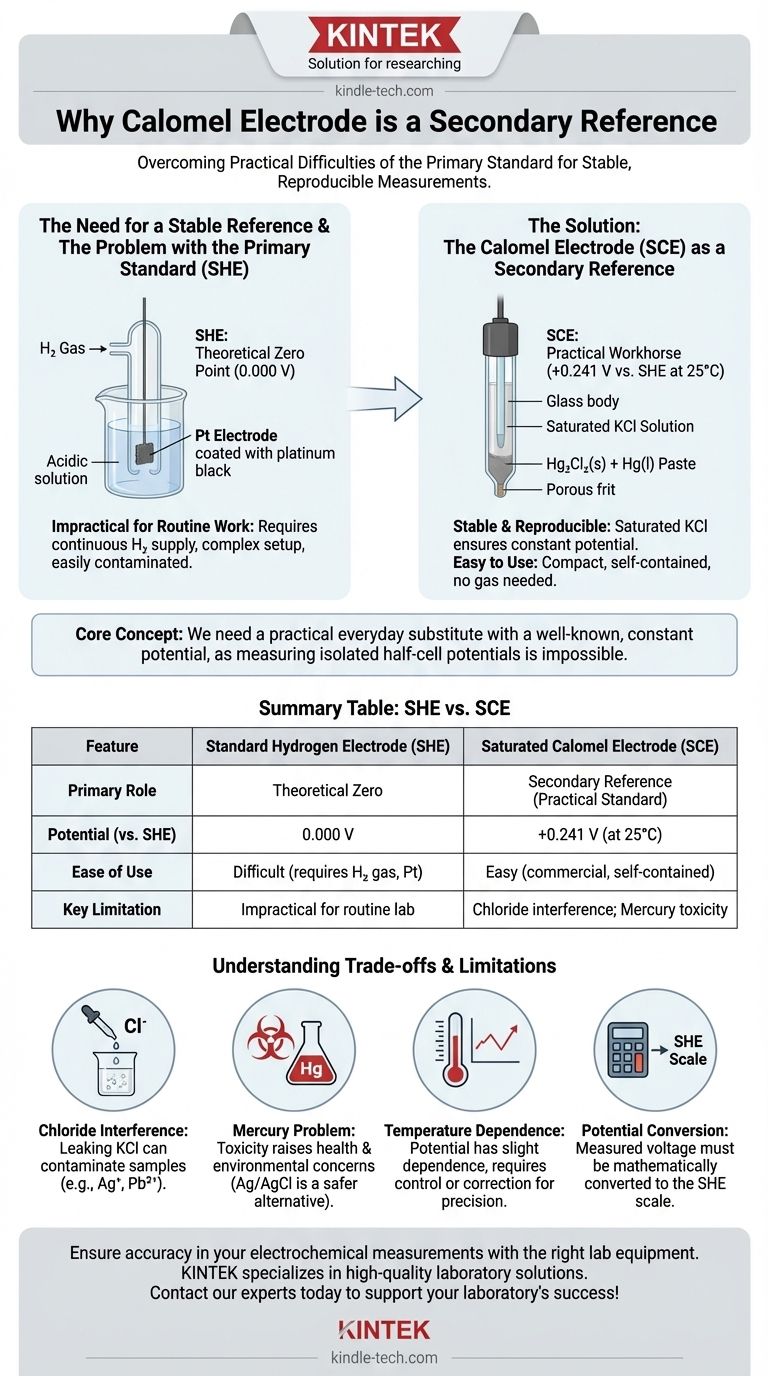
The calomel electrode is used as a secondary reference electrode because it provides a stable, reproducible, and convenient potential to measure against, overcoming the significant practical difficulties of using the primary standard, the Standard Hydrogen Electrode (SHE). While the SHE is the theoretical zero point for all electrochemical measurements, it is too cumbersome and sensitive for routine laboratory work, creating the need for a reliable secondary standard like calomel.
The core concept is simple: in electrochemistry, you cannot measure a half-cell's potential in isolation. You need a stable baseline. The Standard Hydrogen Electrode is the official, but impractical, baseline. The calomel electrode serves as a practical, everyday substitute with a well-known, constant potential.
The Need for a Stable Reference
To understand the role of a secondary electrode, we must first understand why a reference is needed at all.
The "Zero Point" Problem
An electrochemical cell's voltage is the potential difference between two half-cells. It is impossible to measure the absolute potential of a single electrode.
Therefore, the scientific community defined one specific half-cell as the universal zero point. This allows all other half-cell potentials to be measured and reported relative to a common standard.
The Primary Standard: An Impractical Ideal
The Standard Hydrogen Electrode (SHE) is the universal primary reference. By definition, its potential is exactly 0.000 volts under standard conditions (1 M H+ activity, 1 atm H₂ gas pressure, 25°C).
However, the SHE is extremely difficult to set up and maintain. It requires a continuous supply of purified hydrogen gas and a specially prepared platinum electrode that is easily contaminated, making it unsuitable for most daily laboratory applications.
The Calomel Electrode: The Practical Workhorse
Because the SHE is so impractical, scientists needed a secondary reference electrode—one that is easy to use but has a potential that is precisely known and constant relative to the SHE. The Saturated Calomel Electrode (SCE) became a popular choice for this role.
Stable and Reproducible Potential
The SCE's potential is based on the reversible reaction: Hg₂Cl₂(s) + 2e⁻ ⇌ 2Hg(l) + 2Cl⁻.
The potential of this electrode depends on the concentration of chloride ions (Cl⁻). By using a saturated solution of potassium chloride (KCl), the chloride ion concentration is kept constant and well-defined, which in turn fixes the electrode's potential at a stable value (+0.241 V vs. SHE at 25°C).
Ease of Construction and Use
Unlike the SHE, a calomel electrode is compact, portable, and commercially available as a self-contained unit. It requires no gas cylinders or complex preparation, making it exceptionally convenient for routine measurements.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Limitations
While convenient, the calomel electrode is not without its drawbacks, which are critical to understand for accurate measurements.
Interference from Chloride Ions
The electrode's internal KCl solution can slowly leak through the porous frit or salt bridge into the sample being tested. If the sample contains ions that precipitate with chloride (like silver, Ag⁺, or lead, Pb²⁺), it will contaminate the sample and cause erroneous readings.
The Mercury Problem
The use of mercury (Hg) and its salts presents significant health and environmental disposal concerns. Due to mercury's toxicity, many laboratories have phased out calomel electrodes in favor of silver/silver chloride (Ag/AgCl) electrodes, which serve the same purpose but are safer to handle.
Dependence on Temperature
The potential of the SCE is stable but does have a slight dependence on temperature. For highly precise work, the temperature must be controlled, or a correction factor must be applied.
The Need for Potential Conversion
Because the calomel electrode's potential is not zero, any voltage measured against it must be mathematically converted to the SHE scale for standardized reporting. To find the potential of your test electrode vs. SHE, you must add the calomel electrode's potential to your measured value.
Making the Right Choice for Your Measurement
Choosing and using a reference electrode properly is fundamental to good electrochemical practice.
- If your primary focus is establishing a universal standard: All final, reported potentials must be calculated and presented relative to the SHE scale, the defined zero point of electrochemistry.
- If your primary focus is routine laboratory analysis: A secondary reference like the calomel or Ag/AgCl electrode is the correct choice for its convenience, stability, and ease of maintenance.
- If your sample contains ions sensitive to chloride: You must use a chloride-free reference electrode system, such as a double-junction electrode, to prevent measurement errors caused by precipitation.
Ultimately, understanding the role of a secondary reference is about recognizing the difference between the theoretical standard and the practical tool required to get the job done.

Summary Table:
| Feature | Standard Hydrogen Electrode (SHE) | Saturated Calomel Electrode (SCE) |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Role | Primary Reference (Theoretical Zero) | Secondary Reference (Practical Standard) |
| Potential (vs. SHE) | 0.000 V | +0.241 V (at 25°C) |
| Ease of Use | Difficult (requires H₂ gas, Pt electrode) | Easy (commercial, self-contained) |
| Key Limitation | Impractical for routine lab work | Chloride interference; Mercury toxicity |
Ensure the accuracy and reliability of your electrochemical measurements with the right lab equipment. KINTEK specializes in providing high-quality laboratory equipment and consumables. Whether you are setting up a new lab or optimizing your existing processes, our expertise can help you select the perfect tools for your needs. Contact our experts today to discuss how we can support your laboratory's success!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Reference Electrode Calomel Silver Chloride Mercury Sulfate for Laboratory Use
- Gold Disc Electrode
- Metal Disc Electrode Electrochemical Electrode
- Rotating Platinum Disk Electrode for Electrochemical Applications
- Copper Sulfate Reference Electrode for Laboratory Use
People Also Ask
- Which electrode is used as a reference? A Guide to Accurate Electrochemical Measurements
- What are the four main types of sensors? A Guide to Power Source and Signal Type
- What is the reference electrode for mercury mercury chloride? Discover the Saturated Calomel Electrode (SCE)
- Why is a Saturated Calomel Electrode (SCE) used as a reference electrode in microbial fuel cell research?
- What are the characteristics of a saturated calomel electrode for neutral solutions? Understanding its stability and limitations.

















