure Diamond Synthesis
- How plasma is used in diamond coating films? Unlock the Power of MPCVD for Superior Coatings
- Are CVD diamonds synthetic? Discover the Truth About Lab-Grown Diamonds
- Can a diamond tester tell the difference between lab grown and natural diamonds? The Surprising Truth
- What is a CVD diamond machine? Unlock the Power of Lab-Grown Diamond Engineering
- What are the advantages of microwave plasma? Faster, Purer Processing for Demanding Applications
- Which inclusions are found in lab-grown diamonds? Uncover the Signs of Man-Made Creation













