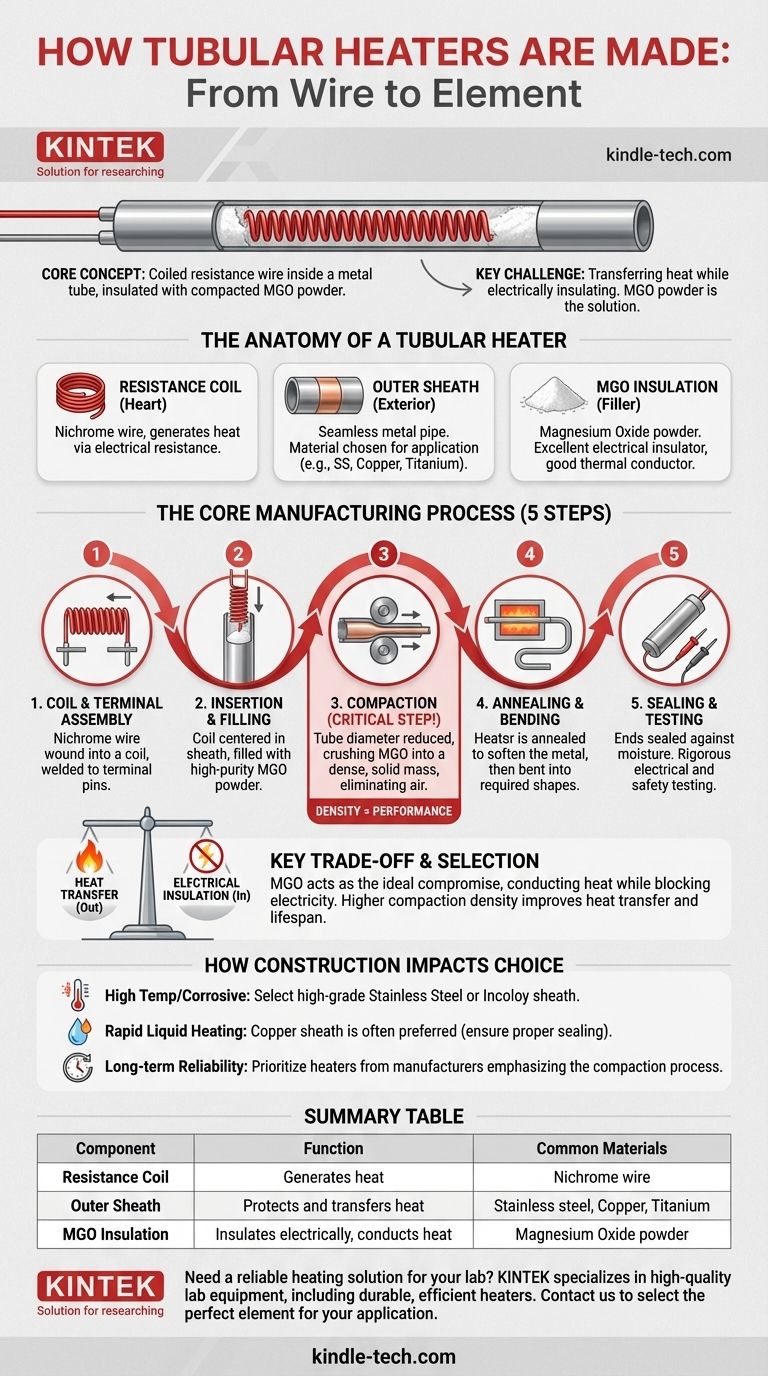
At its core, a tubular heater is made by encasing a coiled resistance wire inside a metal tube, insulating it with a special powder, and then compacting the entire assembly. This process creates a remarkably durable and efficient heating element by ensuring the heat generated by the wire can escape while the electricity cannot.
The central challenge in heater design is transferring heat efficiently while maintaining perfect electrical insulation. Tubular heater manufacturing solves this by using Magnesium Oxide (MGO) powder, a unique material that conducts heat well but blocks electricity, and then compacting it to create a solid, stable, and safe heating element.

The Anatomy of a Tubular Heater
To understand the manufacturing process, you must first understand the three critical components that work in concert. Each material is chosen for its specific thermal and electrical properties.
The Resistance Coil
The heart of the heater is a coil of nichrome (nickel-chromium) wire. This specific alloy is used for its high electrical resistance and its ability to withstand repeated heating and cooling cycles without degrading. The wire is wound into a precise coil to fit the required length and produce the exact wattage needed.
The Outer Sheath
This is the seamless metal pipe that forms the heater's exterior. The material is chosen based on the application. Common options include stainless steel for high temperatures and corrosion resistance, copper for its excellent thermal conductivity in water heating, or even titanium for aggressive chemical environments.
The MGO Insulation
The space between the resistance coil and the outer sheath is filled with Magnesium Oxide (MGO) powder. This material is the key to the heater's performance. It has high dielectric strength (it's an excellent electrical insulator) but also possesses good thermal conductivity, allowing heat to move from the coil to the sheath efficiently.
The Core Manufacturing Process: From Wire to Element
Creating a tubular heater is a multi-step process where precision at each stage is critical for the final product's safety and longevity.
Step 1: Coil and Terminal Assembly
First, the nichrome resistance wire is precisely wound into a coil. This coil is then welded to terminal pins, which will serve as the external electrical connection points. The resistance of this assembly is carefully measured to ensure it will produce the correct heat output.
Step 2: Insertion and Filling
The coil and terminal pin assembly is carefully centered inside the outer metal sheath. The entire tube is then filled with the high-purity MGO powder, ensuring the coil remains perfectly positioned and is completely surrounded by the insulating material.
Step 3: Compaction (The Critical Step)
This is the most important stage of the process. The filled tube is passed through a rolling mill or swaging machine that reduces its diameter. This compaction crushes the MGO powder into a solid, dense mass, eliminating all air pockets. This dense MGO provides superior heat transfer and locks the coil in place, preventing electrical shorts.
Step 4: Annealing and Bending
After compaction, the heater is often brittle. It is heated in a furnace in a process called annealing, which softens the metal sheath and makes it malleable. The heater can then be bent into the various complex shapes required for specific applications without damaging the internal components.
Step 5: Sealing and Testing
Finally, the ends of the heater are sealed to prevent moisture from contaminating the MGO, which would compromise its insulating properties. Every heater undergoes rigorous testing, including checks for electrical resistance and high-voltage insulation tests to ensure its safety and performance.
Understanding the Key Trade-off: Heat Transfer vs. Insulation
The entire design of a tubular heater hinges on a fundamental engineering principle. You need to move energy (heat) out, but keep electricity in.
Why MGO is the Ideal Compromise
Air is a fantastic electrical insulator, but it is also a terrible thermal conductor. If the tube were filled with air, the resistance coil would quickly overheat and burn out because its heat would be trapped. MGO powder, especially when compacted, solves this by providing a pathway for heat while still acting as a strong barrier for electricity.
The Impact of Compaction Density
A more densely compacted heater offers better heat transfer and a longer lifespan because it removes more performance-killing air gaps. However, extreme compaction can make the heater more difficult to bend. Manufacturers must balance the need for thermal efficiency with the mechanical requirements of the final shape.
How Construction Impacts Your Choice
The way a tubular heater is made directly affects its performance in your application.
- If your primary focus is high temperatures or corrosive environments: Select a heater with a high-grade stainless steel or Incoloy sheath, as this protective layer is the most critical component for survival.
- If your primary focus is rapid and efficient liquid heating: A copper sheath is often preferred, but ensure the heater has been properly sealed to prevent moisture contamination of the MGO.
- If your primary focus is long-term reliability in any application: Prioritize heaters from manufacturers who emphasize their compaction process, as this step is the single most important factor in preventing premature failure.
Understanding this robust construction process empowers you to select the right heater with confidence, knowing it is engineered for safety, efficiency, and durability.
Summary Table:
| Component | Function | Common Materials |
|---|---|---|
| Resistance Coil | Generates heat | Nichrome wire |
| Outer Sheath | Protects and transfers heat | Stainless steel, Copper, Titanium |
| MGO Insulation | Insulates electrically, conducts heat | Magnesium Oxide powder |
Need a reliable heating solution for your lab? The robust construction of tubular heaters is key to their performance in demanding environments. At KINTEK, we specialize in high-quality lab equipment, including durable and efficient heaters designed for precision and longevity. Let our experts help you select the perfect heating element for your specific application. Contact us today to discuss your laboratory needs!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Molybdenum Disilicide (MoSi2) Thermal Elements Electric Furnace Heating Element
- Silicon Carbide SiC Thermal Heating Elements for Electric Furnace
- Custom PTFE Teflon Parts Manufacturer for Non-Standard Insulator Customization
- CF KF Flange Vacuum Electrode Feedthrough Lead Sealing Assembly for Vacuum Systems
- Ultra-Vacuum Electrode Feedthrough Connector Flange Power Electrode Lead for High-Precision Applications
People Also Ask
- Why is it necessary to use a silica-sheathed platinum thermocouple in Hubnerite chlorination? Get Precise Kinetic Data
- How effective is electrical resistance heating? It's 100% efficient at the point of use.
- Why is a K-type thermocouple used to monitor substrate temperature during plasma treatment? Protect Material Integrity
- Why does the temperature of the heating element increase? To Drive Efficient Heat Transfer
- What is the melting point of tungsten? Discover the Metal That Withstands Extreme Heat
- What happens when tungsten is heated? Harnessing Extreme Heat for Demanding Applications
- What is the most common type of temperature sensor? The Unmatched Versatility of Thermocouples
- How do coaxial heating coils in a TDS system determine hydrogen trap activation energy? Precise Thermal Control Guide













