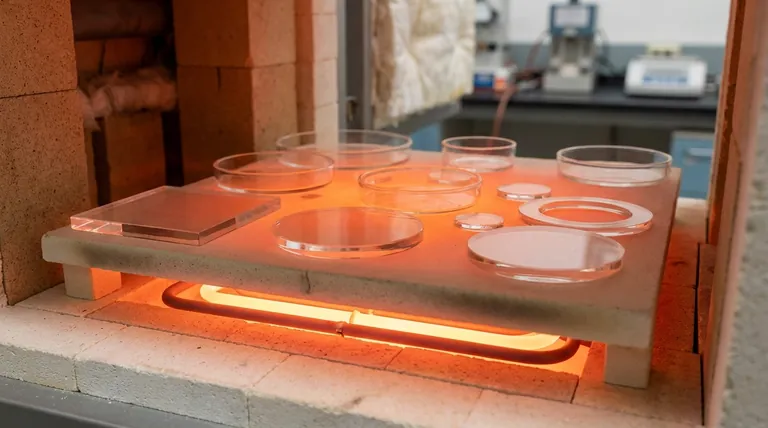
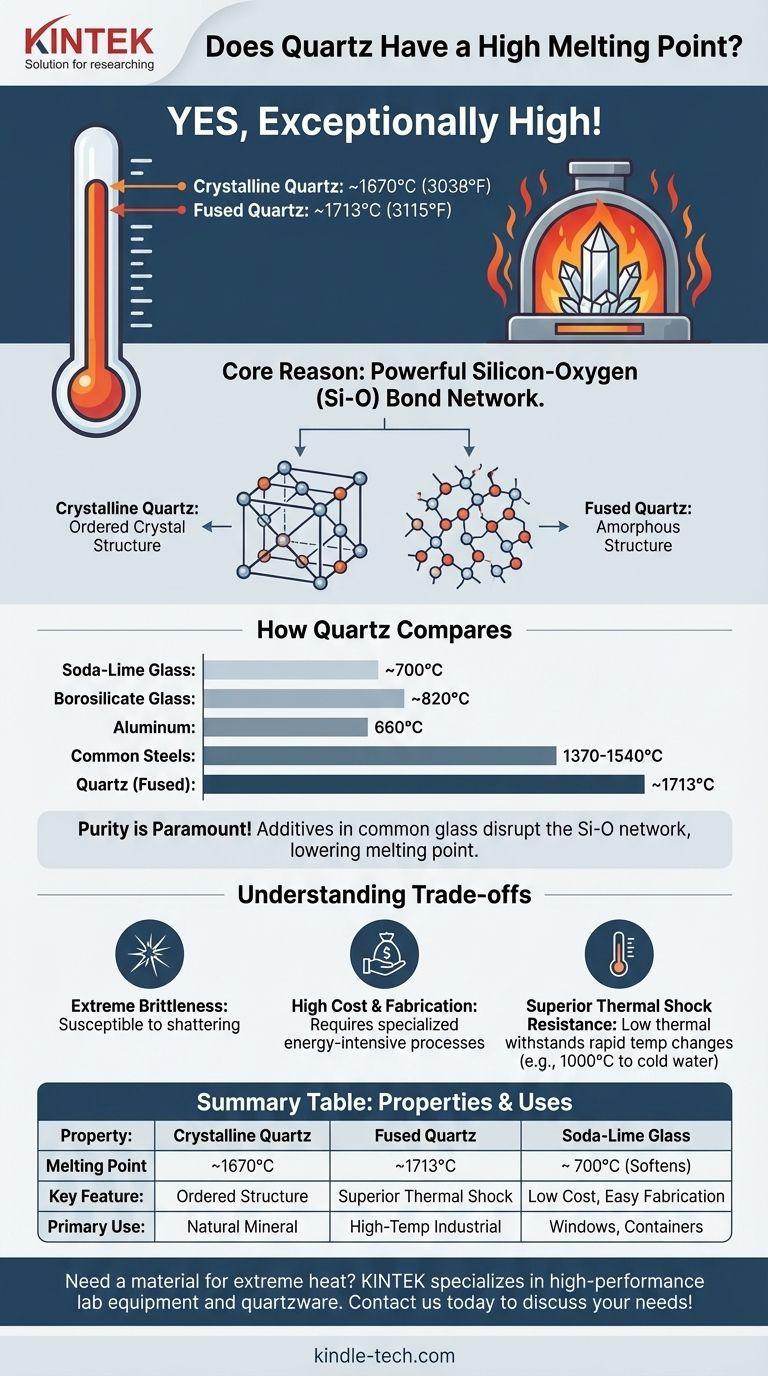
Yes, quartz has an exceptionally high melting point. Its crystalline form melts at approximately 1670°C (3038°F), while its non-crystalline form, known as fused quartz, melts around 1713°C (3115°F). This remarkable thermal stability is due to the immense strength of the chemical bonds holding its structure together, making it a superior material for high-temperature applications.
The core reason for quartz's high melting point is the powerful network of silicon-oxygen bonds that form its structure. Breaking these bonds requires a tremendous amount of thermal energy. This intrinsic strength, combined with the purity of the material, makes it fundamentally different from and far more heat-resistant than conventional glass.

Why Temperature Affects Quartz Differently
To understand why quartz withstands such high temperatures, we must look at its atomic structure. This is where it fundamentally differs from common materials like glass or metal.
The Power of Silicon-Oxygen Bonds
Quartz is a specific crystalline form of **silicon dioxide (SiO₂) **. Each silicon atom is bonded to four oxygen atoms in a strong, stable, and repeating tetrahedral structure. These covalent bonds are incredibly robust and require a massive amount of energy to disrupt, which directly translates to a very high melting point.
Crystalline Quartz vs. Fused Quartz
The term "quartz" can refer to two forms. Crystalline quartz is the mineral found in nature with a precise, ordered atomic lattice. When this is melted and rapidly cooled, it forms fused quartz, which is an amorphous (non-crystalline) solid. Fused quartz, also called fused silica, has even slightly better thermal performance and is what is typically used in high-temperature industrial applications.
The Role of Purity
As the reference material notes, purity is paramount. The strength of quartz comes from its uniform SiO₂ network. Common glass, like soda-lime glass, has additives such as sodium oxide. These additives deliberately disrupt the silicon-oxygen network to lower the melting point, making the glass easier and cheaper to manufacture.
How Quartz Compares to Other Materials
Placing the melting point of quartz in context reveals just how robust it is for thermal applications.
Superiority Over Standard Glass
There is a vast difference between quartz and other types of glass. Soda-lime glass, used for windows and bottles, begins to soften around 700°C. Borosilicate glass (like Pyrex) has better thermal resistance but still melts well below quartz, typically around 820°C.
Performance Against Common Metals
Quartz also surpasses many common industrial metals. For example, aluminum melts at a mere 660°C. Many common steels melt in the range of 1370-1540°C, still significantly lower than the melting point of quartz.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While its melting point is exceptional, quartz is not the perfect material for every situation. Its properties create specific challenges and limitations.
Extreme Brittleness
Like other ceramics, quartz is very brittle. While it can withstand immense heat, it is susceptible to shattering from mechanical shock or physical impact. Its hardness does not equate to toughness.
Fabrication and Cost
The very property that makes quartz desirable—its high melting point—also makes it difficult to work with. Melting and shaping quartz requires specialized equipment and consumes a great deal of energy, making it significantly more expensive to produce than conventional glass.
Thermal Shock Resistance is Key
For many applications, the most important property is not the melting point itself but thermal shock resistance. This is where fused quartz truly excels. It has an extremely low coefficient of thermal expansion, meaning it barely changes size when heated or cooled. You can heat it to over 1000°C and plunge it into cold water without it cracking, a feat that would destroy most other materials.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Selecting a material requires balancing thermal performance with other practical considerations.
- If your primary focus is pure temperature resistance: Quartz is an elite choice, outperforming nearly all glasses and many common metals.
- If your primary focus is surviving rapid temperature changes: Fused quartz is one of the best materials available due to its unparalleled thermal shock resistance.
- If your primary focus is cost, manufacturability, or toughness: Borosilicate glass or a specific metal alloy may offer a more practical balance of properties for your project.
Ultimately, understanding the unique thermal characteristics of quartz allows you to confidently select a material built to withstand the most demanding high-temperature environments.
Summary Table:
| Property | Crystalline Quartz | Fused Quartz | Soda-Lime Glass |
|---|---|---|---|
| Melting Point | ~1670°C (3038°F) | ~1713°C (3115°F) | ~700°C (Softens) |
| Key Feature | Ordered Crystal Structure | Superior Thermal Shock | Low Cost, Easy Fabrication |
| Primary Use | Natural Mineral | High-Temperature Industrial Applications | Windows, Containers |
Need a material that can withstand extreme heat? Quartz's exceptional thermal stability, with a melting point exceeding 1670°C, makes it ideal for demanding laboratory and industrial processes. At KINTEK, we specialize in high-performance lab equipment and consumables, including quartzware designed for superior heat resistance and durability. Let our experts help you select the right materials for your application. Contact KINTEK today to discuss your high-temperature needs!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- High Temperature Resistant Optical Quartz Glass Sheet
- Optical Window Glass Substrate Wafer Single Double Sided Coated K9 Quartz Sheet
- 1700℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- Electrode Polishing Material for Electrochemical Experiments
- KF Ultra-High Vacuum Observation Window 304 Stainless Steel Flange High Borosilicate Glass Sight Glass
People Also Ask
- What are the thermal properties of quartz? Unlocking Extreme Temperature Stability for Your Lab
- What is the high temperature of quartz? Key Thresholds for Crystalline vs. Fused Silica
- What is the working temperature of quartz glass? Master Its High-Temp Limits & Applications
- What is optical quartz? The Ultimate Material for UV and High-Temp Optics
- What are the uses of quartz glass? Essential for Extreme-Temperature and UV Applications



















