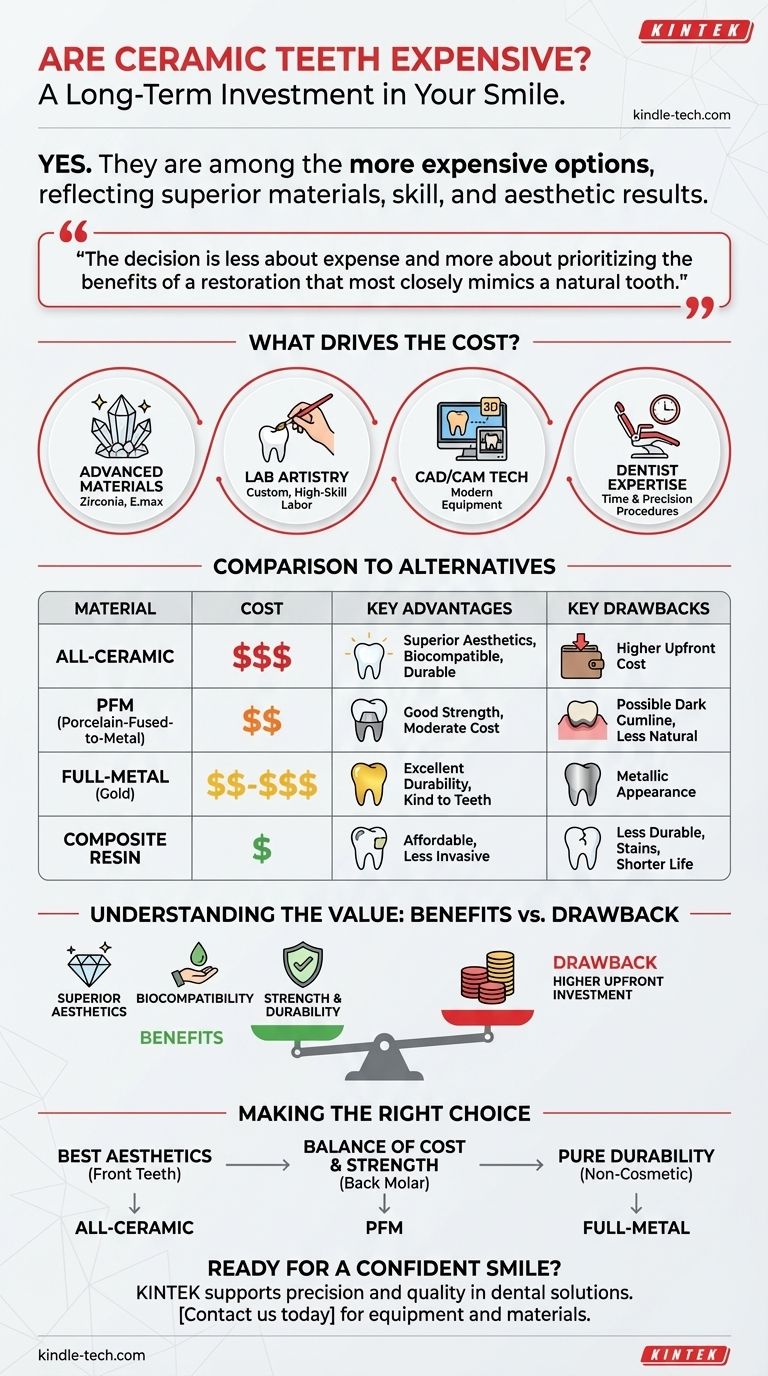
Yes, as a general rule, all-ceramic dental restorations are among the more expensive options available. This higher cost is a direct reflection of the advanced materials used, the specialized skill required from both the dentist and the dental laboratory, and the superior aesthetic results they provide compared to most alternatives.
While ceramic teeth carry a higher upfront cost than metal-based or composite options, this price point reflects their value as a long-term investment in unparalleled aesthetics, biocompatibility, and durability. The decision is less about expense and more about prioritizing the benefits of a restoration that most closely mimics a natural tooth.

What Drives the Cost of Ceramic Restorations?
The price of a ceramic crown, veneer, or implant is not arbitrary. It is the result of several factors, each adding to the final cost you see on a treatment plan.
The Cost of Advanced Materials
High-performance dental ceramics, such as Zirconia or Lithium Disilicate (E.max), are sophisticated materials engineered for both strength and beauty. They are significantly more expensive to produce than the metal alloys used in traditional crowns.
The Role of the Dental Laboratory
Creating a ceramic restoration is a form of artistry. A highly skilled dental technician must meticulously layer porcelain or mill a ceramic block to perfectly match the color, translucency, and shape of your natural teeth. This custom, high-skill labor is a primary cost driver.
Advanced Manufacturing Technology (CAD/CAM)
Many modern dental offices use CAD/CAM (Computer-Aided Design/Computer-Aided Manufacturing) technology, such as the CEREC system. This allows for 3D scanning and in-office milling of a ceramic crown in a single visit. The significant capital investment in this equipment is factored into the treatment price.
The Dentist's Expertise and Time
Placing a ceramic restoration, especially a cosmetic one like a veneer, requires meticulous tooth preparation and bonding procedures. This demands more chair time and a higher level of clinical expertise from your dentist compared to placing a traditional metal crown.
How Ceramic Compares to Other Materials
To understand if ceramic is "expensive," you must compare it to the primary alternatives. Each material serves a different purpose at a different price point.
Versus Porcelain-Fused-to-Metal (PFM)
PFM crowns have been a reliable standard for decades and are typically less expensive than all-ceramic options. They have a metal substructure for strength with porcelain baked on top for appearance. Their primary drawback is aesthetics; a dark metal line can become visible at the gumline over time.
Versus Full-Metal Crowns (Gold)
Gold alloy crowns are known for their exceptional durability and kindness to opposing teeth. Their cost is highly dependent on the price of precious metals but is often comparable to or sometimes even higher than ceramic. Their obvious disadvantage is their metallic appearance, making them suitable only for back molars.
Versus Composite Resin
For smaller cosmetic fixes, composite resin (used for bonding) is a much more affordable and less invasive alternative. However, it is not as strong, durable, or stain-resistant as ceramic and has a significantly shorter lifespan, often requiring more frequent replacement.
Understanding the Trade-offs: Is the Cost Justified?
The higher price of ceramic teeth comes with a distinct set of benefits and a few considerations.
The Benefit: Superior Aesthetics
No other material can replicate the translucency and life-like appearance of a natural tooth better than all-ceramic. For front teeth, where appearance is paramount, ceramic is the undisputed gold standard.
The Benefit: Biocompatibility
Ceramics are highly biocompatible, meaning they are inert and well-tolerated by the tissues in your mouth. This eliminates the risk of metal allergies or gum irritation that can sometimes occur with PFM restorations.
The Benefit: Strength and Durability
Modern ceramics like zirconia are incredibly strong and resistant to wear, making them suitable for use even on molars that endure heavy chewing forces. They are durable, long-lasting solutions.
The Drawback: Higher Upfront Investment
The primary barrier for most patients is the initial cost. While they are a durable long-term solution, the upfront financial commitment is greater than for other materials.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Your choice of material should be a collaborative decision with your dentist, based on the tooth's location, your budget, and your aesthetic priorities.
- If your primary focus is the most natural appearance for front teeth: An all-ceramic crown or veneer is the definitive choice for the best possible cosmetic outcome.
- If your primary focus is maximum durability for a back molar on a tighter budget: A Porcelain-Fused-to-Metal (PFM) crown provides a good balance of strength and acceptable aesthetics.
- If your primary focus is a non-cosmetic restoration where strength is the only factor: A full-gold crown remains one of the most durable and long-lasting options available.
Ultimately, choosing a ceramic restoration is an investment in achieving a result that is nearly indistinguishable from a healthy, natural tooth.
Summary Table:
| Material | Typical Cost | Key Advantages | Key Drawbacks |
|---|---|---|---|
| All-Ceramic | Higher | Superior aesthetics, biocompatibility, durability | Higher upfront cost |
| Porcelain-Fused-to-Metal (PFM) | Moderate | Good strength, lower cost than all-ceramic | Possible dark gumline, less natural look |
| Full-Metal (Gold) | Moderate to High | Excellent durability, kind to opposing teeth | Metallic appearance (not for visible teeth) |
| Composite Resin | Lower | Affordable, less invasive | Less durable, stains easily, shorter lifespan |
Ready to Achieve a Confident, Natural-Looking Smile?
Choosing the right dental restoration is a significant decision for your oral health and confidence. At KINTEK, we understand that precision and quality are paramount in dental lab work. While we specialize in providing high-quality lab equipment and consumables for various industries, we recognize the importance of advanced materials and technology in creating lasting dental solutions.
If you're a dental professional looking to enhance your practice with reliable equipment or materials, or if you have questions about the technology behind superior dental restorations, our team is here to support you.
Contact us today to learn how KINTEK’s expertise can help you deliver the best outcomes for your patients.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Dental Porcelain Zirconia Sintering Ceramic Furnace Chairside with Transformer
- Vacuum Dental Porcelain Sintering Furnace
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- 1700℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace Bottom Lifting Muffle Furnace
People Also Ask
- Is ceramic the same as porcelain teeth? A Guide to Choosing the Right Dental Material
- What is the purpose of a burnout furnace? Create the Perfect Mold for Flawless Metal Casting
- What temperature do you fire zirconia? Master the Sintering Cycle for Peak Strength & Aesthetics
- What is the major drawback of all-ceramic restorations in the posterior of the mouth? Overcoming Fracture Risk for Long-Lasting Results
- Can ceramic teeth stain? Why High-Quality Dental Ceramics Resist Discoloration
- What is the primary function of a porcelain furnace in dental ceramics? Master Restoration Aesthetics and Durability
- What does a dental furnace do? Achieve Perfect, Lifelike Dental Restorations
- What are the characteristics of dental ceramics? Achieve Superior Esthetics and Durability



















