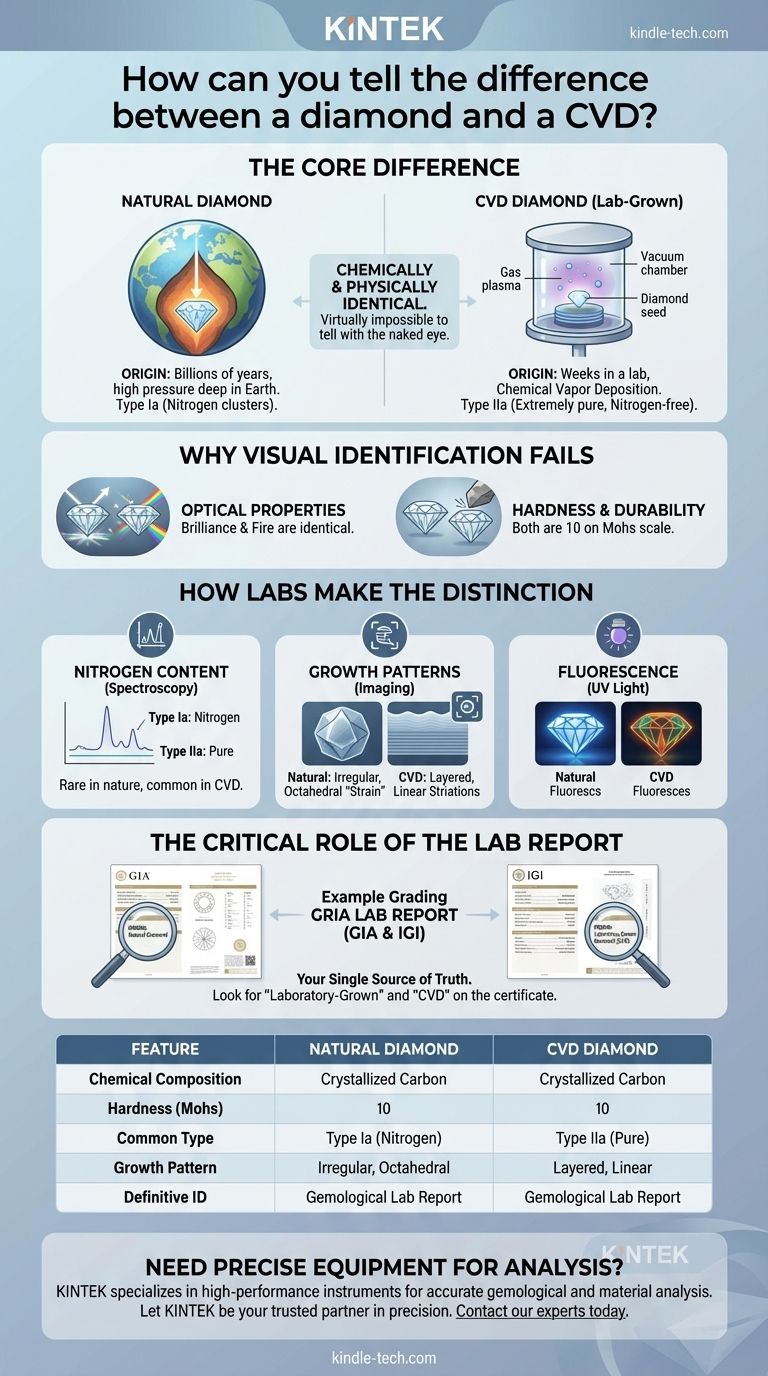
At its core, a CVD diamond is chemically and physically identical to a natural diamond, making it virtually impossible for a consumer to tell the difference with the naked eye. The only definitive way for a non-expert to distinguish them is by reviewing a grading report from a reputable gemological laboratory, such as the GIA or IGI, which will explicitly state if the diamond is laboratory-grown.
The fundamental difference between a natural diamond and a CVD lab-grown diamond is not in their substance, but in their origin. This origin story leaves behind microscopic clues in the diamond's atomic structure and growth patterns, which can only be deciphered using highly specialized laboratory equipment.
What is a CVD Diamond?
A True Diamond, Born in a Lab
First, it is crucial to understand that a CVD (Chemical Vapor Deposition) diamond is a real diamond. It is not a simulant like cubic zirconia or moissanite.
CVD diamonds share the same chemical composition (crystallized carbon) and physical properties as natural diamonds, including maximum hardness (10 on the Mohs scale), brilliance, and fire.
The CVD Growth Process
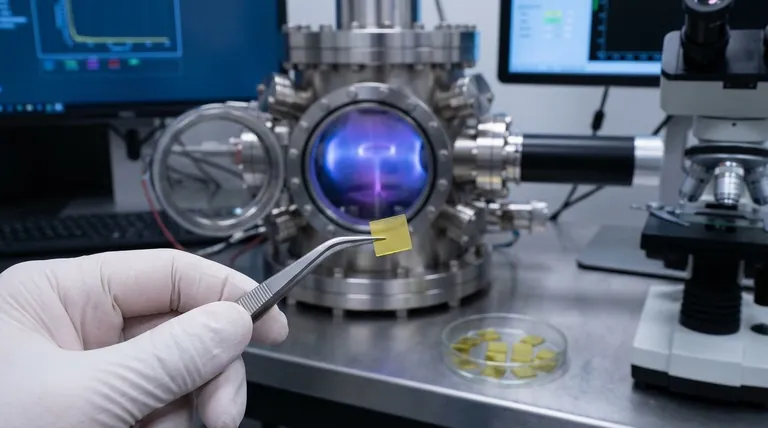
The CVD process mimics the way diamonds form in interstellar gas clouds. A thin slice of a pre-existing diamond, known as a "seed," is placed in a vacuum chamber.
This chamber is then filled with carbon-rich gases (like methane) and heated to extreme temperatures. Microwave energy ionizes the gases, causing carbon atoms to break free and deposit onto the diamond seed, growing the diamond layer by layer over several weeks.
Why Visual Identification Fails
Identical Optical Properties
Because they are chemically the same, light behaves identically whether it passes through a natural diamond or a CVD diamond. This means key characteristics like brilliance (white light reflection) and fire (dispersion of light into colors) will appear the same.
No Difference in Hardness or Durability
You cannot use a scratch test or any traditional hardness test to differentiate between them. Both will scratch any other mineral and will resist damage in the same way during daily wear.
How Gemological Labs Make the Distinction
Gemologists do not rely on standard jeweler's loupes. They use advanced spectroscopic and imaging instruments to find the subtle markers left behind by the diamond’s unique growth environment.
The Telltale Sign: Nitrogen Content
Nearly all natural diamonds (around 98%) are Type Ia, meaning they contain nitrogen atoms in small clusters. This nitrogen was present in the earth as the diamond formed over billions of years.
CVD diamonds, however, are grown in a nitrogen-free environment and are almost always Type IIa. Type IIa diamonds are exceptionally pure and rare in nature, making this a powerful primary indicator for labs.
Uncovering Growth Patterns
Natural diamonds grow in an octahedral (eight-sided) crystal shape. Under specialized imaging equipment, this creates a distinct, somewhat irregular "strain" pattern.
CVD diamonds grow in one direction, layer by layer, which can create a subtle, linear "striation" or layered pattern that is not found in natural stones.
Analyzing Fluorescence
When exposed to ultraviolet (UV) light, diamonds can fluoresce, or glow. While many natural diamonds fluoresce blue, CVD diamonds often exhibit unique fluorescence in shades of orange, yellow, or green, sometimes in very regular, geometric patterns that betray their artificial origin.
The Critical Role of the Lab Report
Your Single Source of Truth
Since specialized equipment is required for a definitive analysis, the grading report is the consumer's most important tool. Reputable labs like the GIA (Gemological Institute of America) and IGI (International Gemological Institute) invest millions in the research and technology to make this distinction.
What to Look For on the Certificate
A modern lab report will not be ambiguous. Look for clear statements in the "Origin" or "Comments" sections.
Key terms include "Laboratory-Grown Diamond" and a specific mention of the growth method, such as "CVD". The report for a natural diamond will simply state "Natural Diamond."
Making an Informed Decision
Choosing between a natural and a CVD diamond depends entirely on your personal priorities. The key is transparency.
- If your primary focus is provenance and rarity: A natural diamond with a GIA report confirming its origin is the correct choice.
- If your primary focus is budget and size: A CVD diamond offers the same visual beauty and durability as a natural stone, often at a significantly lower price, allowing you to get a larger stone for your budget.
- If you are verifying a stone you already own: The only way to be certain of its origin is to submit it to a reputable gemological lab for testing.
Ultimately, understanding the science behind diamond identification empowers you to purchase with confidence, ensuring you know the precise origin of your stone.

Summary Table:
| Feature | Natural Diamond | CVD Diamond |
|---|---|---|
| Chemical Composition | Crystallized Carbon | Crystallized Carbon |
| Hardness (Mohs Scale) | 10 | 10 |
| Common Type | Type Ia (Nitrogen clusters) | Type IIa (Extremely pure) |
| Growth Pattern | Irregular, Octahedral | Layered, Linear Striations |
| Definitive Identification | Gemological Lab Report (e.g., GIA) | Gemological Lab Report (e.g., IGI) |
Need precise, reliable equipment for advanced material analysis?
The sophisticated techniques described in this article—like spectroscopy and imaging—require high-performance lab equipment to execute. KINTEK specializes in providing the precise, durable instruments and consumables that laboratories need for accurate gemological, chemical, and material analysis.
Let KINTEK be your trusted partner in precision. Whether you're a gemological lab, a research institution, or an industrial facility, our range of equipment is designed to deliver the accuracy and reliability your work demands.
Contact our experts today to discuss how we can support your specific laboratory needs and help you achieve unparalleled analytical results.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- CVD Diamond for Thermal Management Applications
- Cylindrical Resonator MPCVD Machine System Reactor for Microwave Plasma Chemical Vapor Deposition and Lab Diamond Growth
- CVD Diamond Domes for Industrial and Scientific Applications
- CVD Diamond Dressing Tools for Precision Applications
- Microwave Plasma Chemical Vapor Deposition MPCVD Machine System Reactor for Lab and Diamond Growth
People Also Ask
- What is the frequency of MPCVD? A Guide to Choosing 2.45 GHz vs. 915 MHz for Your Application
- Are CVD diamonds good? Real Diamonds with Ethical Origins & Better Value
- Can I buy lab diamonds? Your Guide to Modern, Ethical, and Affordable Diamonds
- What is the process for CVD diamond? Building a Diamond Atom by Atom
- Why is MW-CVD preferred for high-purity diamond optical windows? Achieve Zero-Contamination Material Growth
- How long does it take to make a diamond in a machine? From Weeks to Billions of Years
- Will CVD diamond change color? Discover the Science of Permanent, Stable Color
- Which is better lab grown or natural diamond? A Clear Guide to Choosing Your Perfect Stone
















