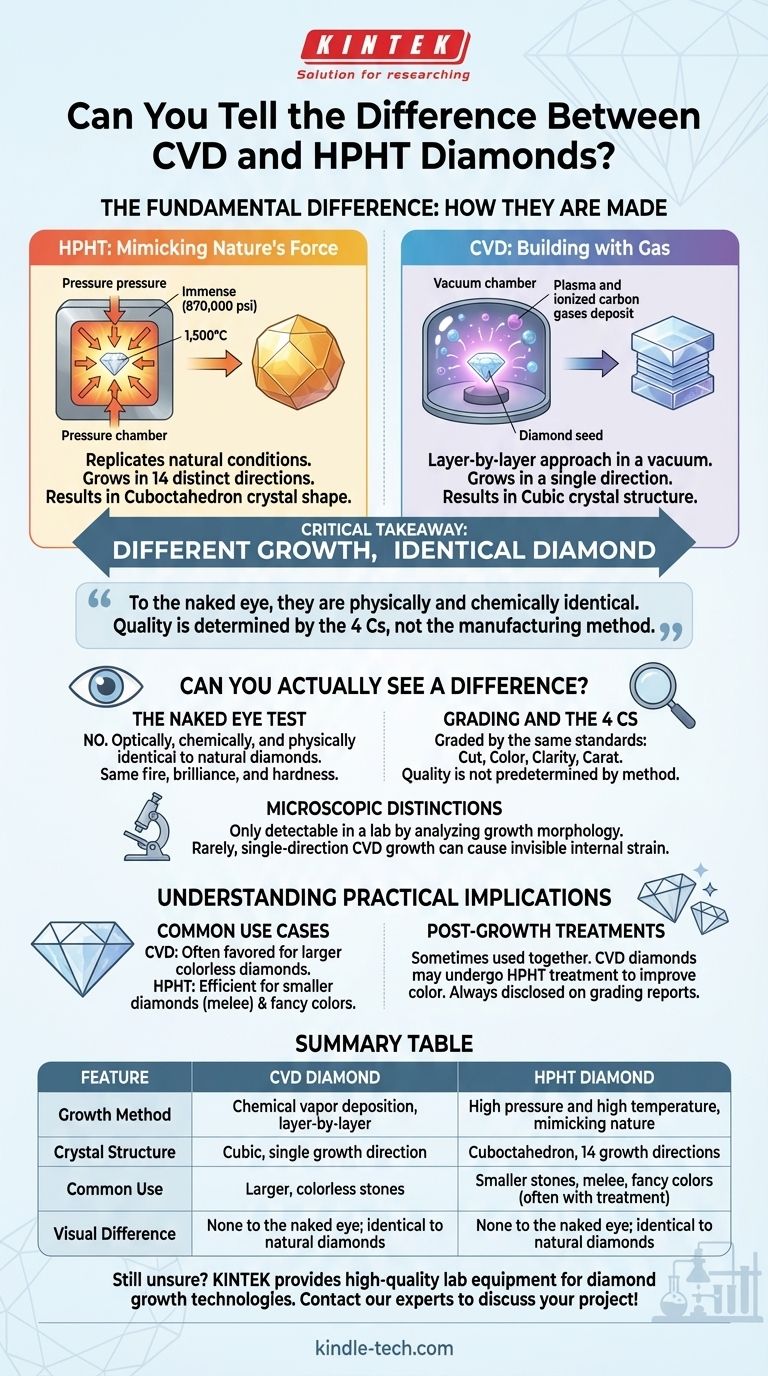
From a technical standpoint, the primary difference between a CVD (Chemical Vapor Deposition) and an HPHT (High Pressure, High Temperature) diamond is how they are grown. HPHT diamonds are created by mimicking the intense pressure and heat of the Earth's mantle, causing them to grow in a cuboctahedron shape with 14 distinct directions. In contrast, CVD diamonds are grown layer-by-layer in a vacuum chamber, resulting in a cubic crystal structure with a single growth direction.
The critical takeaway is that while their creation methods and microscopic growth patterns differ, both HPHT and CVD processes produce real diamonds. To the naked eye, they are physically and chemically identical, and any difference in quality is determined by the final grading of the 4 Cs, not the manufacturing method itself.

The Fundamental Difference: How They Are Made
Understanding the two methods reveals why their internal structures differ. Each process is a distinct technological pathway to creating a genuine diamond.
HPHT: Mimicking Nature's Force
The HPHT method seeks to replicate the natural diamond-forming conditions found deep within the Earth.
A small diamond "seed" is placed in a chamber with carbon and subjected to immense pressure (over 870,000 pounds per square inch) and extreme heat (around 1,500°C). This forces the carbon to dissolve and crystallize onto the seed, growing a new, larger diamond.
This multi-directional growth results in a cuboctahedron crystal shape, similar to many natural diamonds.
CVD: Building with Gas
The CVD method takes a more additive, layer-by-layer approach.
A diamond seed is placed inside a sealed vacuum chamber filled with carbon-rich gases. These gases are ionized into a plasma, which causes the carbon atoms to break away and deposit onto the diamond seed.
This process builds the diamond in a single direction, resulting in a cubic crystal structure.
Can You Actually See a Difference?
For a buyer, the most important question is whether these technical differences translate into a visible one. The answer is unequivocally no.
The Naked Eye Test
You cannot tell the difference between an HPHT and a CVD diamond just by looking at them. Both methods produce stones that are optically, chemically, and physically identical to natural diamonds.
They exhibit the same fire, brilliance, and hardness because they are both crystallized carbon.
Grading and the 4 Cs
Gemological laboratories grade HPHT and CVD diamonds using the exact same standard as natural diamonds: the 4 Cs (Cut, Color, Clarity, and Carat).
The manufacturing method does not predetermine the quality. A poorly controlled HPHT process can create a low-quality diamond, just as a masterfully executed CVD process can create a flawless one.
Microscopic Distinctions
The only way to differentiate them is with advanced laboratory equipment. Gemologists can identify the diamond's origin by analyzing its growth morphology—the distinct internal patterns left by the HPHT or CVD process.
In very rare cases, the single-direction growth of a CVD diamond can result in internal strain, but this is typically invisible without extreme magnification and does not impact the stone's beauty or durability.
Understanding the Practical Implications
While visually indistinguishable, the two methods have different production tendencies which can influence the market.
Common Use Cases
Generally, the CVD process is often favored for creating larger colorless diamonds.
The HPHT process is very efficient for producing smaller diamonds, often used for melee (the small accent stones in a piece of jewelry).
The Role of Post-Growth Treatments
Sometimes these processes are used together. A diamond may be grown using the CVD method and then subjected to HPHT treatment afterward to improve or change its color.
This is especially common in the creation of fancy-colored lab-grown diamonds. A grading report will always disclose these treatments.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Ultimately, the debate between HPHT and CVD is academic for the consumer. Your focus should be on the final quality and beauty of the stone, not its manufacturing history.
- If your primary focus is quality and beauty: Judge the diamond on its 4 Cs and certification report, regardless of whether it is HPHT or CVD.
- If your primary focus is the largest possible stone for your budget: You may find that many of your options are CVD-grown, as this method is commonly used for producing larger carats.
- If your primary focus is a specific fancy color: Be aware the stone may have undergone a multi-step process (e.g., CVD growth plus HPHT treatment), and focus on the final, certified color grade.
Choose the diamond that you find beautiful and that meets your standards for quality and value, as its fundamental identity as a diamond is never in question.
Summary Table:
| Feature | CVD Diamond | HPHT Diamond |
|---|---|---|
| Growth Method | Chemical vapor deposition, layer-by-layer | High pressure and high temperature, mimicking nature |
| Crystal Structure | Cubic, single growth direction | Cuboctahedron, 14 growth directions |
| Common Use | Larger, colorless stones | Smaller stones, melee, fancy colors (often with treatment) |
| Visual Difference | None to the naked eye; identical to natural diamonds | None to the naked eye; identical to natural diamonds |
Still unsure which lab-grown diamond is right for your needs? At KINTEK, we specialize in providing high-quality lab equipment and consumables for advanced material synthesis, including diamond growth technologies. Whether you are a researcher, jeweler, or manufacturer, our expertise can help you achieve precise, reliable results. Contact our experts today to discuss how our solutions can support your diamond production or analysis projects!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- CVD Diamond Domes for Industrial and Scientific Applications
- Cylindrical Resonator MPCVD Machine System Reactor for Microwave Plasma Chemical Vapor Deposition and Lab Diamond Growth
- CVD Diamond Optical Windows for Lab Applications
- Microwave Plasma Chemical Vapor Deposition MPCVD Machine System Reactor for Lab and Diamond Growth
- CVD Diamond Cutting Tool Blanks for Precision Machining
People Also Ask
- What is the hardness of CVD diamond? The Ultimate Guide to Engineered Super-Materials
- What is the application of diamond coating? Solve Complex Wear, Heat, and Corrosion Problems
- How is something diamond coated? A Guide to CVD Growth vs. Plating Methods
- What is the newly discovered mechanism for diamond formation during CVD? Explore the Graphite-to-Diamond Transition
- What are the applications of CVD diamonds? From Jewelry to High-Tech Tools



















