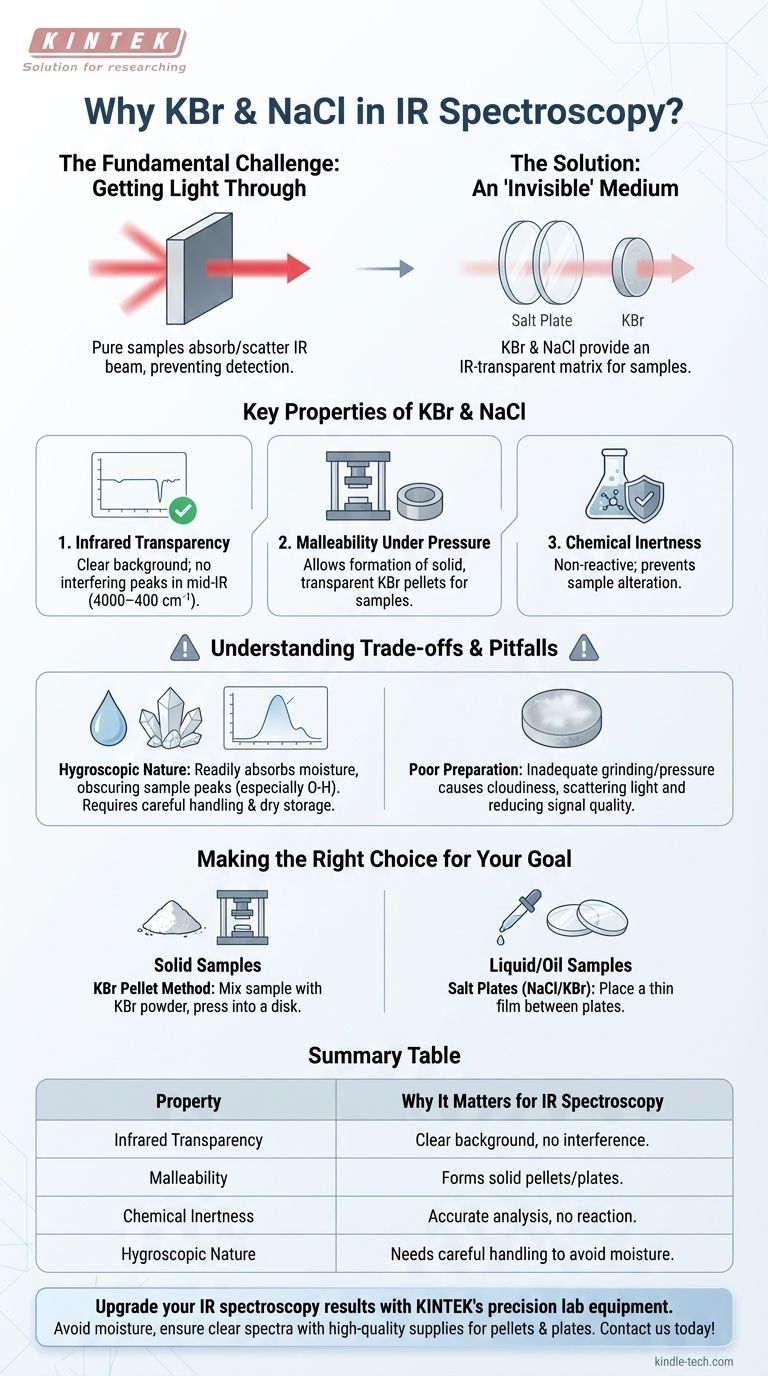
In short, KBr (potassium bromide) and NaCl (sodium chloride) are used in IR spectroscopy because they possess two critical properties: they are transparent to infrared radiation and they are soft, malleable salts. This unique combination allows them to act as a window or a solid matrix for a sample, permitting the IR beam to pass through and analyze the substance of interest without adding any interfering signals.
The core challenge in IR spectroscopy is preparing a sample that is thin and uniform enough for infrared light to pass through. KBr and NaCl solve this problem by providing a chemically inert, IR-transparent medium to hold the sample in the spectrometer's beam path.

The Fundamental Challenge: Getting Light Through the Sample
Why Pure Samples Are Often Unsuitable
Most organic and inorganic compounds, especially in their solid or pure liquid forms, are too thick or dense. They will absorb or scatter the entire infrared beam, preventing any light from reaching the detector.
This makes it impossible to obtain a useful spectrum, which relies on measuring the specific frequencies of light that the sample's molecular bonds absorb.
The Need for an 'Invisible' Medium
To get a usable signal, the sample must be diluted and supported in a medium that is effectively invisible to infrared light.
This carrier medium, whether it's a solid pellet or a liquid-cell window, must not have any of its own molecular vibrations that absorb in the mid-infrared region. If it did, its own spectrum would overlap and obscure the spectrum of the sample.
Key Properties of KBr and NaCl
1. Infrared Transparency
This is the primary reason for their use. Alkali halide salts like KBr and NaCl have simple ionic bonds. Their vibrational frequencies are so low that they fall far outside the typical mid-IR range (4000–400 cm⁻¹) used for analysis.
Because they don't absorb light in this region, they provide a perfectly clear background, ensuring that every peak observed in the spectrum comes solely from the sample being tested.
2. Malleability Under Pressure
As noted in sample preparation guides, KBr becomes plastic when subjected to high pressure. This physical property is essential for the common KBr pellet method.
When the finely ground sample is mixed with KBr powder and pressed in a die, the KBr flows and fuses together. It forms a solid, semi-transparent disk that locks the dispersed sample particles in a fixed, uniform matrix.
3. Chemical Inertness
Both KBr and NaCl are generally non-reactive salts. They do not chemically react with the vast majority of samples, ensuring the substance being analyzed remains unaltered during the preparation and measurement process.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Pitfalls
The Hygroscopic Nature of Alkali Halides
The most significant pitfall is that KBr and NaCl are hygroscopic, meaning they readily absorb moisture from the atmosphere.
Water (H₂O) has very strong and broad IR absorption bands, particularly the O-H stretching vibration. If the KBr or NaCl is contaminated with moisture, these water peaks will appear in the spectrum and can easily mask important peaks from the sample.
The Impact of Poor Preparation
This is why proper technique is critical. The KBr must be kept perfectly dry, often stored in a desiccator or oven. When making a pellet, a vacuum is often applied to the die to remove any trapped air and moisture.
If a pellet is not ground finely enough or pressed with sufficient pressure, it can appear cloudy. This cloudiness causes the IR light to scatter, leading to a poor baseline and reduced signal quality in the final spectrum.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The right application of these salts depends on the physical state of your sample.
- If your primary focus is analyzing a solid sample: The KBr pellet technique is the standard method, where you mix your sample with dry KBr powder and press it into a thin disk.
- If your primary focus is analyzing a liquid or oil: You will use salt plates made of NaCl or KBr, placing a thin film of your liquid between two of these transparent plates.
Ultimately, these simple salts are the unseen workhorses that make the powerful technique of IR spectroscopy possible for a wide range of materials.
Summary Table:
| Property | Why It Matters for IR Spectroscopy |
|---|---|
| Infrared Transparency | Provides a clear background; no interfering peaks in the mid-IR range (4000–400 cm⁻¹). |
| Malleability | Allows formation of solid, transparent pellets (KBr) or plates for liquid samples. |
| Chemical Inertness | Prevents reaction with samples, ensuring accurate analysis. |
| Hygroscopic Nature | Requires careful handling to avoid moisture contamination, which can obscure sample peaks. |
Upgrade your IR spectroscopy results with KINTEK's precision lab equipment.
Whether you're preparing solid samples with the KBr pellet method or analyzing liquids with salt plates, the right tools are crucial for avoiding moisture contamination and ensuring clear, accurate spectra. KINTEK specializes in high-quality lab equipment and consumables designed for reliability and ease of use, helping you achieve consistent, interference-free results.
Contact us today to explore our range of IR spectroscopy supplies and get expert support for your laboratory needs!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- kbr pellet press 2t
- Lab Infrared Press Mold
- Automatic Laboratory Hydraulic Press for XRF & KBR Pellet Press
- Laboratory Hydraulic Pellet Press for XRF KBR FTIR Lab Applications
- Laboratory Manual Hydraulic Pellet Press for Lab Use
People Also Ask
- How much sample is needed for IR? Optimize Your Analysis with Minimal Material
- Why do we use KBr in IR spectroscopy? Achieve Clear, High-Quality Solid Sample Analysis
- Why KBr is used for IR spectroscopy? The Ideal Medium for Solid Sample Analysis
- How do you prepare a KBr pellet for IR spectroscopy? Master the Key Steps for a Clear Spectrum
- What are the safety precautions for KBr? Achieve Flawless FTIR Pellet Preparation and Data Accuracy



















