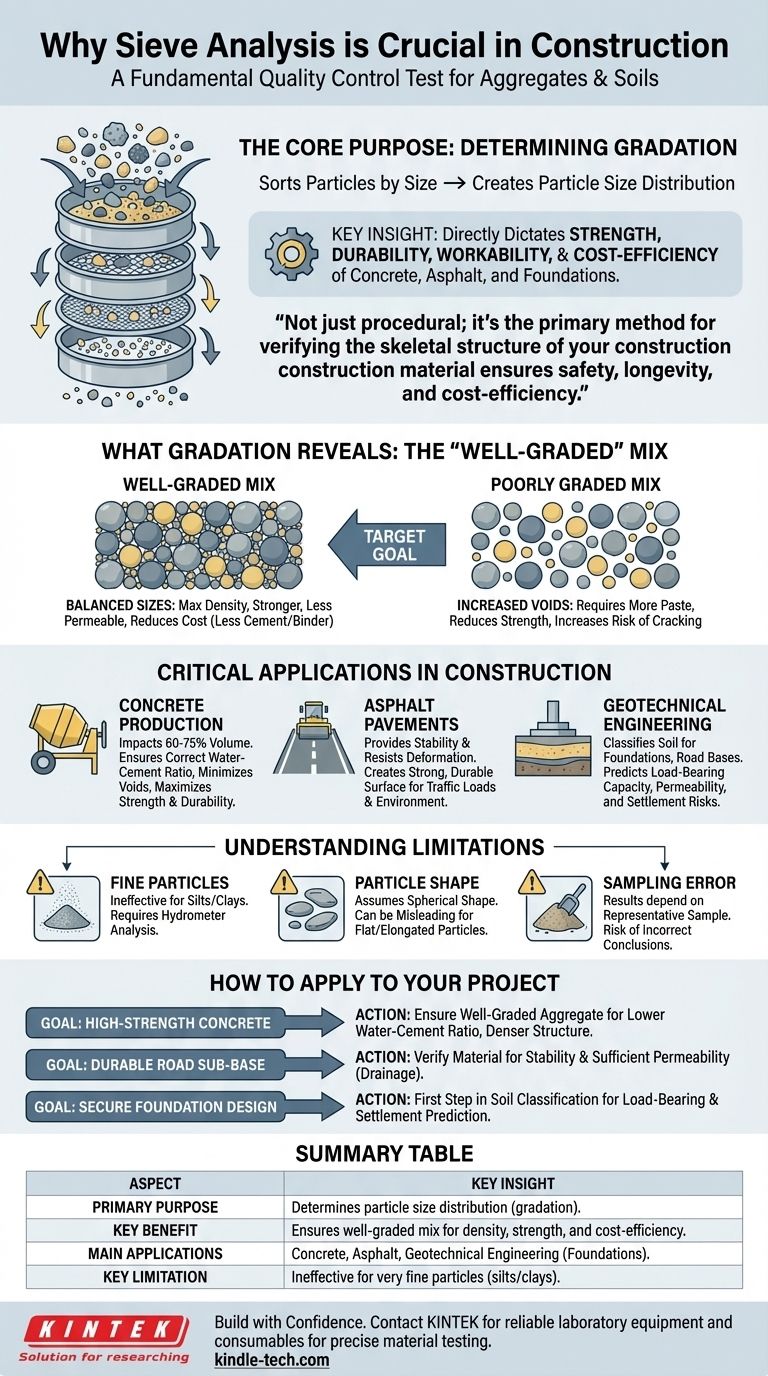
At its core, sieve analysis is the fundamental quality control test for the most common materials in the construction industry: aggregates and soils. It is critically important because it determines the particle size distribution, or gradation, of these materials. This gradation directly dictates the strength, durability, workability, and economic viability of essential products like concrete, asphalt, and structural foundations.
Sieve analysis is not merely a procedural step; it is the primary method for verifying that the skeletal structure of your construction material—the aggregate—is correctly proportioned to ensure project safety, longevity, and cost-efficiency.

What Sieve Analysis Reveals: The Concept of Gradation
The entire purpose of a sieve analysis is to understand the physical makeup of a granular material. It sorts particles by size, providing a blueprint of the material's internal structure.
Defining Particle Size Distribution
A sieve analysis involves passing a sample of aggregate or soil through a series of stacked mesh screens (sieves) with progressively smaller openings.
By weighing the material retained on each sieve, you can calculate the percentage of particles within each size range. This data, known as the particle size distribution or gradation, is the key output.
The Importance of a "Well-Graded" Mix
A well-graded aggregate contains a balanced mix of particle sizes. Smaller particles fill the voids between larger ones, creating a dense, interlocked structure.
This density is crucial. It minimizes the amount of expensive cement or asphalt binder needed to fill the gaps, directly reducing costs. More importantly, it results in stronger, less permeable, and more durable end products.
Why This Test Is the Industry Standard
Sieve analysis remains the go-to method for gradation for several practical reasons.
As noted, the advantages include its ease of use and minimal investment costs. The equipment is simple, the procedure is straightforward, and it delivers accurate and reproducible results in a relatively short time.
Critical Applications in Construction
The data from a sieve analysis informs critical decisions across nearly every vertical of civil and structural engineering. Ignoring it introduces significant risk.
For Concrete Production
Aggregate makes up 60-75% of concrete's volume. Its gradation impacts everything from cost to performance. A poor gradation leads to increased voids, requiring more cement paste and water, which in turn reduces strength and increases the risk of cracking.
For Asphalt Pavements
In asphalt, the aggregate skeleton is what provides stability and resists deformation under traffic loads. Sieve analysis ensures the aggregate mix has the proper interlocking characteristics to create a strong, durable pavement surface that can withstand wear and environmental stress.
For Geotechnical Engineering
For foundations, embankments, and road sub-bases, sieve analysis is used to classify soil. This classification helps engineers predict critical soil behaviors like load-bearing capacity, permeability (drainage), and susceptibility to frost heave, preventing structural settlement and failure.
Understanding the Limitations
While indispensable, sieve analysis is not a perfect tool. A true expert understands its boundaries and when to supplement it with other tests.
Ineffectiveness for Very Fine Particles
Sieve analysis is only effective for coarse-grained soils like sand and gravel. It cannot accurately measure the distribution of very fine particles like silts and clays, which can have a massive impact on soil behavior. For these materials, a hydrometer analysis is required.
The Assumption of Particle Shape
The test inherently assumes particles are roughly spherical, allowing them to pass through square sieve openings. If the aggregate contains many flat or elongated particles, the sieve analysis results can be misleading and may not accurately reflect the material's true packing density and workability.
The Risk of Sampling Error
The results of a sieve analysis are only as good as the sample provided. A small, non-representative sample from a large stockpile can lead to incorrect conclusions about the entire material source, introducing significant quality control risk into a project.
How to Apply This to Your Project
The results of a sieve analysis should directly inform material selection and design based on your specific engineering goal.
- If your primary focus is high-strength concrete: Ensure you have a well-graded aggregate to minimize voids, which allows for a lower water-cement ratio and creates denser, stronger concrete.
- If your primary focus is a durable road sub-base: Use sieve analysis to verify the material meets specifications for stability and has sufficient permeability for proper drainage, preventing water damage.
- If your primary focus is foundation design: Rely on sieve analysis as the first step in soil classification to assess load-bearing capacity and predict potential settlement issues.
Ultimately, this simple, cost-effective test is a fundamental pillar of risk management in modern construction.
Summary Table:
| Sieve Analysis Aspect | Key Insight |
|---|---|
| Primary Purpose | Determines particle size distribution (gradation) of aggregates and soils. |
| Key Benefit | Ensures a well-graded mix for maximum density, strength, and cost-efficiency. |
| Main Applications | Concrete production, asphalt pavements, and geotechnical engineering (foundations). |
| Key Limitation | Ineffective for very fine particles like silts and clays; requires supplemental testing. |
Ensure your construction materials meet the highest standards of quality and safety.
Accurate sieve analysis is the foundation of durable, cost-effective construction projects. KINTEK specializes in providing reliable laboratory equipment and consumables for precise material testing. Our expertise supports laboratories in achieving consistent, reproducible results for critical quality control.
Let us help you build with confidence. Contact our experts today to discuss your specific lab equipment needs for aggregate and soil analysis.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Test Sieves and Vibratory Sieve Shaker Machine
- Three-dimensional electromagnetic sieving instrument
- Laboratory Vibratory Sieve Shaker Machine Slap Vibrating Sieve
- Laboratory Wet Three-Dimensional Vibratory Sieve Shaker Machine
- Custom PTFE Teflon Parts Manufacturer for PTFE Mesh F4 Sieve
People Also Ask
- How do I choose a sieve size? A Step-by-Step Guide to Building the Perfect Sieve Stack
- What are the ASTM standard sieves? Ensure Accurate Particle Size Analysis with Precision Sieves
- What are the pros and cons of sieving? A Guide to Accurate Particle Size Analysis
- What were possible sources of error in sieve analysis? Avoid These Common Pitfalls for Accurate Results
- What are the factors affecting sieve analysis? Ensure Accurate Particle Size Distribution
- What are the two methods of sieve analysis? Choose the Right Method for Accurate Particle Sizing
- What is the primary purpose of using laboratory standard sieves? Optimize Composting Pre-treatment for Pig Manure
- What is verification of sieves? Ensure Accurate Particle Size Analysis



















