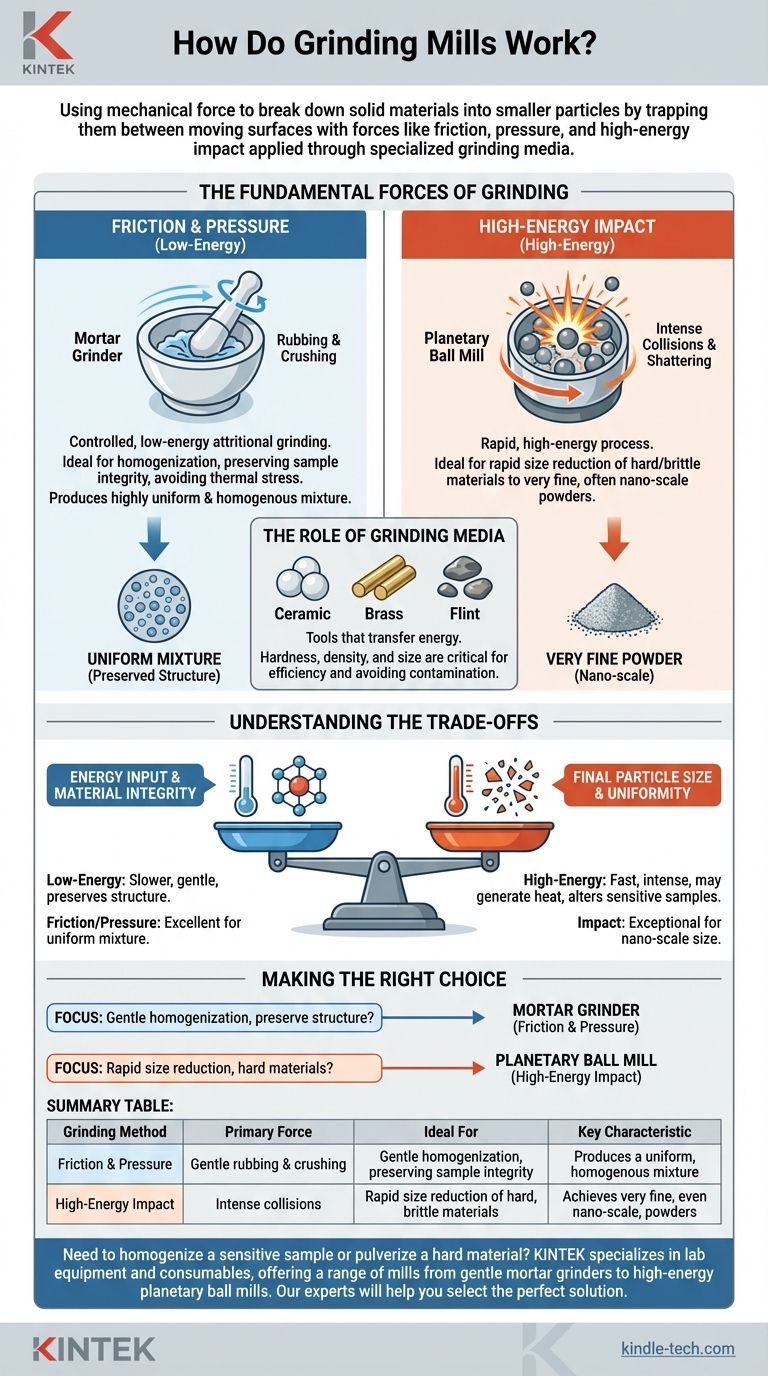
At their core, grinding mills work by using mechanical force to break down solid materials into smaller particles. This is accomplished by trapping the material between moving surfaces, where forces like friction, pressure, and high-energy impact are applied through specialized grinding media like ceramic balls, brass rods, or flint pebbles.
The specific type of force a mill applies—whether gentle friction and pressure or high-energy impact—is the most critical factor, determining its suitability for different materials and the final characteristics of the ground powder.
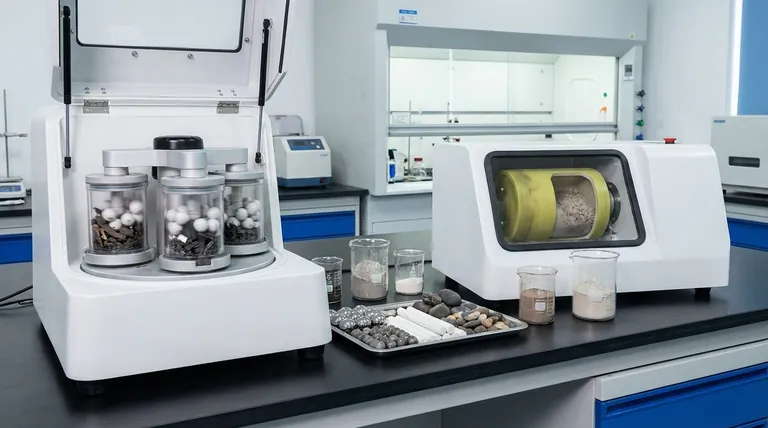

The Fundamental Forces of Grinding
To understand how different mills operate, you must first understand the primary forces they leverage to achieve particle size reduction.
Friction and Pressure
This method relies on the rubbing and crushing action between two surfaces. It is a controlled, low-energy process often referred to as attritional grinding.
The classic example is a mortar grinder. The pestle applies consistent pressure against the material and the mortar walls, while the rotating motion generates friction. This combination gently shears and crushes particles.
This approach is ideal for applications where maintaining the sample's integrity is critical, as it avoids the thermal stress that can be generated by more aggressive methods.
High-Energy Impact
This method uses intense, repeated collisions to shatter material. It is a high-energy process designed for rapid and significant size reduction.
Planetary ball mills are a prime example of this principle. Grinding balls and the sample material are placed inside a rotating bowl. The high-speed rotation causes the balls to collide with extreme force, pulverizing the material through high-energy impact.
This powerful action is highly effective for breaking down very hard or brittle materials into extremely fine powders.
The Role of Grinding Media
The grinding media are the tools that transfer energy from the mill to the material. These can be balls, rods, or other shapes made from materials like ceramics, flint, brass, or lead.
The choice of media is critical. Its hardness, density, and size directly influence the efficiency of the grinding process and can prevent contamination of the final product.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Choosing the right grinding method involves balancing speed, energy input, and the desired outcome. There is no single best approach; each has distinct advantages and disadvantages.
Energy Input vs. Material Integrity
High-energy impact mills are extremely fast and effective, but the intense force can generate significant heat. This can alter or destroy sensitive organic and inorganic samples.
Conversely, low-energy friction and pressure mills are much slower. However, their gentle action is ideal for mixing and homogenizing samples without causing thermal damage, preserving the material’s original structure.
Final Particle Size vs. Uniformity
Impact grinding is exceptionally good at reducing materials to very fine, often nano-scale, particle sizes.
Friction and pressure grinding excels at producing a highly uniform and homogenous mixture. The consistent, gentle action ensures that all parts of the sample are processed equally, which is crucial for sample preparation and analysis.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
The optimal grinding mill is the one whose mechanical action is best suited to your material and your goal.
- If your primary focus is gentle homogenization and preserving a sample's chemical structure: A low-speed, friction-based mill like a mortar grinder is the correct choice.
- If your primary focus is rapid size reduction of hard materials to a very fine powder: A high-energy, impact-based system like a planetary ball mill is required for the task.
Ultimately, effective material processing depends on matching the mechanical grinding principle to the properties of your material and the requirements of your final product.
Summary Table:
| Grinding Method | Primary Force | Ideal For | Key Characteristic |
|---|---|---|---|
| Friction & Pressure | Gentle rubbing & crushing | Gentle homogenization, preserving sample integrity | Produces a uniform, homogenous mixture |
| High-Energy Impact | Intense collisions | Rapid size reduction of hard, brittle materials | Achieves very fine, even nano-scale, powders |
Need to homogenize a sensitive sample or pulverize a hard material?
The right grinding mill is critical for your results. KINTEK specializes in lab equipment and consumables, offering a range of mills from gentle mortar grinders to high-energy planetary ball mills. Our experts will help you select the perfect solution to ensure efficient processing and preserve your sample's integrity.
Contact KINTEK today to optimize your grinding process!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Single Horizontal Jar Mill
- Laboratory Test Sieves and Sieving Machines
- High Energy Planetary Ball Mill Machine for Laboratory Horizontal Tank Type
- Laboratory Horizontal Planetary Ball Mill Milling Machine
- High-Energy Omnidirectional Planetary Ball Mill Machine for Laboratory
People Also Ask
- Why use zirconia ball milling jars for SiC/ZTA composite powders? Ensure High Purity & Efficient Particle Refinement
- What is the ball mill based on the principle of? Impact and Attrition for Efficient Grinding
- Why are excellent sealing and corrosion resistance required for WC-10Co ball milling? Ensure High-Purity Mixing Results
- What are the advantages of polyurethane ball mill jars for silicon nitride? Ensure Purity & Prevent Metal Contamination
- Why are tungsten carbide grinding jars and balls preferred for high-purity lithium ceramic powders? Ensure Peak Purity.



















