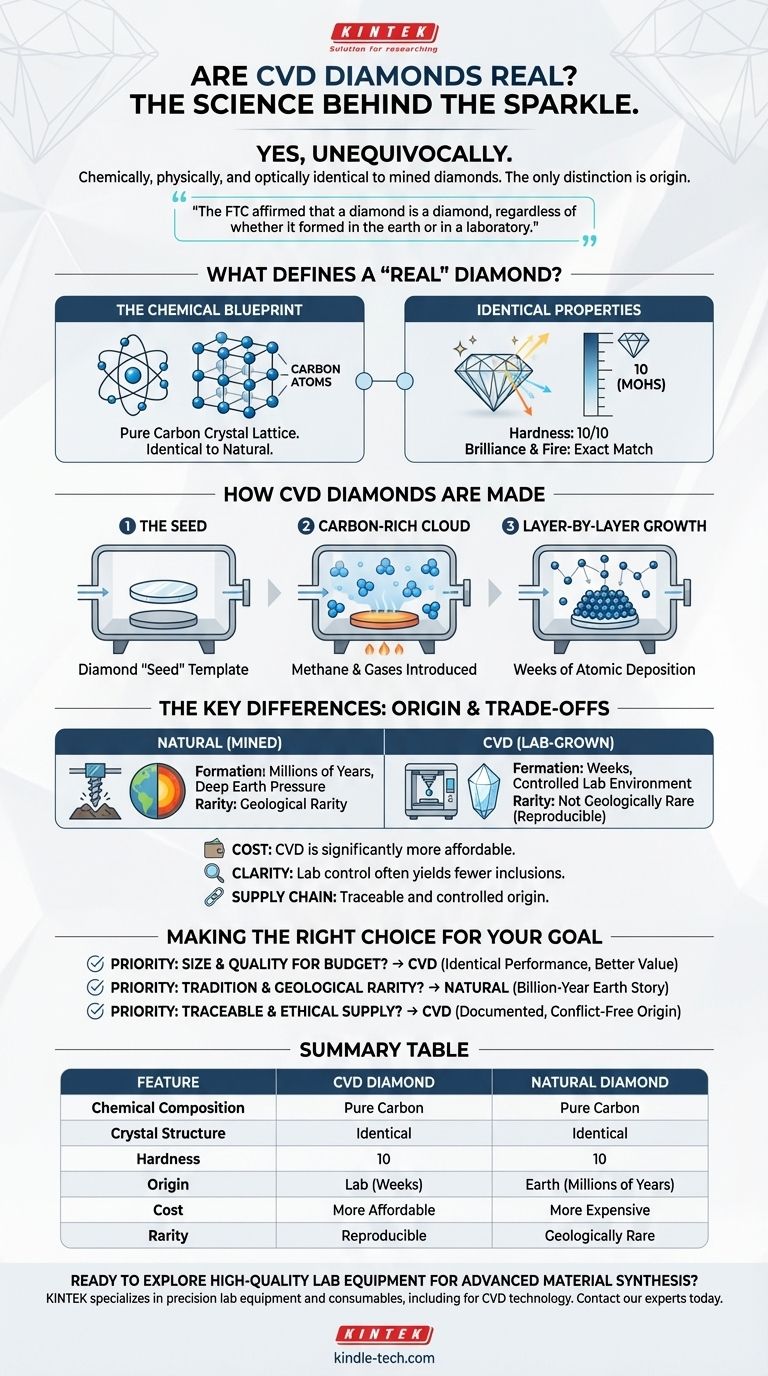
Yes, unequivocally. A CVD diamond is a real diamond in every sense that matters scientifically. It is not a simulant like cubic zirconia; it possesses the exact same chemical structure, physical properties, and optical brilliance as a diamond mined from the earth. The only difference is its origin.
The core takeaway is that the distinction between a natural diamond and a lab-grown CVD diamond is not about substance—it's about origin. Both are crystallized carbon, and in 2018, the U.S. Federal Trade Commission (FTC) officially affirmed that a diamond is a diamond, regardless of whether it formed in the earth or in a laboratory.

What Defines a "Real" Diamond?
To understand why a CVD diamond is real, we must first define what a diamond is at a fundamental level. Its identity is based on material composition and structure, not its formation history.
The Chemical Blueprint: Pure Carbon
A diamond is simply carbon atoms arranged in a specific crystal lattice structure. This unique, rigid bond is what gives the stone its legendary hardness and durability.
CVD diamonds are made of the exact same carbon atoms arranged in the exact same crystal structure. Chemically, they are indistinguishable from their mined counterparts.
Identical Physical and Optical Properties
Because the underlying structure is identical, all the properties we value in a diamond are present in a CVD stone. This includes:
- Hardness: It rates a 10 on the Mohs scale, just like a natural diamond.
- Brilliance & Fire: It reflects and refracts light in precisely the same way, creating the signature sparkle.
To the naked eye, even that of a trained jeweler, there is no visual difference between a high-quality natural diamond and a high-quality CVD diamond.
How CVD Diamonds Are Made
The process of Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD) mimics natural diamond growth in a highly controlled and accelerated environment. It’s a process of building a diamond atom by atom.
The Diamond "Seed"
The process begins with a "seed"—a very thin, flat slice of a high-quality diamond (either natural or another lab-grown diamond). This seed provides the template for the new diamond's crystal structure.
A Carbon-Rich Cloud
This seed is placed inside a sealed vacuum chamber which is then filled with a mixture of carbon-heavy gases, such as methane.
Layer-by-Layer Growth
The chamber is heated to extreme temperatures, causing the gases to break apart and release their carbon atoms. These atoms then fall and deposit onto the diamond seed, building up new layers and growing the diamond vertically. This process continues for several weeks until the desired size is reached.
The Key Differences: Origin, Not Substance
While the final product is the same, the journey it takes to get there is fundamentally different. This is where the true distinction lies.
Formation: Deep Earth vs. Laboratory
Natural diamonds form over millions of years under immense pressure and heat deep within the Earth's mantle. CVD diamonds are created in a matter of weeks under highly controlled laboratory conditions.
Official Recognition
The scientific and regulatory consensus is clear. The FTC's 2018 ruling removed the word "natural" from the official definition of a diamond. This legally recognizes that lab-grown stones are not fakes or simulants, but a different category of genuine diamond.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Choosing between a mined and a lab-grown diamond involves weighing a set of practical and philosophical considerations. The "better" choice depends entirely on your personal priorities.
Cost and Production
Because the production process is efficient and not dependent on finite geological resources, CVD diamonds are significantly more affordable than natural diamonds of comparable size and quality.
Rarity and Market Value
Natural diamonds are a finite resource, and their rarity is a major component of their traditional market value and mystique. Lab-grown diamonds can be produced on demand, so they do not possess this same quality of geological rarity.
Clarity and Quality Control
The controlled environment of a lab allows for a high degree of supervision. This often results in diamonds with exceptional clarity and fewer of the inclusions (tiny internal flaws) that can be found in natural stones.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Ultimately, the question isn't whether a CVD diamond is real, but which type of real diamond aligns with your values.
- If your primary focus is maximum size and quality for your budget: A CVD diamond delivers the identical material and visual performance at a more accessible price.
- If your primary focus is the tradition and romance of geological rarity: A natural diamond carries the unique story of its billion-year formation deep within the Earth.
- If your primary focus is a traceable and controlled supply chain: Lab-grown diamonds offer a clear and documented origin, bypassing the complexities of traditional mining.
Both paths lead to a genuine diamond; the choice simply reflects which origin story holds more value for you.
Summary Table:
| Feature | CVD Diamond | Natural Diamond |
|---|---|---|
| Chemical Composition | Pure Carbon | Pure Carbon |
| Crystal Structure | Identical | Identical |
| Hardness (Mohs Scale) | 10 | 10 |
| Origin | Laboratory (Weeks) | Earth's Mantle (Millions of Years) |
| Typical Cost | More Affordable | More Expensive |
| Rarity | Not Geologically Rare | Geologically Rare |
Ready to explore high-quality lab equipment for advanced material synthesis?
KINTEK specializes in precision lab equipment and consumables, serving the exact needs of laboratories engaged in cutting-edge research and production, including CVD technology. Our expertise ensures you have the reliable tools needed for consistent, high-quality results.
Contact our experts today to discuss how KINTEK can support your laboratory's specific requirements and help you achieve your research and production goals.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Chemical Vapor Deposition CVD Equipment System Chamber Slide PECVD Tube Furnace with Liquid Gasifier PECVD Machine
- Customer Made Versatile CVD Tube Furnace Chemical Vapor Deposition Chamber System Equipment
- Split Chamber CVD Tube Furnace with Vacuum Station Chemical Vapor Deposition System Equipment Machine
- RF PECVD System Radio Frequency Plasma-Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition RF PECVD
- 1200℃ Split Tube Furnace with Quartz Tube Laboratory Tubular Furnace
People Also Ask
- What are the different types of thin films? A Guide to Optical, Electrical, and Functional Coatings
- What are the steps of the CVD process? A Guide to Precision Thin Film Deposition
- What color diamonds are CVD? Understanding the Process from Brown Tint to Colorless Beauty
- How does PECVD work? Enable Low-Temperature, High-Quality Thin Film Deposition
- What is the process of vacuum vapor deposition? Mastering CVD and PVD Thin-Film Coating



















