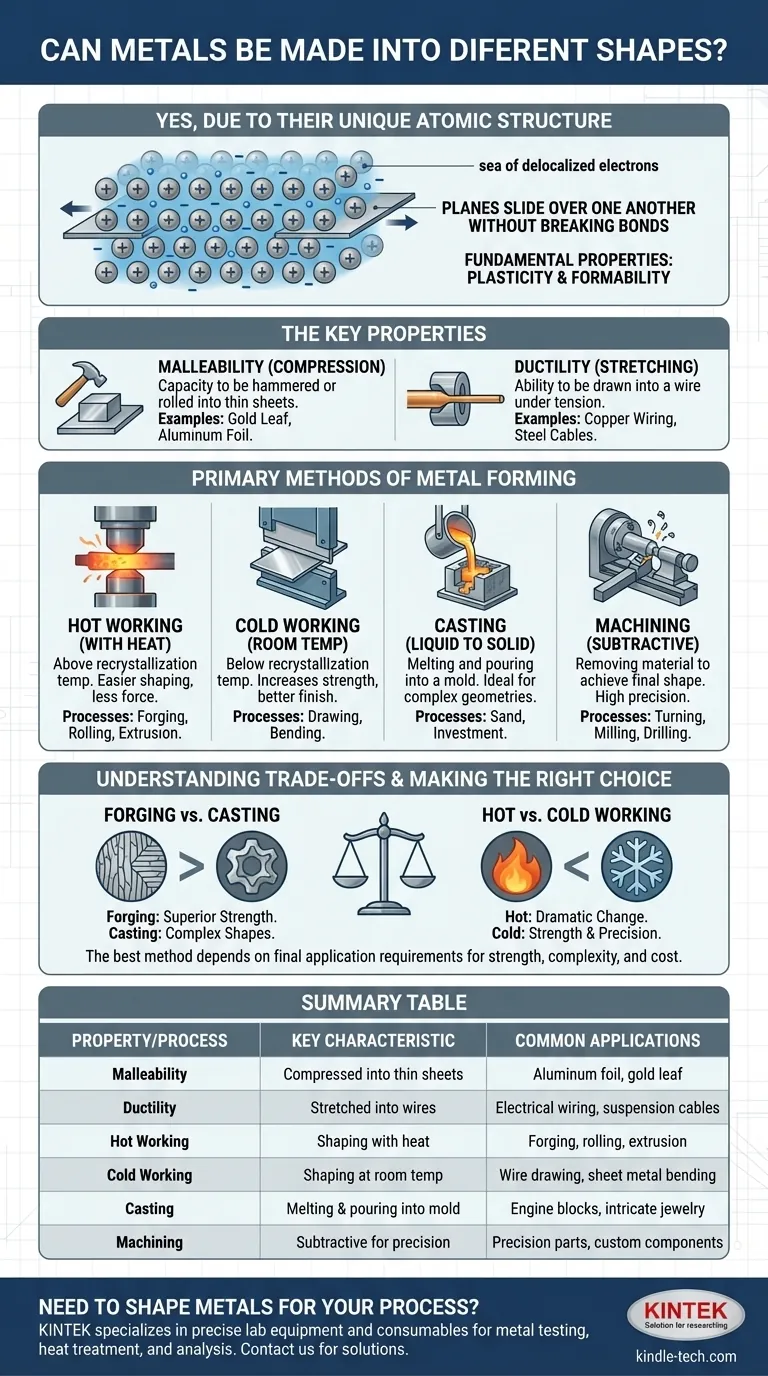
Yes, the ability to be formed into a vast array of shapes is one of the most fundamental and valuable properties of metals. This unique characteristic is not an accident; it is a direct result of their atomic structure. Understanding how and why metals can be shaped is the foundation of modern engineering, manufacturing, and technology.
The unique "sea of electrons" in a metal's atomic structure gives it inherent plasticity, allowing it to be bent, stretched, and compressed into new shapes without fracturing. This shaping is achieved through a range of processes, primarily categorized by whether the metal is heated (hot working), shaped at room temperature (cold working), or melted and poured (casting).

The Fundamental Properties That Allow Shaping
The versatility of metals is not magic; it originates from their specific atomic arrangement and the bonds that hold them together. These properties have distinct names and implications.
Metallic Bonding: The Atomic Key
Unlike other materials where electrons are fixed between specific atoms, metals consist of a lattice of positive ions sitting in a "sea" of shared, delocalized electrons.
This structure allows planes of atoms to slide over one another under force without breaking the metallic bond. This is the core reason metals can deform plastically (permanently change shape) rather than shattering like glass.
Malleability: The Ability to Be Compressed
Malleability is a metal's capacity to be hammered, pressed, or rolled into thin sheets without breaking. It describes a material's resistance to compressive forces.
Gold is the most malleable metal, capable of being hammered into a translucent leaf just a few atoms thick. Aluminum's high malleability is what allows it to be rolled into the thin foil used in kitchens.
Ductility: The Ability to Be Stretched
Ductility is a metal's ability to be drawn out into a wire under tensile stress (pulling). This property is crucial for creating everything from electrical wiring to suspension bridge cables.
Copper is exceptionally ductile, making it the standard for electrical wires. Steel's combination of ductility and high strength allows it to be formed into the reinforcing bars (rebar) that give concrete its tensile strength.
Primary Methods of Metal Forming
Engineers and artisans use a variety of techniques to exploit the inherent plasticity of metals. These methods are broadly grouped by temperature and the nature of the shaping force.
Hot Working: Shaping with Heat
Heating a metal above its recrystallization temperature makes it significantly softer and more ductile. This allows for massive shape changes with less force and without hardening the material.
Common hot working processes include forging (shaping with hammers or presses), rolling (passing hot metal through rollers to reduce its thickness), and extrusion (pushing hot metal through a shaped die).
Cold Working: Shaping at Room Temperature
Cold working is performed below the metal's recrystallization temperature. While it requires more force, it increases the metal's strength and hardness through a process called strain hardening.
Processes like drawing (pulling metal through a die to create wire) and bending sheet metal are typically done cold to achieve better surface finish and dimensional accuracy.
Casting: From Liquid to Solid
Casting involves melting the metal completely and pouring the liquid into a mold of the desired shape. It is ideal for creating complex or intricate geometries that would be difficult or impossible to achieve by other means.
Everything from engine blocks to jewelry is made through casting methods like sand casting or investment casting.
Machining: The Subtractive Approach
Unlike the methods above which form the metal, machining is a subtractive process. It starts with a larger piece of metal (a block, bar, or rod) and removes material using cutting tools to achieve the final shape.
Turning (on a lathe), milling (with a rotating cutter), and drilling are all machining operations used for creating parts with high precision.
Understanding the Trade-offs
No single forming method is best for every application. The choice of process involves a critical balance of cost, desired final properties, and geometric complexity.
Hot Working vs. Cold Working
Hot working allows for dramatic shape changes and uses less energy, but the final product has a rougher surface finish and less dimensional precision.
Cold working produces a stronger, harder part with a smooth finish and tight tolerances. However, it makes the metal less ductile, and only limited shape changes are possible before the metal must be heat-treated (annealed) to restore its ductility.
Forging vs. Casting
Casting can create almost any shape, no matter how complex. However, the cooling process can introduce porosity and a weaker, non-uniform grain structure.
Forging a part aligns the metal's internal grain structure with the shape of the part, creating exceptional strength and fatigue resistance. This is why critical components like aircraft landing gear and high-quality hand tools are forged.
The Impact on Material Properties
It is critical to understand that the shaping process changes the metal. Cold working makes it stronger but more brittle. Hot working refines the grain structure. The speed of cooling in casting dictates the final properties. Every step of fabrication is an integral part of the final component's performance.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The best method for shaping a metal is entirely dependent on the final application's requirements for strength, complexity, and cost.
- If your primary focus is maximum strength and durability: Forging or cold working processes are often superior as they refine the metal's internal grain structure.
- If your primary focus is creating a highly complex or intricate shape: Casting or modern additive manufacturing (3D printing) are the most effective methods.
- If your primary focus is mass production of simple shapes like sheets or wires: Rolling and drawing are the most efficient and economical choices.
- If your primary focus is achieving high precision and a smooth surface finish: Machining is typically required, often as a final step after an initial forming or casting process.
Understanding these foundational methods is the first step toward harnessing the immense versatility of metals for any application.
Summary Table:
| Property/Process | Key Characteristic | Common Applications |
|---|---|---|
| Malleability | Can be compressed into thin sheets | Aluminum foil, gold leaf |
| Ductility | Can be stretched into wires | Electrical wiring, suspension cables |
| Hot Working | Shaping above recrystallization temperature | Forging, rolling, extrusion |
| Cold Working | Shaping at room temperature for strength | Wire drawing, sheet metal bending |
| Casting | Melting and pouring into a mold | Engine blocks, intricate jewelry |
| Machining | Subtractive process for high precision | Precision parts, custom components |
Need to shape metals for your laboratory or manufacturing process? KINTEK specializes in providing the precise lab equipment and consumables needed for metal testing, heat treatment, and analysis. Whether you're working with forging, casting, or machining, our solutions help you achieve the right material properties and precision for your applications. Contact us today to discuss how we can support your metal shaping and fabrication needs!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Automatic Laboratory Hydraulic Press for XRF & KBR Pellet Press
- Automatic Laboratory Hydraulic Pellet Press Machine for Lab Use
- Laboratory Hydraulic Press Split Electric Lab Pellet Press
- Laboratory Manual Hydraulic Pellet Press for Lab Use
- Laboratory Hydraulic Pellet Press for XRF KBR FTIR Lab Applications
People Also Ask
- Why is a laboratory hydraulic press utilized for electrolyte pelletizing? Unlock High Ionic Conductivity
- What is the function of a bench-top laboratory hydraulic press for XRF? Maximize Accuracy in Prosopis juliflora Analysis
- What is KBr disc method? A Complete Guide to IR Spectroscopy Sample Prep
- How is a laboratory hydraulic press used for LLZTO pellets? Achieve 93% Density in Solid-State Battery Research
- What role does a laboratory hydraulic press play in preparing solid model materials? Standardize for Precise Data.



















