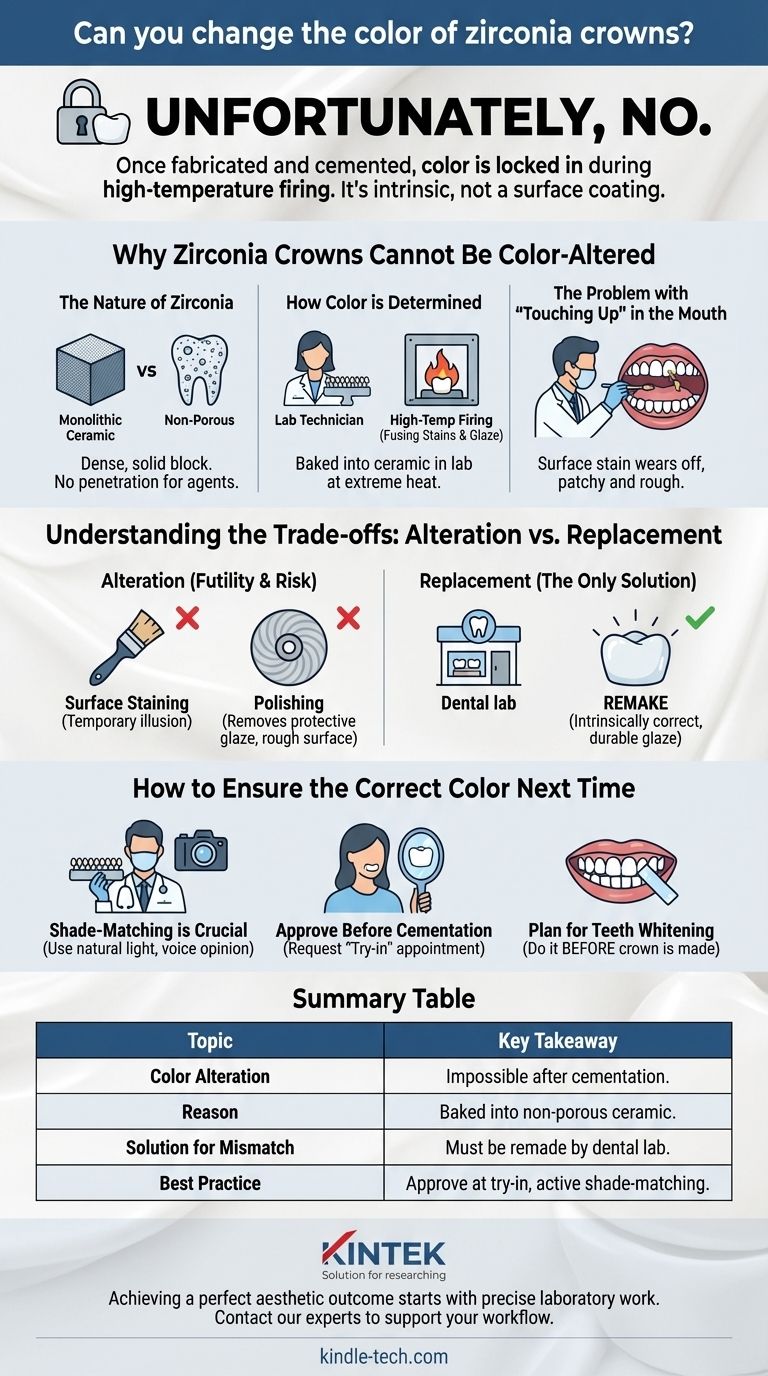
Unfortunately, no. Once a zirconia crown has been fabricated and permanently cemented in your mouth, its color cannot be changed. The color is intrinsic to the material and is locked in during a high-temperature firing process in the dental laboratory, making any post-cementation color alteration impossible.
A zirconia crown's color is not a surface coating; it's an integral part of the ceramic that is finalized before it ever reaches your dentist's office. The only definitive solution for a color mismatch is to have the crown remade.
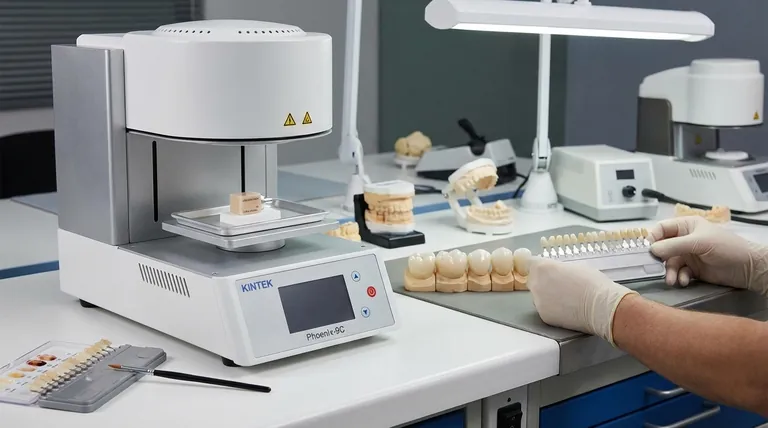

Why Zirconia Crowns Cannot Be Color-Altered
To understand this limitation, you must first understand the material itself and how it's made. A zirconia crown is not like a natural tooth that can be whitened or a painted wall that can be recoated.
The Nature of Zirconia
Zirconia is a type of monolithic ceramic, meaning it's crafted from a single, solid block of material. It is incredibly dense and non-porous.
This non-porous nature is a major advantage for durability and stain resistance, but it is also the primary reason its color cannot be changed. There is no way for whitening agents or color pigments to penetrate the surface.
How Color is Determined
The final shade of a zirconia crown is determined in the dental lab through a multi-step process.
First, the lab technician selects a block of zirconia that closely matches the shade prescribed by your dentist. Then, special stains and glazes are applied to the surface to mimic the subtle color variations and translucency of a natural tooth.
Critically, these stains are then fused to the zirconia in a porcelain furnace at extremely high temperatures. This process permanently bakes the color and a hard, glass-like glaze onto the crown's surface.
The Problem with "Touching Up" in the Mouth
Applying an external stain to a crown that is already in the mouth is not a viable solution. Any surface stain applied chairside would not bond permanently to the non-porous, glazed ceramic.
It would wear off quickly with normal chewing and brushing, resulting in a patchy, unnatural appearance and a rough surface texture that attracts plaque.
Understanding the Trade-offs: Alteration vs. Replacement
When faced with a color mismatch, patients often hope for a simple fix. However, attempting an alteration introduces more problems than it solves, making replacement the only professionally accepted standard.
The Futility of Surface Staining
A chairside staining kit might seem like a quick fix, but it is a temporary and cosmetic illusion at best. It is not a durable or long-term solution and is not recommended by dental professionals for permanent restorations.
The Risk of Polishing
Aggressively polishing the crown in an attempt to lighten it is also ineffective. This will not change the base shade of the zirconia. Instead, it will remove the protective glaze layer applied in the lab.
An unglazed crown feels rough, loses its natural luster, and becomes much more susceptible to staining from coffee, tea, or wine, potentially making the aesthetic problem worse over time.
The Certainty of a Remake
The only way to definitively correct the color of a zirconia crown is to remove it and fabricate a new one. This ensures the color is intrinsically correct and the surface has the proper durable glaze for longevity and aesthetics.
How to Ensure the Correct Color Next Time
Achieving a perfect match is a collaborative process between you, your dentist, and the dental lab. Being an active participant is the best way to ensure a satisfactory outcome.
Step 1: Shade-Matching is Crucial
The process begins with shade matching. Your dentist will use a shade guide, often taking photos in different lighting conditions (especially natural light) to get the most accurate reading. Don't be afraid to voice your opinion during this stage.
Step 2: Approve the Crown Before Cementation
For front teeth, it is common to have a "try-in" appointment. The new crown is placed temporarily (without permanent cement) to allow you to see it in your mouth and approve the color and shape. This is the absolute best time to request a change.
Step 3: Plan for Teeth Whitening
If you are considering whitening your natural teeth, you must do it before the crown is made. A crown can then be matched to your new, brighter shade. A crown's color is permanent and will not change with whitening treatments, which only affect natural tooth enamel.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Navigating this situation can be frustrating, but your actions should be guided by your ultimate goal.
- If you are unhappy with a current crown: Your only path to a permanent solution is to speak with your dentist about fabricating a new crown.
- If you are getting a new crown in the future: Be actively involved in the shade-matching process and ask for a "try-in" to approve the final look before it's permanently cemented.
- If your primary focus is a brighter overall smile: Complete any teeth whitening treatments before your dentist takes the final impression for your new crown.
Ultimately, achieving the right aesthetic outcome depends on clear communication and careful planning before the restoration is permanently placed.
Summary Table:
| Topic | Key Takeaway |
|---|---|
| Color Alteration | Impossible after the crown is cemented. |
| Reason | Color is baked into the non-porous ceramic during high-temperature firing. |
| Solution for Mismatch | The crown must be remade by a dental lab. |
| Best Practice | Be actively involved in shade-matching and approve the crown at a try-in appointment. |
Achieving a perfect aesthetic outcome starts with precise laboratory work. KINTEK specializes in providing dental laboratories with the high-quality equipment and consumables needed for consistent, reliable results. If your lab is dedicated to crafting perfect zirconia restorations, contact our experts today to discover how our solutions can support your workflow and enhance your final product.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Dental Porcelain Zirconia Sintering Ceramic Furnace Chairside with Transformer
- Vacuum Dental Porcelain Sintering Furnace
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- 1700℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- 600T Vacuum Induction Hot Press Furnace for Heat Treat and Sintering
People Also Ask
- What makes zirconia translucent? The Science Behind Modern Dental Aesthetics
- What is a dental oven? The Precision Furnace for Creating Strong, Aesthetic Dental Restorations
- What is one of the newest applications for dental ceramics? Monolithic Zirconia for Full-Arch Bridges
- What is the price of zirconia sintering furnace? Invest in Precision, Not Just a Price Tag
- What is the effect of zirconia sintering temperature? Master the Key to Strength and Stability



















