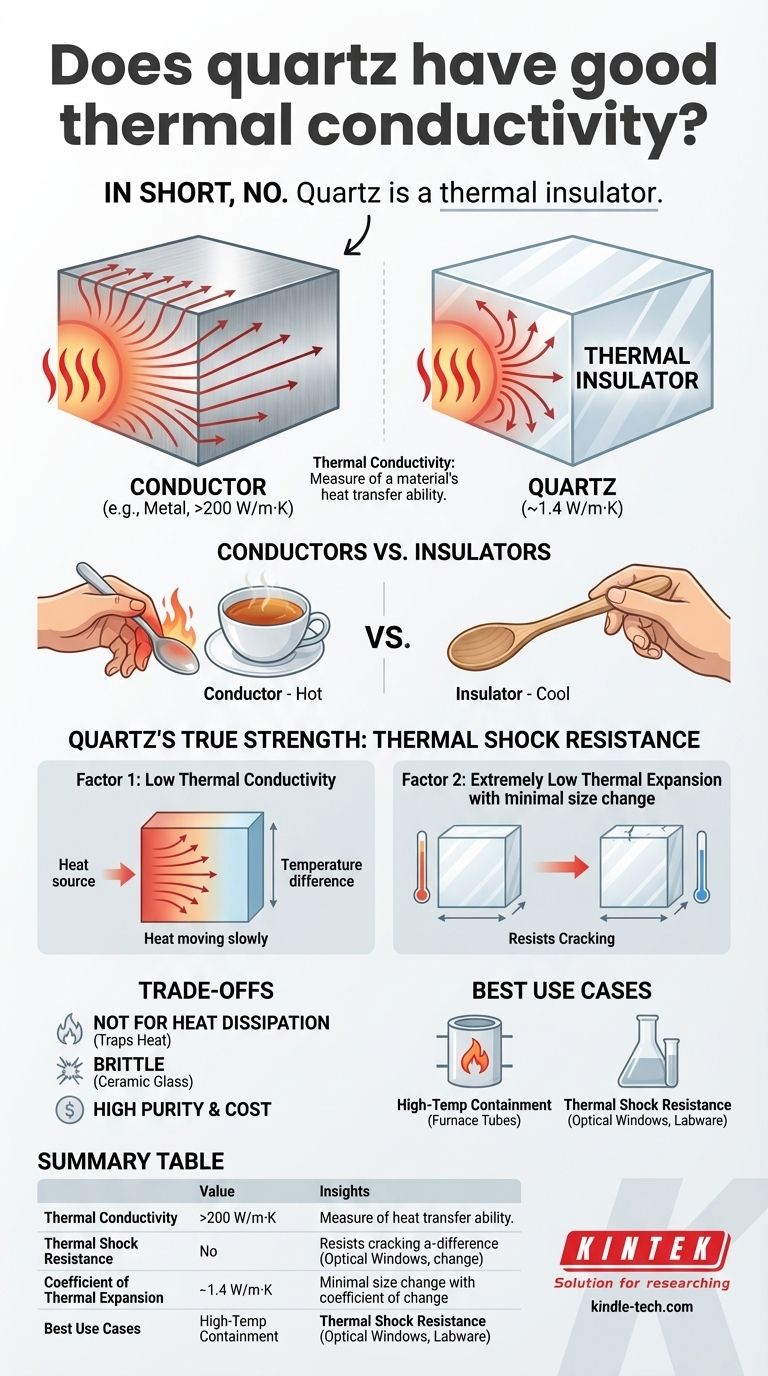
In short, quartz is a poor thermal conductor. It is actually a thermal insulator, meaning it resists the flow of heat. Its primary thermal advantages are not in conducting heat, but in its exceptional ability to withstand high temperatures and, most importantly, extreme changes in temperature without cracking.
The defining thermal characteristic of quartz is not conductivity, but rather its extraordinary thermal stability. It combines a high melting point with an extremely low coefficient of thermal expansion, making it uniquely resistant to thermal shock.

What is Thermal Conductivity?
Defining Heat Transfer
Thermal conductivity is a measure of a material's ability to transfer heat. Materials with high conductivity move heat quickly, while those with low conductivity do so slowly.
This property is measured in watts per meter-Kelvin (W/m·K). A higher number signifies a better conductor.
Conductors vs. Insulators
Think of a metal spoon versus a wooden spoon in a hot cup of tea. The metal spoon (a conductor) quickly becomes too hot to touch because it efficiently transfers heat from the tea to your hand.
The wooden spoon (an insulator) remains cool to the touch. It has low thermal conductivity and blocks the flow of heat. Quartz behaves much more like the wooden spoon than the metal one.
Quartz's Thermal Profile: A Superior Insulator
The Conductivity Numbers
Fused quartz has a thermal conductivity of approximately 1.4 W/m·K. While this is slightly higher than common soda-lime glass (~1 W/m·K), it is drastically lower than true thermal conductors.
For comparison, aluminum has a conductivity of over 200 W/m·K, and copper is nearly 400 W/m·K. This confirms quartz is firmly in the category of thermal insulators.
The Critical Distinction: Conductivity vs. Thermal Shock Resistance
The reference to quartz's "superior" thermal properties is not about conductivity. It refers to its unparalleled ability to survive thermal shock—a rapid, dramatic change in temperature.
This resistance comes from the combination of two key factors.
Factor 1: Low Thermal Conductivity
Because heat moves slowly through quartz, a rapid temperature change on its surface doesn't immediately affect the interior. This creates a massive temperature difference across the material.
Factor 2: Extremely Low Thermal Expansion
This is the secret to quartz's stability. The coefficient of thermal expansion describes how much a material expands or contracts when its temperature changes. Quartz has an exceptionally low one.
Even when a huge temperature difference exists between its surface and interior, neither part expands or contracts enough to create the internal stress that would cause a lesser material, like regular glass, to shatter.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Not for Heat Dissipation
Because it is a thermal insulator, quartz is an exceptionally poor choice for any application that requires moving heat away from a source. It will trap heat, not dissipate it.
Brittleness Remains a Factor
While thermally robust, quartz is still a ceramic glass. It is brittle and has poor resistance to mechanical shock or physical impact. Its strength is in temperature, not physical force.
Purity and Cost
The remarkable properties of quartz, particularly fused quartz, are due to its very high purity (silicon dioxide). This purity makes it more expensive and difficult to manufacture than conventional glasses.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Choosing quartz depends entirely on your thermal goal.
- If your primary focus is high-temperature containment: Quartz is an excellent choice for furnace tubes, crucibles, and reaction chambers due to its high melting point and insulating properties.
- If your primary focus is thermal shock resistance: Quartz is the definitive choice for optical windows, lenses, or labware that will be exposed to rapid heating and cooling cycles.
- If your primary focus is rapid heat transfer: Quartz is the wrong material; you must use a metal conductor like aluminum or copper for applications like heat sinks or heat exchangers.
Understanding these distinct properties allows you to leverage quartz not as a conductor, but as a uniquely stable thermal insulator.
Summary Table:
| Property | Value / Description | Key Insight |
|---|---|---|
| Thermal Conductivity | ~1.4 W/m·K | Very low; classifies quartz as a thermal insulator, not a conductor. |
| Thermal Shock Resistance | Extremely High | Its primary thermal advantage; resists cracking from rapid temperature changes. |
| Coefficient of Thermal Expansion | Exceptionally Low | The key reason for its superior thermal shock resistance. |
| Best Use Cases | High-temperature containment, optical windows, labware | Ideal for applications requiring thermal stability, not heat dissipation. |
Need a reliable thermal solution for your lab? Quartz's exceptional thermal stability makes it ideal for furnace tubes, crucibles, and optical components that must withstand extreme temperatures and rapid changes. At KINTEK, we specialize in high-purity quartz lab equipment and consumables designed for superior performance and durability.
Contact our experts today to find the perfect quartzware for your specific laboratory needs!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Engineering Advanced Fine Alumina Al2O3 Ceramic Rod Insulated for Industrial Applications
- Zirconia Ceramic Gasket Insulating Engineering Advanced Fine Ceramics
- 10L Heating Chilling Circulator Cooling Water Bath Circulator for High and Low Temperature Constant Temperature Reaction
- High Temperature Constant Temperature Heating Circulator Water Bath Chiller Circulator for Reaction Bath
- 100L Chilling Circulator Cooling Water Circulator for Low Temperature Constant Temperature Reaction Bath Water Bath Cooling
People Also Ask
- What functions do high-purity alumina support rods serve in sCO2 experiments? Ensure High-Temp Material Integrity
- What is the process of alumina tube manufacturing? From Powder to High-Performance Ceramic
- Why is an alumina insulation disk required in a CCPD reactor? Enhance Coating Quality with Floating Potential
- What are the functions of spring-loaded alumina ceramic rods? Ensure Data Purity in Electrode Test Assemblies
- What is the maximum temperature for alumina tube? Unlock Its Full Potential with High Purity


















