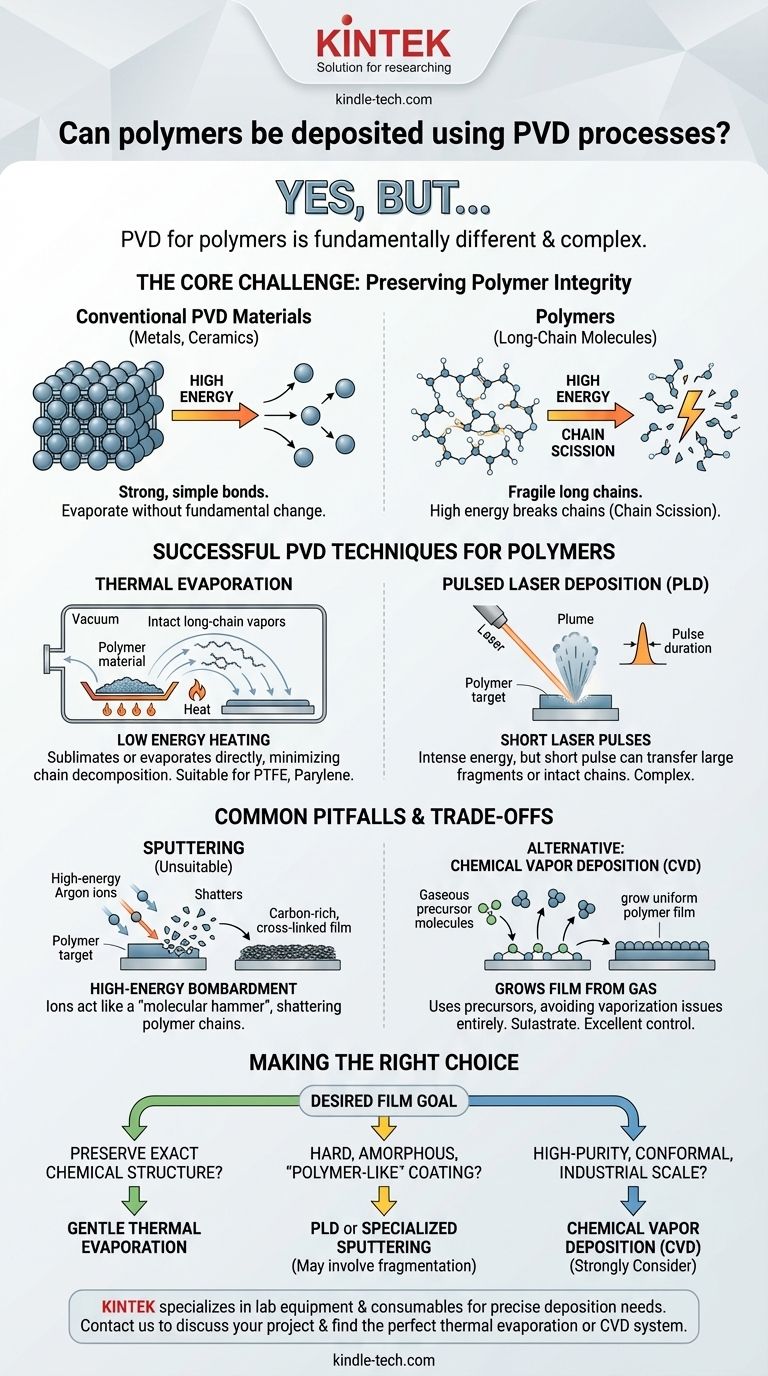
Yes, polymers can be deposited using Physical Vapor Deposition (PVD), but the process is fundamentally different and more complex than depositing metals or ceramics. The primary challenge lies in converting the solid polymer source material into a vapor without destroying the long-chain molecules that define its properties. Successfully creating a polymer thin film via PVD requires specialized techniques that carefully manage energy to prevent chemical decomposition.
The central challenge of using PVD for polymers is not simply vaporizing the material, but doing so gently enough to preserve the fragile, long-chain molecular structure. Success hinges on selecting a low-energy deposition method that avoids breaking these chains apart.
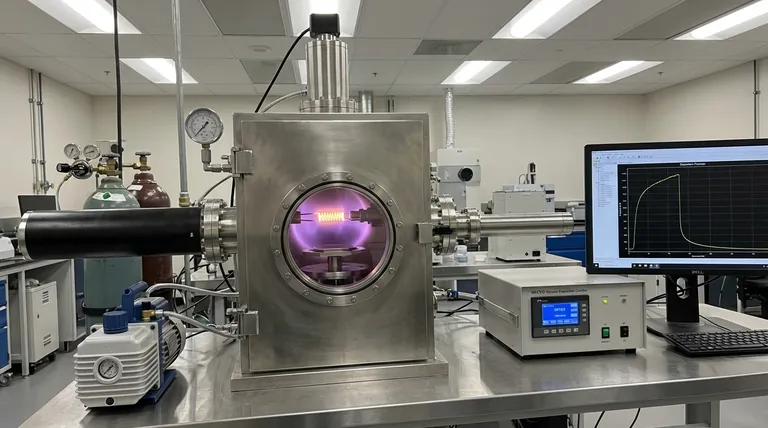

The Core Challenge: Preserving Polymer Integrity
To understand why depositing polymers is difficult, we must first understand their structure compared to conventional PVD materials like metals.
The Fragility of Long-Chain Molecules
Metals and ceramics are held together by strong, simple atomic or ionic bonds. They can be heated or bombarded with energy, causing individual atoms to evaporate without changing their fundamental nature.
Polymers, in contrast, consist of very long chains of repeating molecular units (monomers). The bonds within the chain are strong, but the overall structure can be easily broken apart—a process called chain scission—by the high heat or energetic particle impacts common in many PVD processes.
From Solid Source to Thin Film
Standard PVD involves vaporizing a source material, transporting that vapor through a vacuum, and condensing it onto a substrate to form a thin film.
When this process is applied to a polymer, the energy required to create a vapor is often high enough to break the molecular chains. The resulting film may not be the original polymer but rather a collection of its fragmented parts, possessing entirely different and often undesirable properties.
Successful PVD Techniques for Polymers
Despite the challenges, several PVD methods have been adapted to successfully deposit polymer thin films, primarily by limiting the energy applied to the source material.
Thermal Evaporation
Thermal evaporation is one of the most common methods for polymer PVD. The polymer source material is heated in a high vacuum using a resistive heat source, like a crucible or boat.
The key is to heat the material just enough for it to sublimate or evaporate directly from a solid to a gas. This lower-energy approach minimizes the decomposition of the polymer chains, making it suitable for materials like PTFE (Teflon) and parylene.
Pulsed Laser Deposition (PLD)
In Pulsed Laser Deposition (PLD), a high-power laser beam is focused on the polymer target. The intense, short burst of energy ablates the material, ejecting a plume of vapor that travels to the substrate.
While the energy is high, the extremely short pulse duration can, in some cases, transfer large molecular fragments or even intact polymer chains from the target to the substrate. This makes it a viable, though more complex, option for depositing certain functional polymers.
Common Pitfalls and Trade-offs
Choosing a PVD process for polymers involves navigating critical trade-offs and understanding the limitations of common techniques.
Why Sputtering Is Often Unsuitable
Sputtering is a dominant PVD process for metals, but it is generally a poor choice for polymers. It works by bombarding the source target with high-energy ions (like Argon).
This energetic bombardment acts like a molecular hammer, shattering the delicate polymer chains. The material that lands on the substrate is often a carbon-rich, cross-linked film that bears little resemblance to the original polymer.
The Alternative: Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD)
For creating high-quality, uniform polymer films, Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD) is often a superior alternative.
Instead of vaporizing a solid polymer, CVD uses gaseous precursor molecules (monomers) that react and bond together directly on the substrate surface to "grow" the polymer film. This provides excellent control over film thickness and properties, avoiding the decomposition issues inherent to PVD.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Your choice of deposition method should be dictated entirely by the desired properties and function of the final polymer film.
- If your primary focus is preserving the exact chemical structure of a specific polymer: Gentle thermal evaporation is your most reliable PVD option, though process control is critical.
- If your primary focus is creating a hard, amorphous, "polymer-like" coating: Processes that involve some fragmentation and re-assembly on the substrate, such as PLD or even specialized sputtering, may be acceptable.
- If your primary focus is high-purity, conformal polymer films at an industrial scale: You should strongly consider moving away from PVD and investigating Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD) as a more robust and controllable process.
By understanding the delicate balance between deposition energy and molecular integrity, you can successfully leverage vacuum processes to engineer advanced polymer thin films.
Summary Table:
| Method | Suitability for Polymers | Key Consideration |
|---|---|---|
| Thermal Evaporation | Good | Uses low heat to gently vaporize polymers like PTFE, minimizing chain scission. |
| Pulsed Laser Deposition (PLD) | Possible | Short laser pulses can transfer polymer fragments, but control is complex. |
| Sputtering | Poor | High-energy ion bombardment typically shatters polymer chains. |
| Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD) | Excellent (Alternative) | Grows polymer films from gas precursors, avoiding vaporization issues entirely. |
Need to deposit a functional polymer thin film? The right equipment is critical for success. KINTEK specializes in lab equipment and consumables, serving precise laboratory deposition needs. Our experts can help you select the perfect thermal evaporation or CVD system to achieve your film's required properties while preserving polymer integrity.
Contact our team today to discuss your project and discover the ideal solution for your laboratory.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- HFCVD Machine System Equipment for Drawing Die Nano-Diamond Coating
- 915MHz MPCVD Diamond Machine Microwave Plasma Chemical Vapor Deposition System Reactor
- CVD Diamond Cutting Tool Blanks for Precision Machining
- Vacuum Hot Press Furnace Machine for Lamination and Heating
- Laboratory Test Sieves and Sieving Machines
People Also Ask
- How do you calculate coating coverage? A Practical Guide to Accurate Material Estimation
- What is the hot filament chemical vapour deposition of diamond? A Guide to Synthetic Diamond Coating
- What is the process of coating deposition? A Step-by-Step Guide to Thin Film Engineering
- What is direct current DC magnetron sputtering? A Guide to High-Quality Thin Film Deposition
- How do CVD diamonds grow? A Step-by-Step Guide to Lab-Grown Diamond Creation



















