In practice, neither CVD nor HPHT diamonds are inherently better. Modern advancements in both technologies allow them to produce gems that are chemically, physically, and optically identical to each other and to natural diamonds. The final quality and beauty of a diamond depend on its grading across the 4Cs (Cut, Color, Clarity, Carat), not the specific method used to grow it.
While buyers often seek a "winner" between CVD and HPHT, this is a misplaced focus driven by competing marketing claims. The critical insight is that the growth method is a technical detail, not a determinant of quality. The focus should be on the individual diamond's certification and characteristics.

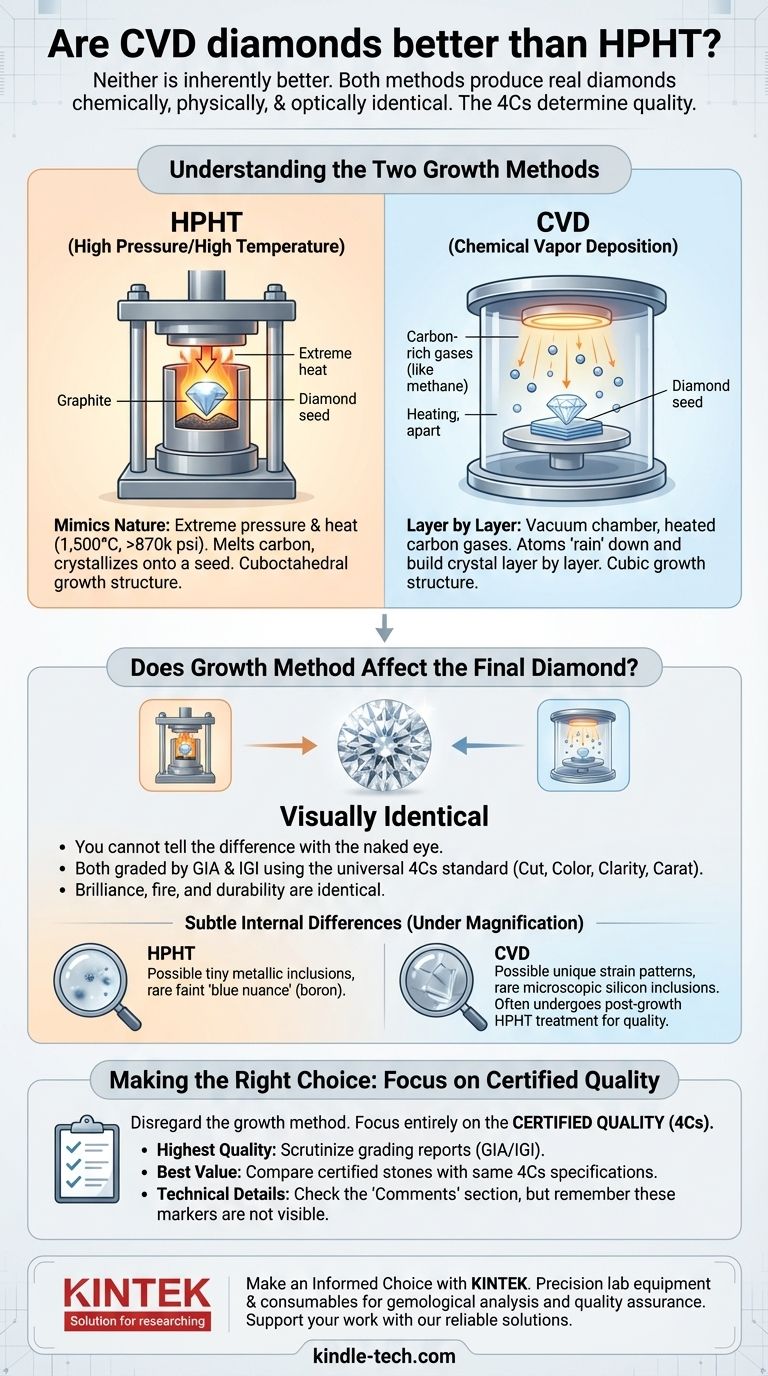
Understanding the Two Growth Methods
To make an informed decision, it's essential to understand how each process works. Both begin with a tiny diamond "seed" but use fundamentally different environments to grow it.
The HPHT Method: Mimicking Nature
The High Pressure/High Temperature (HPHT) method replicates the conditions deep within the Earth where natural diamonds form.
A diamond seed is placed in a large mechanical press along with carbon material, such as graphite. It is then subjected to immense pressure (over 870,000 psi) and extreme heat (around 1,500°C), causing the carbon to melt and crystallize onto the diamond seed.
Historically, trace amounts of nitrogen in the growth chamber could give HPHT diamonds a yellowish or brownish tint. However, modern process refinements have largely eliminated this issue, allowing for the consistent production of high-color (D-F) gems.
The CVD Method: Building Layer by Layer
Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD) is a newer technique that grows a diamond in a vacuum chamber. Think of it as 3D printing on an atomic level.
A diamond seed is placed inside the chamber, which is then filled with carbon-rich gases (like methane). These gases are heated until they break apart, allowing carbon atoms to "rain" down and attach to the diamond seed, building the crystal layer by layer.
CVD diamonds often undergo a secondary HPHT treatment after growth. This is a standard finishing step that improves the diamond's color and clarity, ensuring the final product meets the highest quality standards.
Does the Growth Method Affect the Final Diamond?
For the buyer, the distinctions between the two methods are almost entirely academic. Once the diamond is cut and polished, the origin story becomes irrelevant to its beauty and durability.
Visual Appearance and the 4Cs
You cannot tell the difference between a CVD and an HPHT diamond with the naked eye. Both are real diamonds, and both are graded by gemological labs like GIA and IGI using the universal 4Cs standard.
Their brilliance, fire, and durability are identical. A well-cut "Excellent" grade CVD diamond will be more brilliant than a poorly cut "Good" grade HPHT diamond, and vice versa. The cut quality is far more impactful on appearance than the growth method.
Subtle Internal Differences
Under high magnification, a trained gemologist may be able to identify the growth method based on the diamond's internal growth patterns (morphology).
- HPHT diamonds grow in a cuboctahedral shape, and may sometimes contain tiny metallic inclusions from the growth press. Some can also exhibit a very faint "blue nuance" caused by boron.
- CVD diamonds grow in a cubic shape and may have unique strain patterns. On rare occasions, they can contain microscopic silicon inclusions, which are not found in natural or HPHT diamonds.
These are microscopic identifiers, not flaws. They do not affect the diamond's beauty, clarity grade, or physical integrity.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Misconceptions
The debate between CVD and HPHT is often fueled by misinformation. As an informed buyer, your goal is to see past the noise.
The Marketing Claims
Companies that specialize in one method will often present it as superior while highlighting perceived flaws in the other. This is marketing, not objective advice. Both methods are mature technologies capable of producing flawless, colorless diamonds.
The "Post-Treatment" Stigma
Some view the post-growth HPHT treatment of CVD diamonds as a sign of inferiority. This is incorrect. This step should be seen as a standard and permanent enhancement, similar to the routine heat treatment of sapphires to improve their color. It is a quality-assurance process that results in a better, more stable gem.
Price and Availability
The final price of any diamond is determined by its 4Cs and market demand, not its growth method. You will find that for a given size, color, and clarity, the prices for CVD and HPHT diamonds are highly competitive and often indistinguishable.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The best strategy is to disregard the growth method and focus entirely on the certified quality of the individual diamond you are considering.
- If your primary focus is the highest quality (D-F Color, VVS+ Clarity): Both methods produce exceptional gems. Scrutinize the GIA or IGI grading report and choose the stone that best meets your criteria, regardless of how it was grown.
- If your primary focus is finding the best value: Compare certified diamonds with the same 4Cs specifications from both methods. Choose the one that offers a better price or simply appeals more to your eye.
- If you are concerned about minor technical differences: Focus on the "Comments" section of the grading report. However, remember these internal markers are not visible and do not impact the diamond's performance.
Ultimately, the perfect diamond is the one that meets your standards for beauty and budget, and its creation story is secondary to its certified quality.
Summary Table:
| Feature | CVD Diamonds | HPHT Diamonds |
|---|---|---|
| Process | Chemical Vapor Deposition; builds layer-by-layer in a vacuum chamber. | High Pressure/High Temperature; mimics natural Earth conditions. |
| Typical Post-Growth Treatment | Often undergoes HPHT treatment to enhance color and clarity. | Usually none; the process itself achieves high color. |
| Common Identifiers (under magnification) | Cubic growth structure; possible unique strain patterns. | Cuboctahedral growth structure; possible metallic inclusions. |
| Final Product | Chemically, physically, and optically identical to HPHT and natural diamonds. | Chemically, physically, and optically identical to CVD and natural diamonds. |
Make an Informed Choice with KINTEK
Navigating the technical details of lab-grown diamonds can be complex. Whether you're a jeweler, researcher, or gemologist, having the right equipment and consumables is essential for accurate analysis and quality assurance.
KINTEK specializes in precision lab equipment and consumables, serving the exacting needs of the gemological and materials science industries. We provide the tools you need to verify diamond quality, from advanced spectroscopy supplies to sample preparation equipment.
Let us support your work with reliable, high-performance solutions.
Contact our experts today via our Contact Form to discuss how KINTEK can meet your specific laboratory requirements.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- CVD Diamond for Thermal Management Applications
- CVD Diamond Domes for Industrial and Scientific Applications
- CVD Diamond Cutting Tool Blanks for Precision Machining
- CVD Diamond Optical Windows for Lab Applications
- Cylindrical Resonator MPCVD Machine System Reactor for Microwave Plasma Chemical Vapor Deposition and Lab Diamond Growth
People Also Ask
- What is the future value of lab grown diamond? Understanding Its Depreciating Financial Worth
- Are CVD diamonds fake? Discover the Truth About Lab-Grown Diamonds
- What is the future of CVD diamond? Unlocking Next-Gen Electronics & Thermal Management
- What is the difference between CVD and original diamond? Choose the Right Diamond for Your Needs
- What are the common sources of contamination during CVD diamond growth? Improve Purity and Quality Control



















