Yes, absolutely. Nitrogen gas can be heated, and its ability to accept and transfer thermal energy is a fundamental physical property. In fact, heating nitrogen is a common and critical process in countless industrial and scientific applications, chosen specifically for its predictable behavior and chemical stability at high temperatures.
The core reason for heating nitrogen is not just to transfer energy, but to do so within a controlled, inert atmosphere. This prevents unwanted chemical reactions like oxidation, which is critical for high-precision processes in manufacturing and research.

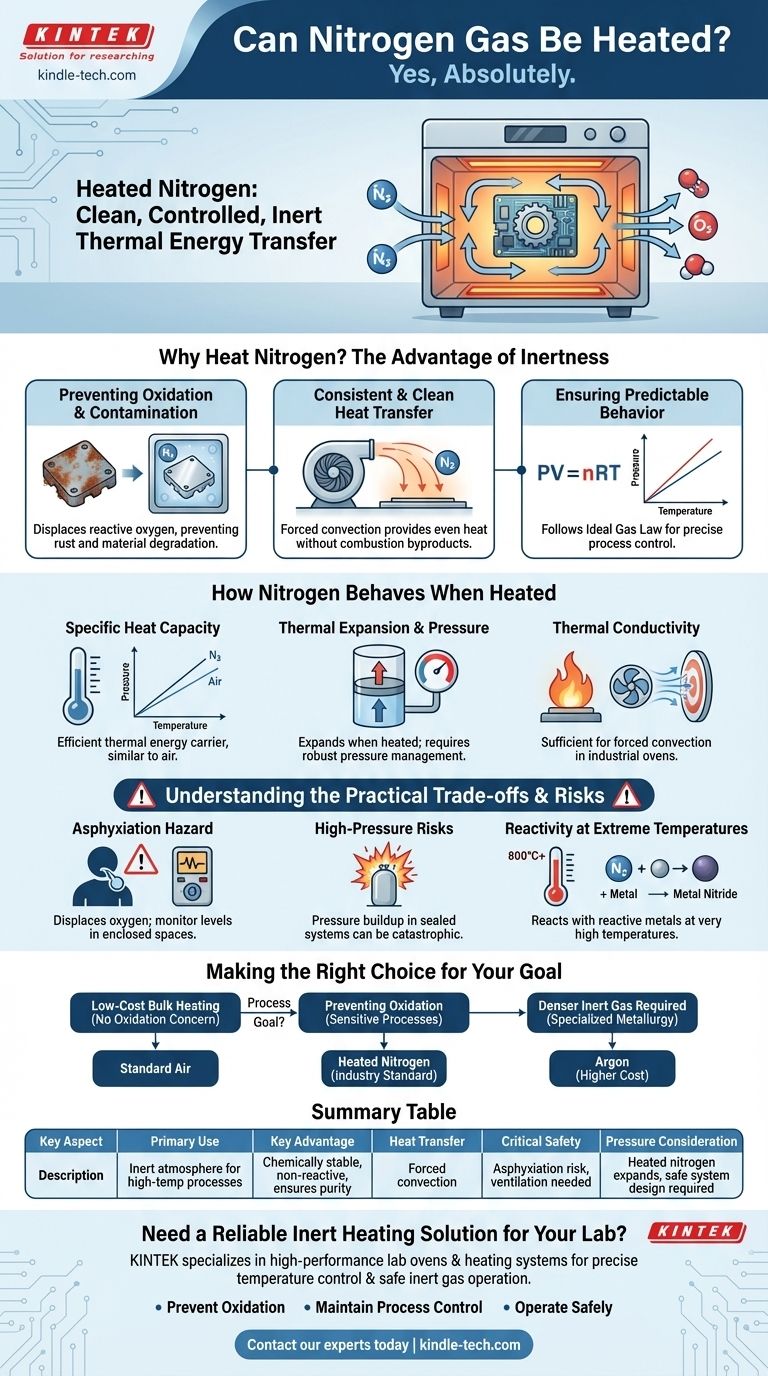
Why Heat Nitrogen? The Advantage of Inertness
The primary value of nitrogen is what it doesn't do. It is largely non-reactive under most conditions, making it an ideal medium for applying heat without causing chemical changes to the target materials.
Preventing Oxidation and Contamination
The air around us is about 21% oxygen, which is highly reactive, especially at elevated temperatures. This reactivity causes oxidation—rust on iron is a common example.
In sensitive processes like electronics manufacturing or metal heat-treating, oxidation can ruin components. By flooding an oven or chamber with heated nitrogen, you displace the oxygen, creating a safe, inert environment for the procedure.
Providing Consistent and Clean Heat Transfer
Heated nitrogen provides a very clean method of convective heat transfer. Unlike direct flame heating, there are no combustion byproducts to contaminate surfaces. This ensures that the only thing affecting the material is the thermal energy itself.
Ensuring Predictable Behavior
Nitrogen behaves as a near-ideal gas. This means its response to changes in temperature, pressure, and volume is governed by predictable physical laws (like the Ideal Gas Law, PV=nRT).
Engineers can reliably calculate the exact amount of energy needed to heat the gas to a specific temperature and the resulting pressure increase, allowing for highly precise process control.
How Nitrogen Behaves When Heated
Understanding a few key properties is essential for any practical application involving heated nitrogen.
Specific Heat Capacity
Specific heat capacity is the amount of energy required to raise the temperature of a certain amount of a substance. Nitrogen's specific heat is very similar to that of air.
This means it can absorb and hold a significant amount of thermal energy, making it an efficient carrier for transferring heat from a source to a product.
Thermal Expansion and Pressure
Like any gas, nitrogen expands when heated or, if confined to a fixed volume, its pressure will increase dramatically.
This is the most critical safety and design consideration. Any system designed to heat nitrogen must be able to withstand the target operating pressure or allow for controlled expansion.
Thermal Conductivity
Thermal conductivity is a measure of how well a substance transfers heat. Gases, in general, are poor conductors of heat compared to liquids or solids.
However, nitrogen's conductivity is sufficient for applications that use forced convection—using fans or blowers to circulate the hot gas—which is the standard method in industrial ovens and heating chambers.
Understanding the Practical Trade-offs and Risks
While incredibly useful, working with heated nitrogen requires a clear understanding of the potential hazards and limitations.
The Foremost Risk: Asphyxiation
Nitrogen is not toxic, but it is an asphyxiant. It displaces oxygen from the air. In an enclosed or poorly ventilated space, a nitrogen leak can lower oxygen levels to a dangerous point without any warning signs like a smell or color.
This is the single most important safety consideration. Any area using nitrogen should be monitored for oxygen levels.
High-Pressure Hazards
Heating nitrogen in a sealed, rigid container can cause a catastrophic pressure buildup, leading to an explosion. All systems must be designed with robust pressure relief valves and engineered to operate safely at the intended temperatures and pressures.
Reactivity at Extreme Temperatures
While nitrogen is valued for its inertness, this property has limits. At very high temperatures (often over 700-800°C), it can begin to react with highly reactive metals like magnesium, titanium, and lithium to form metal nitrides. This is a niche concern but is critical for certain high-temperature metallurgical applications.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting the right gas for your heating application depends entirely on your process requirements, balancing cost, safety, and the need for chemical inertness.
- If your primary focus is low-cost bulk heating and oxidation is not a concern: Standard compressed, heated air is almost always the most economical choice.
- If your primary focus is preventing oxidation in a sensitive process (e.g., electronics soldering, food packaging, chemical processing): Heated nitrogen is the industry standard and the correct technical solution.
- If your primary focus is a specialized application requiring a denser inert gas (e.g., certain types of welding or metallurgy): Argon may be required, though it comes at a higher cost.
Ultimately, choosing to heat nitrogen is a strategic decision to leverage its chemical stability for precise, clean, and predictable thermal control.
Summary Table:
| Key Aspect | Description |
|---|---|
| Primary Use | Creating an inert atmosphere to prevent oxidation during high-temperature processes. |
| Key Advantage | Chemically stable and non-reactive under most conditions, ensuring material purity. |
| Heat Transfer Method | Primarily via forced convection for efficient energy distribution. |
| Critical Safety Consideration | Risk of asphyxiation due to oxygen displacement; requires proper ventilation and monitoring. |
| Pressure Consideration | Heated nitrogen expands; systems must be designed to handle pressure increases safely. |
Need a Reliable Inert Heating Solution for Your Lab?
Heating nitrogen safely and effectively requires the right equipment. KINTEK specializes in high-performance lab ovens and heating systems designed for precise temperature control and safe operation with inert gases like nitrogen.
Our solutions help you:
- Prevent Oxidation: Ensure the integrity of sensitive materials during heat treatment.
- Maintain Process Control: Achieve consistent, repeatable results with reliable equipment.
- Operate Safely: Mitigate risks with systems built to handle the pressures and hazards of heated gases.
Let KINTEK provide the reliable lab equipment your processes demand. Contact our experts today to discuss your specific application needs.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1200℃ Controlled Atmosphere Furnace Nitrogen Inert Atmosphere Furnace
- 1400℃ Controlled Atmosphere Furnace with Nitrogen and Inert Atmosphere
- 1700℃ Controlled Atmosphere Furnace Nitrogen Inert Atmosphere Furnace
- Controlled Nitrogen Inert Hydrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- Vertical Laboratory Tube Furnace
People Also Ask
- What is an inert atmosphere heat treatment? Protect Your Metals from Oxidation & Decarburization
- What is an example of an inert atmosphere? Discover the Best Gas for Your Process
- How do you make an inert atmosphere? Master Safe, Pure Processes with Inerting
- What gases are used in inert atmospheres? Choose the Right Gas for Non-Reactive Environments
- Can nitrogen be used for brazing? Key Conditions and Applications Explained



















